Most of the fears about vaccinations are related to the consequences that they can cause. In order that vaccination does not frighten possible side effects, it is necessary to understand: in which cases the reaction of the body to the vaccination is absolutely normal and reflects the processes of formation of immunity occurring in it, and in which cases symptoms of undesirable complications requiring medical intervention are observed.
Contents of
- Possible reactions to vaccinations
- Can an allergic reaction to vaccinations be possible?
- BCG vaccination: possible reaction
- Mantoux vaccination response
- Rubella inoculation response
- Response to measles, mumps vaccine
- DTP vaccine response
- Tetanus vaccination response
- Polio vaccine response
- Response to hepatitis vaccine
- Reactionon inoculation against influenza
- Video: Vaccinations: reactions and complications - Komarovsky
Possible reactions to inoculations
Post-vaccination manifestations are subdivided into natural reactions and undesirable complicationsNia.
The body's response to a foreign substance is quite understandable and should be taken adequately if it does not go beyond the norm. The normal state after vaccination can be attributed to local and general reactions.
Local reactions occur, as a rule, immediately and pass for 2-3 days( swelling, itching, redness, pain, etc.).
General affect the whole body. The most common manifestations include fever, sleep disturbance, general malaise.
IMPORTANT: The temperature increase caused by grafting is recommended to "knock down".If the child's organism reacts with hyperthermia for each inoculation, you can give it antipyretic before the subsequent vaccination.
Unwanted complications always require medical examination and appropriate treatment. These include lethargy, afebrile convulsions( against the background of normal body temperature), a temperature above 39 ° C, neurological disorders, anaphylaxis, etc.
Is an allergic reaction to vaccinations possible?
Almost all vaccines, as a potential complication, more or less call an individual allergic reaction.
 Among the components-allergens that make up the vaccines, you should pay attention to:
Among the components-allergens that make up the vaccines, you should pay attention to:
- antibiotics
- chicken protein
- baking yeast
- gelatin, etc.
If you or your child has a tendency to allergies to these components or any others, it should be in advanceinform the doctor about this, to select a suitable vaccine and carry out preventive measures.
INTERESTING: Recent studies have shown that vaccinated children are less likely to develop allergic diseases than unvaccinated children. For example, cases of atopic eczema were recorded in vaccinated children in 22.1% of cases, and in unvaccinated children - in 29.6%.
Serious allergic reactions can occur:
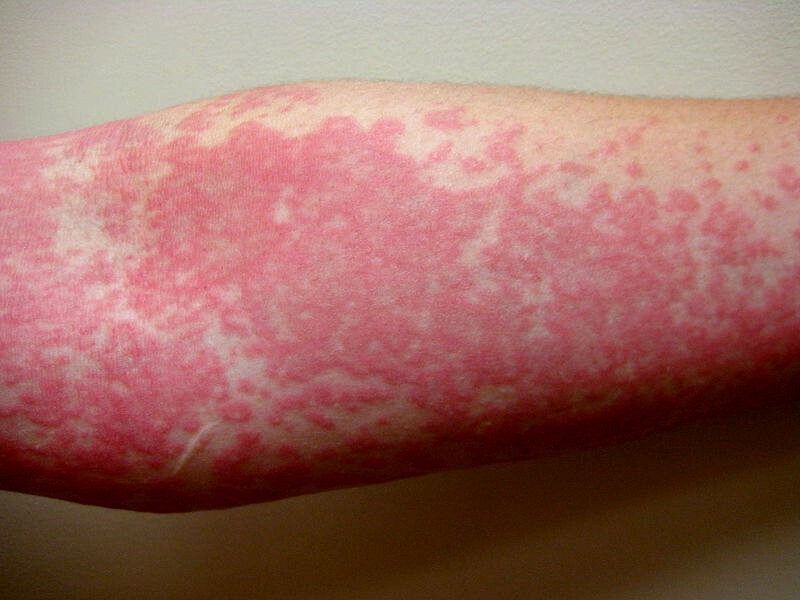
- urticaria - severe skin rash
- Quincke edema - extensive swelling of the facial skin and mucous membranes of the throat and nose, resulting in difficulty breathing
- anaphylactic shock - a sharp decrease in pressure, severe swelling, itching, choking
IMPORTANT: Signs of these complications are manifested after half an hour, so it is important to stay for a while after vaccination in a health care institution for assistance if necessary.
