
Jaundice is a pathology in which yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes occurs, and very often( in 65% of cases) is diagnosed in newborns. In general, such changes with skin cover occur against a background of high content of bilirubin( the main component of bile) in the tissues and blood. In newborns, jaundice is not considered a disease, but a period of adaptation to the environment.
- Types
- Mechanical
- Hemolytic
- conjugation
- Nuclear
- Hepatic
- Neonatal
- jaundice breast milk
- reasons
- Symptoms
- danger and consequences
- Phototherapy
- Pharmacotherapy
- Hofitol
- Ursofalk
- Smecta
- Enterosgel
- Traditional methods
- Sun exposure
- Brothdog rose
- Prevention
Species
There are the following types of jaundice in infants:
to contents ^Mechanical Protection
In this type of jaundice is a change of the normal color of skin, mucous membranes and sclera of the eyeball on a greenish-yellow. The causes of yellowing of the skin can be:
- improper operation of the gallbladder;
- obstruction of the biliary tract;
- abnormal liver function;
- birth injury;
- genetic disorders.
Hemolytic
Very quickly identifiable, since yellowing occurs almost immediately after the birth of the child. At less than 1% of all newborns with jaundice this type is diagnosed. With palpation, there is an increase in the liver and spleen, the child becomes constantly sleepy and sluggish and requires immediate treatment.
The causes may be:
- Rh-conflict between the newborn and the mother;
- different blood types;
- antigenic incompatibility.
Conjugation
This kind of jaundice appears after the flow of long-term postpartum icterus into the pathological jaundice. With conjunctive jaundice, the liver of the newborn does not fully cope with the removal of bilirubin from the body due to poor enzyme binding.
to contents ^Nuclear
One of the most dangerous pathological jaundice, in which there is a sharp increase in bilirubin in the blood and accumulation of it in the brain. There is an intoxication of the nervous system and the body as a whole, which can lead to irreversible consequences for the normal functioning of the baby.
to contents ^Hepatic
Or parenchymal jaundice appears due to damage to liver cells with bilirubin, viruses or bacteria. It is very obvious, with this kind of jaundice, the enlarged liver of the spleen is palpable and it requires medical treatment.
to contents ^Neonatal
The most common type of jaundice in newborns. Neonatal jaundice does not need any kind of treatment, it passes with time itself and does not cause consequences and complications for the child's health.
to table of contents ^Jaundice of breast milk
A rare type of jaundice in children, which appears from too much estrogen in the mother's body. With such jaundice the kid's liver first displays estrogen, and then only bilirubin, so jaundice can last up to three months, while there is no violation of appetite and sleep. Over time, such jaundice passes by itself and does not need treatment, and breastfeeding should not be abandoned.
Reasons for
As a result of such cases, the baby can have a yellowish:
- surplus red blood cells in the body - in newborns the red blood cells decay much faster than in adults, therefore too much bilirubin is released, which can not be excreted;
- inadequate activity of binding substances in the liver - in this case, the lack of necessary enzymes promotes the accumulation of bile pigment in the blood and, as a consequence, the skin becomes yellowish;
- is not an adapted gastrointestinal microflora - bilirubin is excreted from the body by urine and feces, and because the baby's microflora is not completely formed, the necessary metamorphosis does not take place to the full and the body can not completely remove the pigment.
Symptoms of
If, after a couple of weeks, jaundice in a newborn does not disappear, thenshould consult a doctor. Symptoms accompanied by jaundice:
- immediately after birth yellow skin;
- colorless, almost white feces;
- urine becomes dark in color;
- bruising can occur without any apparent cause;
- there is an increase in the liver and spleen during palpation;
- the child is capricious, there is a constant drowsiness, cramps and refusal of food.
Danger and consequences of
If medical help is not provided in time for pathological jaundice, the following consequences may occur:
- intoxication of the nervous system and brain;
- development of albuminemia - a disease in which the protein albumin decreases, and as a consequence - increased bilirubin in the blood;
- ingestion of the pigment into the brain, which causes nuclear jaundice, and as a consequence, deafness, insufficient mental development, seizures and even death;
- inability to control motor reflexes.
Phototherapy of
Phototherapy is the irradiation of a baby with a special lamp. The total irradiation course lasts a total of 96 hours. Radiation emanating from the lamp splits bilirubin into compounds that are not toxic to the newborn's body. The consequences of this method of treatment in the baby can appear peeling of the skin, drowsiness and a loose stool.
