
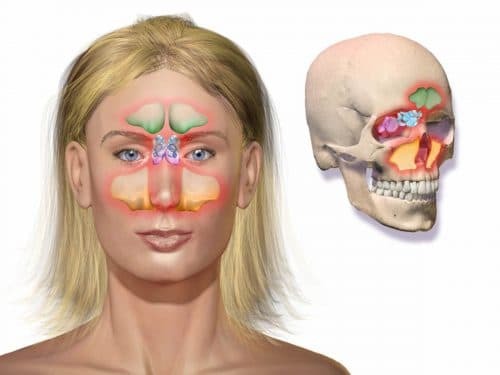
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses. The latter are located in the area of the nose, around the eyes, behind the forehead and cheekbones. As a rule, sinusitis follows a cold or severe rhinitis and is accompanied by a characteristic headache.
In the usual case, inflammation is treated with the help of sprays, tablets, rinsing the nose and warming up. However, in severe disease, more potent drugs are needed - injections.
Contents
- 1 Medications
- 1.1 Mechanism of the disease
- 2 Types
- 2.1 Treatment of the disease
- 2.2 First line antibiotics
- 2.3 Second-line drugs
- 2.4 Symptom withdrawal
- 3 Reviews
Used medications
No need for them is infrequent. And the use of antibiotics or drugs of another group is determined not so much by the severity of the disease as the origin of the disease.
Mechanism of the disease
The cause of sinusitis is not at all a hypothermia or a cold in itself, but a pathogenic microflora:
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- fungi.
Most often the disease provokes the same viruses that cause colds. At the same time, the amount of mucus secreted in the sinus increases, the sinus swells, which blocks the normal drainage of the liquid from the nose. Over time, mucus and fluid accumulate to such an extent that they exert pressure and cause a headache. 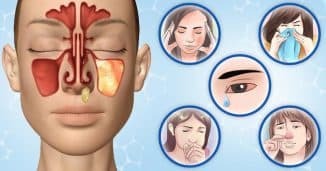
Inside the sinus, an environment is formed that is favorable for the development of fungi and bacteria. The latter not only increases swelling and pain, but can lead to tissue death - purulent sinusitis.
The disease caused by an allergic reaction is slightly different. The mechanism, in fact, the same: swelling of the sinus, irritation, accumulation of mucus and difficulty with its withdrawal. But, since the cause is an external factor, the development of the disease entirely depends on contact with the allergen. While the source of irritation is not found, the disease will not be cured.
Fungal infections usually cause sinusitis on the background of weakened immunity - blood diseases, diabetes mellitus. Fungal maxillary sinusitis is hard to treat.
On video antibiotics used for sinusitis:
Bacteria cause sinusitis on the rhinitis background. Violation of the outflow of liquid from the nose does not allow to be released from bacteria in time. The latter multiply in the nasal cavity and, in the end, find themselves in the maxillary sinuses, which leads to the onset of the disease. Most often, the cause of maxillary sinusitis is Staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus, hemophilia infection.
Types of
The disease can take many forms. Treatment is determined not only by the cause of the disease, but also by the stage of development, severity and form.
- Acute maxillary sinusitis - most often occurs against the background of a severe cold and is accompanied by pressure and pain in the area of inflamed sinuses, a severe headache, purulent discharge from the nose. The disease lasts no more than 4 weeks. Sinuses can inflame up to 3 times a year.
Acute maxillary sinusitis
- With purulent maxillary sinusitis antibiotics are prescribed without fail. If the genyantritis is accompanied by a fever, medications are prescribed in the form of injections.
- Semi-acute - takes 4 to 8 weeks and does not have such pronounced symptoms. Often taken for an ordinary cold.
- Chronic - lasts more than 8 weeks, manifests up to 4 times a year. Purulent discharge is usually not accompanied, but headaches are always - aching, prolonged.
Chronic maxillary sinusitis
- Repeated - so rare isolated cases separate from repetitive ones. Unfortunately, it is the latter form that is characteristic of the disease.
Treatment of
Like any other ailment, sinusitis accompanies a number of symptoms and can cause some complications. The objectives of the treatment are:
- pain relief and pressure reduction;
- improved mucus output and decreased swelling;
- destroying an infection or a virus;
- prevention of the appearance of scar tissue. The latter due to its heterogeneity is a constant irritating factor, and, therefore, provokes the disease.
 How the cuckoo is made with genyantritis and how this procedure is effective, is described in this article.
How the cuckoo is made with genyantritis and how this procedure is effective, is described in this article.
And here is how the treatment of maxillary sinusitis with antibiotics Ceftriaxone will help to understand this article.
How to use a spray for sinusitis Renoflumacil, is described in great detail in this article: http: //prolor.ru/n/ bolezni-n /gajmorit/ rinofluimucil.html
And here's how to use Bioparox in genyantritis, this article will help you understand.
Antibiotics of the first line
Antibiotics are most often used to perform the third task and when conventional oral medications do not work. Assign them makes sense after receiving the results of bacteriosia: antibiotics are not universal and act on a certain group of pathogens.