BCG vaccine: possible reaction
The vaccination against tuberculosis is transferred mainly without complications and consequences. To normal manifestations of the action of the vaccine include:
- Redness. Should not cause concern if it does not extend beyond the site of injection and scar formation.
- Swelling. It is observed in the first days after the injection. In the subsequent edema should not be
- Suppuration. The formation of a small ulcer refers to an acceptable response of the body. The abscess can be opened with the contents outward. Over time, the formation is covered with a layer of crust, and the wound heals. The process can take about 4-4.5 months.
IMPORTANT: Do not treat the suppuration site with green tea, iodine or other antiseptics.
- Scar formation. A small( 2-10 mm) pale hem on the shoulder - the final view, which takes the place of introduction of the vaccine against tuberculosis
- Inflammation. If the infiltrate looks inflamed, i.e.reddened, purulent, with fluid inside, but signs of inflammation are localized and do not touch adjacent skin areas, this should not alarm
- Temperature. Suppuration may cause an increase in temperature to 37.5 ° C.This is normal. If the temperature rises during a subsequent booster at 7 or 14 years of age, you should contact the healthcare institution
- for a desire to scratch. A natural sensation that occurs during the healing process. However, during this period should refrain from strong touch to the site of injection as scratching, rubbing
- In case you have found a child's other symptoms that cause concern, immediately consult a doctor phthisiatrician
- Not quite natural is the lack of a normal reaction, and a trace ofInoculations. This situation can be observed in 5-10% of children with primary vaccination. If BCG place is not much, it means that the vaccination immunity from disease is not formed, or more rarely, a child due to hereditary characteristics of resistant bacteria of tuberculosis and at the genetic level can not they catch
- If there is no trace of the injection is carried out Mantoux test. If the Mantoux test is negative, the BCG vaccination is repeated at once, or in the subsequent booster at age 7
IMPORTANT: The body begins to respond to the vaccine only through 1-1,5 months. Therefore, the response to vaccination may not appear immediately, and this is a variant of the norm.
Complications can appear as:
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes .Occurs when mycobacteria spread and axillary lymph nodes are infected. Augmentation of the node in the armpit - an occasion to visit the doctor
- Extensive suppuration. If a subcutaneous abscess with a size greater than 10 mm develops at the site of injection, you should consult a doctor for surgical intervention
- Rumen extensions. Observed with hereditary predisposition and manifests itself in any skin damage. The scar or keloid acquires a bright color, the blood vessels are visible. In this case, revaccination, as a rule, does not conduct
- Bone diseases( osteitis). Occurs very rarely in case of serious problems in a child with
immunity. Cases of similar consequences are rarely recorded( 0.02% -0.004%). reasons :
- noncompliance contraindications( congenital immune deficiency and AIDS)
- incorrect administration of the preparation( s.c.)
Reaction to vaccination Mantoux
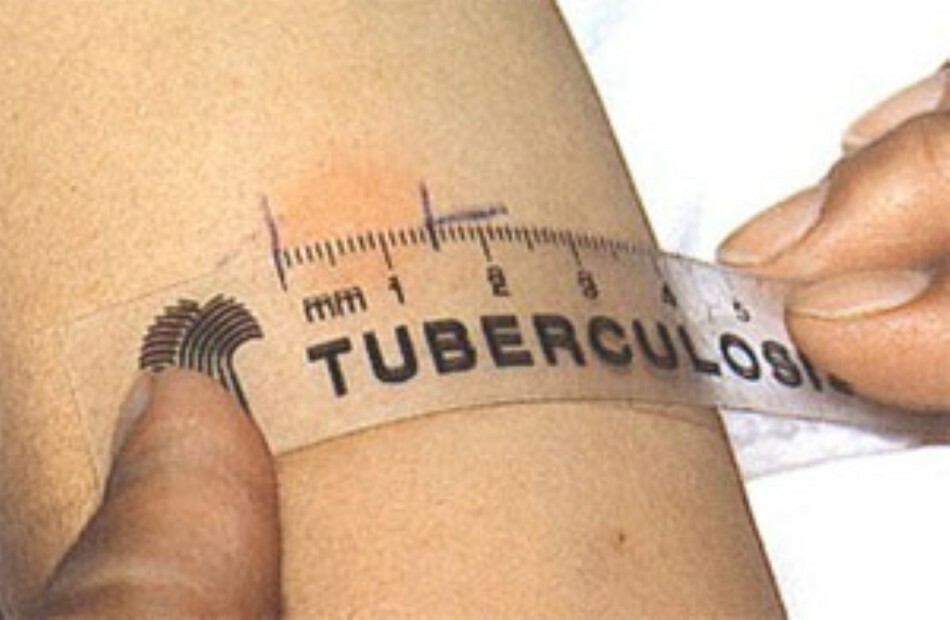
To be precise, the Mantoux not refers to the number of inoculations, and is a test the results of which determine the presence or absence oftuberculosis infection.
