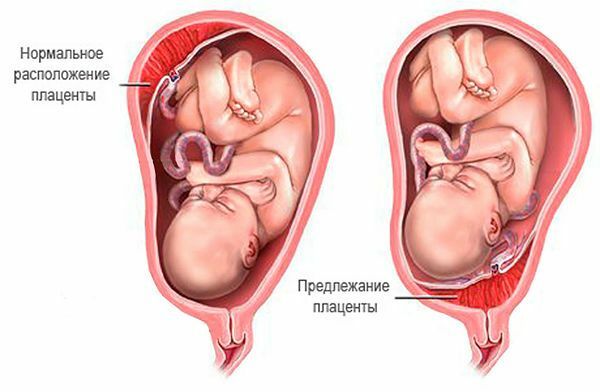
The placenta or a child's place is the basis of the full development of the fetus right up until the birth. Normally, this important organ should be attached near the bottom of the uterus. But in some cases, the placenta is attached to her neck, completely blocking the way to the birth of a new life. This phenomenon is called full placenta previa.
- General description of placenta
- Causes of
- Creation
- Fruit
- Than
- Diagnosis
- Presentation forms
- Treatment
- Childbirth with a similar diagnosis
General characteristics of the placenta
In order to understand how dangerous fullness of the placenta is, it is necessary to understand the role of the placenta andmechanism of its interaction with the organism of the child and mother.
The placental tissue is permeated with so-called villi or small vessels. They practically fuse with the uterus at the place of attachment of the placenta to it. This is necessary to ensure the exchange of substances between mother and child. From the maternal blood, the baby gets nutrition and oxygen through the umbilical cord, and through the placenta the secretion of the substances worked out by him occurs.
The fetus develops and grows, and the uterus grows with it. It increases in size from a matchbox to a "bag" of a height of 35 centimeters. The walls of the uterus are very elastic and can be stretched freely. This is especially evident in the lower part, where the neck is. The placenta is far from being so flexible and stretchy.
If the pregnant woman has a full central presentation of the placenta, the enlarged uterus "pulls" the placenta behind it, and that does not have time to stretch beyond it, since it is not designed for such a significant increase in size. In terms of medical terms, the migration of the placenta at full preposition in comparison with the uterus is slow. As a result, it detaches from the wall of the uterus.
to the table of contents ^Reasons for the emergence of
Experts believe that all causes can be divided into 2 categories - uterine and fetal.
to contents ^Uterine
The occurrence of problems of this kind is due to the fact that the fetus is attached to the uterus because of the anomalies of the endometrium, not where it is supposed to.
Endometrial defects are observed for many reasons, the main ones being.
- Previously instrumental abortions, including spontaneous, with trauma to the mucosa.
- Postponed inflammations or diseases that caused uterine deformity - scars, fibroids, secretory disorders.
- Mucosal atrophy.
- Endometriosis.
- Pathology of the development of the uterus.
- Deterioration of blood supply to the uterus due to chronic liver, kidney and cardiovascular diseases.
The above factors are in most cases observed in women with repeated pregnancies. This is caused by the accumulation of health problems in this category of pregnant women compared with the primiparous.
Fetal
This category of causes of pregnancy pathology is associated with abnormalities in fetal development. Precisely say why there is a delay in the development of the fetal egg at the earliest stages of pregnancy is impossible.
It does not have time to implant on the uterine endometrium in time, and as a result it is located not at the bottom of the uterus, but near its neck. In this place, and laid the placenta. The probability that in the future it completely closes the uterine zoe, in this case, almost 100%.
to contents ^Than
is dangerous Deviations that occur with full placenta previa.
- Bloody discharge and bleeding caused by rupture of the placenta with the uterus. They appear in the middle of pregnancy. Bleeding these are always external, without internal hematomas, usually painless and sudden, often begin at night. They are often provoked by physical exertion, examination of a gynecologist or even a strong cough. Sexual life with full placenta previa( to avoid increased bleeding) it is desirable to minimize or completely abandon it at 25 weeks.
- Anemia or low hemoglobin level of the mother, caused by frequent bleeding.
- Hypotension, accompanied by weakness, weakness, headaches and even fainting.
- Hypoxia of the fetus, which can cause a developmental lag, low birth weight of the baby, anemia in the first year of life, weak immunity.
- Elevated uterine tone, lower abdominal pain and lower back, which can cause a threat of termination of pregnancy.
- Wrong fetal position( transverse, gluteal or oblique).Together with complete or partial overlapping of the uterine throat this makes it impossible for the natural course of labor. Without Caesarean section in this case simply can not do.
