
Bronchitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the bronchi. There may be several types, each of which has a distinctive symptomatology and specific treatment that the doctor should appoint. Remember that self-medication of such a serious disease as bronchitis, at home is just dangerous!
Content
- 1 Types and symptoms
- 2 antibiotics for bronchitis
- 2.1 Antibiotics old generation
- 2.2 Macrolides
- 2.3 Modern antibiotics
- 2.4 Fluoroquinolones
- 2.5 Antibiotics and nebulizer
- 3 Indications / Contraindications
- 4 Possible complications
- 5 Video
Types and
 symptoms Viewedthe inflammatory process can proceed in the following forms:
symptoms Viewedthe inflammatory process can proceed in the following forms:
- purulent - sputum produced during coughing, contains an admixture of pus;For more information on how to treat purulent bronchitis in adults, read the article.
- purulent-serous - characterized by the release of specific sputum, differing in gray and the presence of "fibers" / inclusions of pus;
- fibrinous - phlegm in the patient is very viscous and dense, poorly separated, which causes a narrowing of the lumen of the bronchus and, as a consequence, attacks of bronchospasm;
- hemorrhagic - the inflammatory process affects the blood vessels, thinens their walls and the blood gets into the sputum;
- catarrhal is the most common form of bronchitis, characterized by the accumulation of a large amount of mucus in the upper parts of the bronchi.
 How is treatment with modern means of chronic obstructive bronchitis indicated in the article.
How is treatment with modern means of chronic obstructive bronchitis indicated in the article.
How the treatment of chronic bronchitis with antibiotics is worth reading for information in this article.
Can I breathe over a potato with bronchitis indicated in the article here: http: //prolor.ru/g/lechenie/ stoit-dyshat-nad-kartoshkoj-pri-prostude-kashle.html
This disease can have a different course:
-
 acute bronchitis - always starts suddenly, accompanied bypain in the chest( even with deep breathing), paroxysmal coughing and fever;
acute bronchitis - always starts suddenly, accompanied bypain in the chest( even with deep breathing), paroxysmal coughing and fever; - chronic bronchitis - is a consequence of an untreated acute form, has all of the above main symptoms of bronchitis, but in a less pronounced form, and hyperthermia( increased body temperature) may be absent altogether.
When the patient is examined and the diagnostic is performed, the doctor necessarily differentiates bronchitis according to the functional sign:
- non-obstructive - bronchial constriction, sudden bronchospasm and stifling is not observed;
- obstructive - due to a large amount of viscous sputum or because of the anatomical features of the patient's body, there is a significant narrowing of the bronchial lumen. In this case, the patient complains of shortness of breath, attacks of suffocation, accompanied by a strained dry cough. And here's how to treat obstructive bronchitis in children, you can find out by reading this article.
Antibiotics for bronchitis