Despite the fact that Mantoux is made everywhere by a large number of children every year starting from the age of one year, it is not necessary to say that the injection has no side effects. Among the possible unpleasant consequences Mantoux test is called:
- malaise
- headache
- high temperature
- rash itching swelling
- allergic inflammation of the lymph nodes and vessels
Interpretation of Mantoux test results is carried out three days after measuring the infiltration with a transparent ruler. The following Mantoux reactions stand out:
- Negative( norm). Papula( thickening) and redness absent or not exceeding 1 mm
- Doubtful( variant of the norm). Infiltration not more than 4 mm
- Positive. Sealing larger than 5-6 mm
IMPORTANT: A positive Mantoux test does not necessarily indicate an infection, such a reaction may cause an allergy.
In order to clarify the reasons for the positive result, the following factors are considered:
- The size of the formed after vaccination BCG scar. For example, the diameter of the hem 5-8 mm usually indicates the presence of antibodies to tuberculosis within the next 5-7 years, if scar is not visible, there is no immunity, which means there is a risk of infection
- The presence of any infection shortly before the Mantoux reaction
- Time interval from vaccine immunization. The more time passed, the higher the risk of
- The results of previous measurements. A sharp increase in the size of the infiltrate by 6 mm or more compared to the results of previous years, indicates a possible infection of
- Allergy to Mantoux components
- Pigmentation. If in a couple of weeks the place of injection of the Mantoux sample has clear boundaries and turns brownish, there is a possibility of infection with the tuberculosis mycobacterium
- . Contact with patients, stay in the
- risk zone. Gain effect. If the Mantoux test was carried out too often( more than once a year), an increase in the size of the infiltrate may occur, which is explained by the development of increased sensitivity of lymphocytes to
. In case of a positive test result for tuberculosis or if the child has serious side effects after the sample, contact the TB specialist for furtherdiagnostics.
Response to rubella vaccination

Signs of possible changes in the body after the introduction of the rubella vaccine, you can detect after 5-15 days. So much time is required for active interaction of the body with the drug and the production of antibodies. In addition to local reactions such as redness, swelling and tenderness at the injection site, 5-10% of people may have the following symptoms, which are the norm option:
- high temperature
- rash
- pain in lymph nodes
- cough
- joint pain
- ITP( abnormalitiesin terms of blood coagulability), etc.
These inconveniences caused by the individual manifestation of how the body forms immunity, as a rule, do not need special treatment and pass by themselves.
Serious complications requiring medical care are rare and develop against a background of other chronic diseases. Among them:
- severe allergic reactions
- convulsions without temperature
- meningitis
- encephalitis
Response to measles, mumps
Vaccination against rubella, mumps and measles is carried out simultaneously. In this case, both mono-vaccines and a complex preparation can be used, which includes all components simultaneously. Immunization is transferred mainly well.
The possible response to the measles and mumps vaccine is generally similar to that of the rubella vaccine:
- redness and tightness at the injection site
- fever and seizures on its background
- cough, runny nose
- rashes red
- swelling of the lymph nodes and t.
The appearance of these symptoms can be seen within two weeks after vaccination, but they pass for a couple of days.
Among the consequences not related to normal reaction, the main place is occupied by an allergy to any of the components of the vaccine( neomycin, protein, etc.).To prevent even a slight risk of anaphylactic shock, tell your doctor about any existing allergic reactions.
Response to DPT vaccination
A comprehensive vaccination against pertussis, tetanus and diphtheria causes young parents to be seriously worried. There is a likelihood that immunization will pass unnoticed, and that it will bring a lot of worries and worries.
Whether there is an unwanted reaction in a child to a DTP vaccine will be clear within the first 24 hours. The cause of a possible cough, runny nose or temperature in the following days should be looked for in another.