- Postpartum inflammation of the uterus due to severe labor and low resistance of the maternity organism to infections.
Diagnosis
The recognition and diagnosis of full presentation for further monitoring of the course of migration of the placenta can be carried out at the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy. It is based on complaints about periodically appearing painless bleeding.
With the help of ultrasound, you can determine the position of the fetus. The low-lying placenta does not allow him to descend into the lower part of the uterus. Therefore, on ultrasound, and during examination, it can be found that the presenting part of the baby is above the entrance to the small pelvis. These data also allow diagnosing pathology.
If this examination does not reveal abnormalities of the placenta, then we must look for other causes of bleeding. These can be pathologies in the lower parts of the birth canal.
to contents ^Presentation forms
Placenta previa is often diagnosed in the first half of pregnancy. There are following forms of presentation.
- Central is the most dangerous form. It practically does not give a chance for further improvement of the situation and migration of the placenta to a safe distance in relation to the birth canal.
- Partial , when the yawn is 2/3 obstructed by the back wall, gives a small chance that the position will be further improved.
- Edge .With this form of presentation, the obstruction is about 1/3 of the cervix. In this case, usually only a small proportion of pregnancies terminate with surgical intervention. The child's place in the future independently retreats from the throat and the births pass naturally. And the question is whether the marginal placenta previa can be complete, expectant mothers in this case should not be bothered. They can expect a favorable course of pregnancy.
- Full placenta previa on the posterior wall of the uterus is normal and the safest position for the mother and baby.
- Full placenta previa on the anterior wall of the happens much less often, but this is also not a pathology, but a variant of the norm. Mom should only listen to the advice of specialists, then with her and the baby everything will be in order.
Treatment of
A woman with a diagnosed presentation should be under the enhanced supervision of the attending physician. For adequate medical control, the future mother is prescribed regular blood tests. With negative dynamics of hemoglobin and the detection of a decrease in blood coagulation, iron preparations are prescribed, since the risk of anemia and bleeding is very high.
Means are also needed to improve the blood supply to the fetus. This is Ascorutin, Curantil, vitamin E, folic acid, Trental, Sorbifer, Ferrum Lek and others.
With spotting of patients with such a diagnosis, they are observed in the hospital already from a period of more than 24 weeks. Even with the cessation of bleeding, continuous monitoring continues until delivery.
With a satisfactory condition of a pregnant woman with this diagnosis, she is prescribed a bed rest, preparations for reducing the tone of the uterus and fortifying means - Ginipral, No-sppa, Papaverin, vitamins. In addition, sedatives are prescribed - valerian root, motherwort and others. Laxatives are categorically contraindicated.
If bleeding continues, then injections of magnesia, Magne B6 and other drugs are also prescribed. For intensive and prolonged bleeding, refer to the intensive care unit.
to table of contents ^Childbirth with a similar diagnosis
At 38 weeks pregnant with a diagnosis of placenta previa make a planned operation of cesarean section. To wait for natural birth in this case is dangerous because of the high risk of bleeding due to detachment of the placenta.
It is used with:
- Central presentation.
- Incomplete with the wrong location of the fruit. Scars on the uterus.
- Multiple or high-water pregnancy.
- Narrow pelvis.
- First childbirth at the age of over 30 years.
- Additional risks associated with past pregnancy interruptions or uterine surgery.
- Constant and extensive bleeding.
With other forms of presentation, births can occur naturally, but in order to avoid complications in the maternity hospital, a child resuscitation and an operation room for emergency caesarean section should be ready. The following circumstances are favorable for natural delivery:
- No bleeding or cessation after puncture of the bladder.
- Clear signs of readiness for delivery.
- Normal course of contractions.
- The correct position of the fetus.
Stimulation of labor is not carried out. A fetal bladder is pierced already with a slight independent opening of the cervix. But if at the same time the bleeding increases, then resort to an urgent operation.
After the completion of labor( even if they were physiologically performed), the parturient remains under supervision. She can continue to bleed for a long time because of the reduced contractility of the uterus in the place of her fusion with the placenta. Anemia and hypotension also aggravate the postpartum condition.
On presentation, the child's place often can not spontaneously and completely separate from the body of the uterus, therefore, after an examination, an anesthesia operation should be performed to separate the afterbirth. In rare cases, bleeding at the end of Caesarean section can not be stopped and to save the mother in labor, one must remove the uterus.
Complete placenta previa is not a verdict for maternity, but only a warning to carefully follow all the expert's recommendations, serious preparation for childbirth and a subsequent sparing recovery regimen for a young mother.