to the table of contents ^Medical treatment
Very few medications are possible for use in the treatment of jaundice in newborns, and include:
to the table of contents ^Hofitol
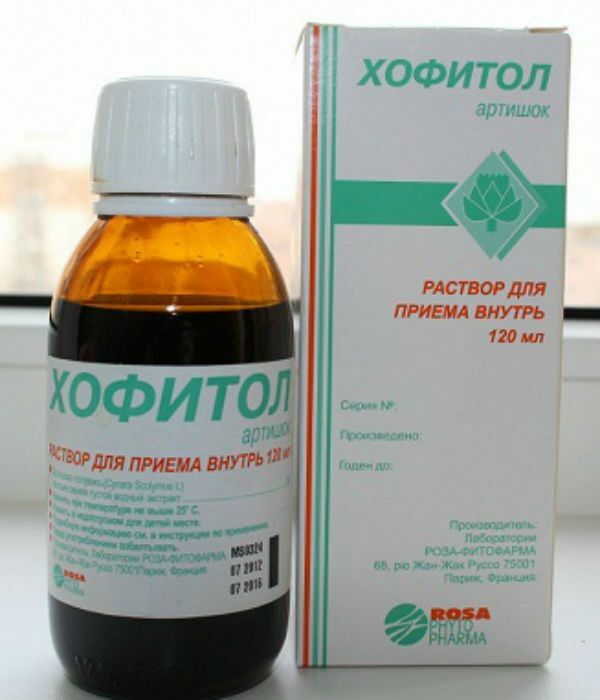
Oral solution. The main substance is the aqueous extract of artichoke leaves of the field. It is prescribed for kidney and liver diseases( hepatitis, nephritis, cholecystitis).
Ursofalk
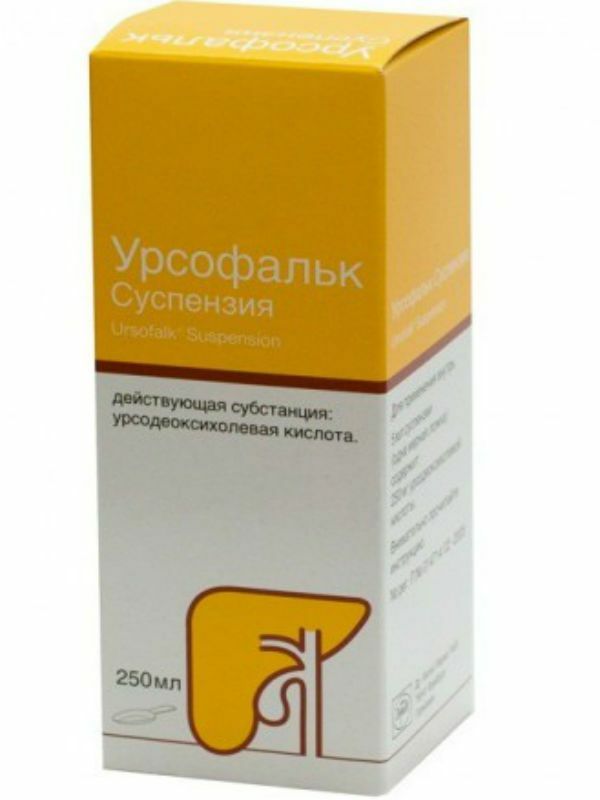
Capsules. The main substance is ursodeoxycholic acid. It is prescribed for the treatment of liver and bile duct diseases.
Smecta

Powder for suspension preparation. The main substance is diosmectite. The drug is given to infants with acute diarrhea.
Enterosgel
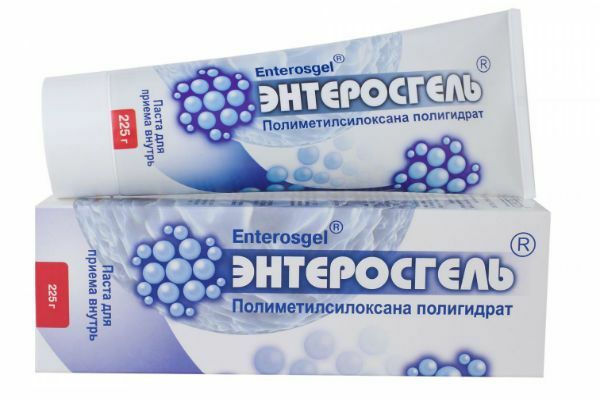
Gel for oral administration. The main substance is the hydrogel of methyl silicic acid. It is prescribed for the treatment of toxic and viral hepatitis, colitis and cholestasis.
Folk methods
Methods of folk ridiculous relief from jaundice:
to table of contents ^Solar exposure
Regular( 30 minutes a day) finding a baby under the sun has a positive effect on getting rid of jaundice. And such a walk strengthens the infant organism.
to the table of contents ^Broth of dogrose
Broth from hips of wild rose very well influences on digestion and the removal of harmful substances from the body. Such a decoction can be consumed by both mother and baby. Normalization of the mother's diet With milk, the child receives all the necessary nutrients, but not following a normal diet can affect the appearance of the jelly. First of all, it is necessary:
- to give up different kinds of smoked food, pickles and other products, with pronounced taste qualities;
- use at least 2 liters of water per day;
- use more fruits, vegetables and other products of natural origin.
Prevention
The only preventive advice for preventing a yellowing in a newborn is sufficient intake of breast milk. With insufficient amount of breast milk, it can be replaced with goat with the addition of folic acid( 0.1 milligram per liter of milk).