To the list of side effects in DPT vaccination include:
- reddening and thickening sites of injection, soreness in the leg
- rise in body temperature to 38.5 ° C .If the body temperature reaches 39 ° C or higher, there is a so-called pronounced
reaction IMPORTANT: As a rule, the pertussis component of the vaccine is hard to tolerate. If the child had a marked reaction to the first injection of DTP, the pediatrician may recommend further ADP vaccination, i.e.exclude the pertussis component.
- change in the behavior of the child : prolonged crying, moodiness or vice versa, apathy and drowsiness, loss of appetite or other reactions unrelated to the child
vomiting, diarrhea
IMPORTANT: Vaccination is carried out in several stages. According to medical observations, the likelihood of a reaction to the vaccine increases with each subsequent vaccination of DTP.
The doctor should be contacted immediately if:

- crying or crying of the child does not abate for several hours
- the temperature rises above 39 ° C
- the site of the injection is strongly swollen( reddening diameter more than 8 cm)
Among the complications are possible:
- without temperature convulsions( 1case for 30,000-40,000)
- allergic reaction( urticaria, anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, etc.)
Scientific evidence of the fact that the consequences of vaccination may be a disruption of the brain are absent.
It should also be aware that the pertussis vaccine may be a cellular( DTP vaccine) and acellular( imported vaccines).More pronounced side effects are observed on the pertussis cell vaccine.
For example, pain after the acellular vaccine is noted in 2.5% of the vaccinated, after the DTP vaccine - in 19%.Increase in rectal temperature to 38 ° C and higher - in 10% and 42%, respectively.
Response to tetanus inoculation
If vaccination is carried out according to the schedule of preventive vaccinations, the tetanus vaccination is done simultaneously with the vaccination against diphtheria and pertussis, i.e.is included in the DTP vaccine. Accordingly, if there is a reaction after vaccination, then its signs are similar to the above mentioned possible side effects from the complex DTP vaccination.
In isolated situations, a tetanus monovalent can be administered. Among the temporary phenomena are recorded cases of coughing, runny nose, nausea, diarrhea, etc. Complications are very rare.
Response to poliomyelitis vaccination
There are various polio vaccination options:
- vaccine may be a component of a combined preparation or be inoculated separately
- may differ in composition and administration: OPV( live as drops) or IPV( inactivated vaccine in the form ofprick)
After taking oral vaccine may occur:
- insignificant temperature increase
- intestinal disorder
- mild allergic reaction
- in rare cases - vaccinoaspoliomyelitis( with serious immunity problems)
When using an inactivated vaccine, the following can be noted:
- local redness and swelling
- slight increase in body temperature
- general malaise
Symptoms go away on their own. If you have more serious complications, you should consult a doctor.
Response to inoculation against hepatitis
There are almost no postvaccinal reactions, or they proceed in mild form. Soreness, itching and redness at the site of injection are considered a natural reaction of the body. In 1% of vaccines, there is a slight hyperthermia, general weakness, headache, vomiting, muscle pain, etc. According to WHO reports on anaphylactic reactions are recorded very rarely.
Response to influenza vaccination

Like any other vaccine, an injection from influenza can cause a local reaction, which indicates that the process of forming immunity against the disease is started. Normal is soreness and a slight inflammation at the injection site.
To the general reaction of the body within the limits of the following symptoms include:
- body temperature 37 - 37.5 ° C
- headache
- weakness
- sleep disturbance, etc.
According to the study, in which 791 children participated, the temperature increase after vaccination was fixed12% of children aged 1-5 years, 5% - at the age of 6-10 years and 5% - at the age of 11-15 years.
If there is an allergy to the components of the vaccine, appropriate reactions are possible. However, the percentage of such cases is very small.
Thus, in most cases, the side effects of vaccines are asymptomatic or mild. The probability of severe complications is low( about 1 case per million) and does not occur on a flat surface. Among the causes of the central place are violations of existing contraindications and an individual allergic reaction.
Obviously, this can not be the reason for refusing to vaccinate. A responsible approach to one's own health can prevent the existing risk of unwanted manifestations after vaccinations and protect you from serious( often fatal) diseases against which the vaccine is administered.
More information about vaccinations can be found in the articles:
- Vaccination and vaccination schedule for children. What do parents need to know about vaccination and vaccination of children?
- Vaccination of children: at risk. When can not I get vaccinated?
- Vaccinations: Myths and Reality