Only antibiotics help cure bronchitis, the rest of the remedy only alleviates the condition of the patient
Many people who have noted the first symptoms of the disease in question, begin treatment of bronchitis with propolis, soda, garlic and other folk remedies and usual tablets against cough - this is fundamentally wrong! Only antibacterial drugs( antibiotics) will be able to rid themselves directly of inflammation and pathogenic microorganisms ( bronchitis has an infectious etiology), and all other methods of treatment and remedies will only alleviate the condition of the patient. This does not mean that you need to immediately and unconditionally go through a course of antibiotic therapy - you will still need to consult a doctor, but the antibiotic used most often for children is indicated in the article.
Important: with acute bronchitis antibiotics are not prescribed at all - this form of inflammation has a viral etiology, and the drugs in question are absolutely useless in the fight for health with viruses.
 Antibiotics can be prescribed in tablets and injections, but most often the tablet form of medicines is used - it allows you to go through the entire course of treatment on an outpatient basis, without the need to be in a hospital. Doctors can prescribe injections with antibacterial drugs in the following cases:
Antibiotics can be prescribed in tablets and injections, but most often the tablet form of medicines is used - it allows you to go through the entire course of treatment on an outpatient basis, without the need to be in a hospital. Doctors can prescribe injections with antibacterial drugs in the following cases:
- body temperature reaches the highest limits and keeps at this level for more than a day;
- in sputum there is pus;
- observed bronchospasm and severe dyspnea.
In addition, antibiotics can also be used in inhalations with a nebulizer - this is generally considered to be the most effective treatment for : the drug is directly on the walls of bronchial tubes affected by the inflammatory process and acts localized.
Antibiotics of the old generation
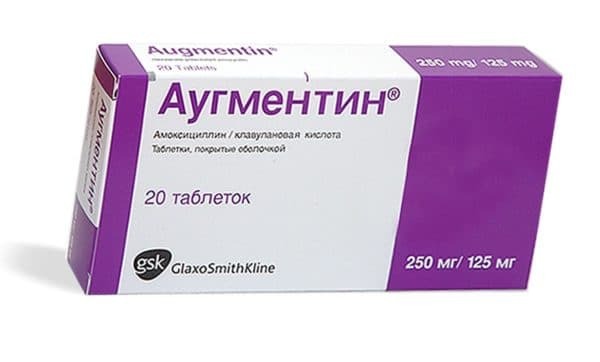
Augmentin - one of the popular means of the old generation
Most often in the treatment of bronchitis of different forms and types, doctors prescribe penicillins - preparations of the old generation, but this has not become less effective. Recommended preparations:
- Augmentin;
- Panklav;
- Amoxiclav.
P  Recommended dosage: 625 mg per treatment. Such receptions per day should be 3( every 8 hours). Important: Penicillins give a very good effect, but the resistance of pathogenic bacteria that provoked bronchitis to these drugs is more often revealed. Therefore, the patient is prescribed a medicine, then the dynamics of the disease progresses( for 3 days) and in the absence of positive "shifts" the antibiotic is replaced with another, more effective.
Recommended dosage: 625 mg per treatment. Such receptions per day should be 3( every 8 hours). Important: Penicillins give a very good effect, but the resistance of pathogenic bacteria that provoked bronchitis to these drugs is more often revealed. Therefore, the patient is prescribed a medicine, then the dynamics of the disease progresses( for 3 days) and in the absence of positive "shifts" the antibiotic is replaced with another, more effective.
Macrolides
If the patient has an individual intolerance and / or hypersensitivity to penicillin antibiotics, macrolides are prescribed. These include:
- Clarithromycin;
- Erythromycin.
They are issued most often in tablet form, so the dosage is calculated as follows: 1 tablet per reception, use should be done every 6-8 hours.
Modern antibiotics
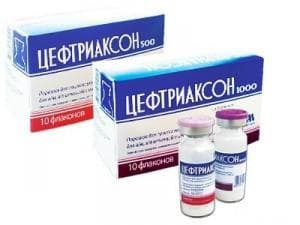 For obstructive bronchitis, antibiotics of a new generation are prescribed - cephalosporins, which are injected into the body only by injection - intramuscularly or intravenously( in especially severe cases).These include:
For obstructive bronchitis, antibiotics of a new generation are prescribed - cephalosporins, which are injected into the body only by injection - intramuscularly or intravenously( in especially severe cases).These include:
- Levofloxacin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Cefuroxime.
Please note: the exact dosage should be prescribed by the attending physician - it will depend on the severity of the course of the disease, the general condition of the patient, the "neglect" of the inflammatory process.
Fluoroquinolones
If the patient has previously been diagnosed with chronic bronchitis, then at the first signs of his exacerbation should take fluoroquinolones - broad-spectrum antibiotics, identical to cephalosporins, but softer / more benign. The most commonly prescribed:
- Moxifloxacin;
- Lefofloxacin;
- Ciprofloxacin.
It is recommended to treat with a short seven-day course, injecting any of the above medications intramuscularly twice a day. What amount of a drug is needed for one injection, only a doctor can determine - in this case, it's unreasonable to make a decision on your own.
The chronic form of bronchitis is always and certainly treated with antibiotics - they will help "drive" the inflammatory process into the stage of long-term remission.
Antibiotics and nebulizer

Nebulizer inhalations are especially effective for bronchitis
Antibiotics can also be used for nebulizer inhalations - the effect will be rendered almost immediately, because in this case the drug will act directed / localized and immediately after ingestion. The most commonly used for this type of treatment is Fluimucil, a drug that contains both an antibacterial agent and a special one for liquefying sputum. An antibiotic is produced in the form of a powder - it is necessary to take one package and dissolve in a small amount of sodium chloride( maximum 5 ml), and the resulting liquid is divided into two inhalations per day.
Fluuimcil inhalations are most effective in purulent bronchitis, but can be prescribed for other types of inflammatory disease.
Indications / contraindications
Antibiotics are sufficiently powerful drugs that have categorical indications and contraindications. You can not thinklessly take antibacterial drugs - in most cases they are absolutely useless, but their negative effects on the work of the intestines, liver and kidneys can already have ( so-called side effects).For those who want to know in more detail how many days to drink antibiotics for bronchitis, you can learn from the article. Therefore, one should know clear indications for the appointment / use of antibiotics for the treatment of various forms / types of bronchitis:
- borderline high body temperature, which can not be reduced by conventional antipyretic;
- purulent sputum;

- developing bronchospasm;
- previously diagnosed with chronic bronchitis.
It is strictly forbidden to prescribe to doctors or take antibiotics on their own when:
- diseases of urinary system of severe course - renal failure / nephropathy;
- violations of the functionality of the liver - selectively, for example, with certain forms of hepatitis;
- peptic ulcer of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract( stomach / duodenum).
Important: it is necessary to exclude allergic reaction to antibiotics - it can develop rapidly, which leads to anaphylactic shock and edema Quincke.
And notice: if shortly before the development of bronchitis the patient has already been treated with antibacterial drugs of any group, then these funds will be absolutely useless in the treatment of any type of bronchitis.
Possible complications of

If you ignore the symptoms of bronchitis, self-treatment, the abandonment of antibacterial drugs can develop quite serious complications of bronchitis:
- pneumonia and pneumothorax;
- bronchial asthma - especially dangerous in this regard is obstructive bronchitis;
- pulmonary hypertension;
- emphysema;
- bronchiectatic disease.
Note: Acute bronchitis with a correctly conducted treatment is cured quickly enough, otherwise the form of the disease will certainly be replaced by a chronic one.
Video
From this video you will learn about the correct treatment of chronic bronchitis:
Frequent recurrences of chronic bronchitis, prolonged obstructive, purulent and / or catarrhal appearance of the disease in question can lead to the development of inflammation in other organs and body systems - as complications otitis( acute /chronic), tonsillitis( compensated / decompensated).