- Antibiotics of penicillin series - amoxicillin, ampicillin. The inconvenience of such a drug in the need to maintain a high concentration: injections are done every 3-4 hours. The drug is administered intravenously and intramuscularly, the dose is determined by the severity of inflammation - from 250 thousand to 60 million units.
Amoxicillin in tablets
In addition, penicillin is a fairly strong allergen and is not suitable for many patients. Despite this, the drug is considered safe, refers to antibiotics of the first line and can be given to children. As a rule, penicillins are effective in various forms of the disease. And here's how to use amoxicillin, including in case of angina in adults, is described in great detail in this article.
- Aminoglycosides - tobramycin, gentamicin. Assign at the rate of 1.5-1.7 mg per 1 kg of body per day. Nyxes do 2 per day. The drug is very active in relation to the hemophilic rod and moraxelle, but does not suppress streptococci and other anaerobic bacteria.
Gentamicin for injection
Aminoglycosides have unpleasant side effects, in particular, affect the auditory nerve, provoking deafness, and irreversible. Therefore, their use should be monitored by a physician.
- Macrolides - clarithromycin, azithromycin. Antibiotics are equally active in relation to moraxelle and streptococci. Clarithromycin is prescribed at 4.5 mg per 1 kg of body weight. The course takes 7-10 days.
Azithromycin in tablets
Azithromycin acts somewhat differently: it is characterized by a long half-life, so drink it like this: 500 mg on the first day and 250 mg for the next 5 days. The injections are prescribed only in severe form, the course - no more than 2 days, after which they switch to tablets.
Macrolides are used in the treatment of genyantritis only if an allergy to penicillin preparations is registered.
- B Lycra on action against macrolides and antibiotics of the group of lincosamides - Linkomycin .The drug has a bacteriostatic effect, and with a high dosage - bactericidal. Active against anaerobic bacteria. You can inject lincomycin intramuscularly - 600 mg 1-2 times a day, and intravenously. Lincomycin is incompatible with calcium gluconate and penicillin preparations.

Lincomycin in tablets
If there is an allergy to all 3 groups of drugs, second-line drugs are prescribed. They include cephalosporins.fluoroquinolines and protected penicillins. These same antibiotics are prescribed in the case of acute purulent sinusitis.
Antibiotics have an effect fairly quickly. If after 3-4 days of improvement is not observed, you need to see a doctor with repeated complaints. No effect - direct indication for antibiotic replacement.
Second-line preparations
An ideal way to determine the correct antibiotic is by bacterial sowing of the contents of the maxillary sinuses. However, for such an analysis, a puncture is necessary. As a result, the doctor usually prescribes the drug based on experience and data on the patient's allergy.
- Protected penicillins - the so-called complex of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Most often they are prescribed in the form of tablets.
Clavulanic acid in tablets
- Cephalosporins - second and third generation. Cefuroxime is taken mostly orally, cefpodoxime and cefodox, on the contrary, are prescribed as injections, as they are poorly absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract - no more than 50%.Intravenous injections. Cefuroxime is prescribed for 1 g every 8 hours, cefotaxime - 2 g every 4-6 hours. Ceftriaxone - 2 g per day for 2 divided doses.
Cefuroxime for injection
- Cefixime poorly inhibits gram-positive bacteria - golden streptococcus, for example. Cefpodoxime is a more effective medicine.
Cefpodoxime powder
- Fluoroquinolines - the effectiveness of drugs reaches 90%.In the form of injections are practically not used. In addition, fluoroquinolines are not given to children and adolescents, as they negatively affect cartilaginous tissues.
- In severe purulent maxillary sinusitis, carbapenems are prescribed - one of the most potent preparations of a wide spectrum. Treatment is carried out only in stationary conditions.
Antibiotics are not only potent, but also have a lot of side effects. Self-medication with their help is unacceptable.
Removing the symptoms of
In addition to destroying the pathogenic microflora, the aim of treatment is to suppress other symptoms - puffiness, irritation, severe headache. In some cases, and here the administration of the drug in the form of an injection is more appropriate.
- Hot shot is a solution of calcium chloride. Received its name for the feeling of heat that the patient will experience after the introduction. Calcium chloride significantly reduces inflammation and is especially effective in cases of allergic sinusitis.

Calcium chloride solution for injection
In pregnancy or disorders in the work of the kidneys, heart, liver, the drug is not prescribed. There is also a hot powder for cold, but how it should be used will help to understand this article.
- Calcium gluconate injections is designated as an adjuvant. In sinusitis, small blood vessels are damaged. Calcium gluconus helps restore the elasticity of the vessel wall, which reduces swelling and restores normal blood supply. Usually, it is used for allergic sinusitis, since it has an anti-allergic effect.
Calcium gluconate is usually administered or taken as part of other drugs - rutoside, paracetamol.
- Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticosteroid. It is a strong anti-inflammatory agent, it also reduces swelling and flushing. It is prescribed for severe forms of sinusitis. The course is organized in such a way that treatment is carried out with minimal effective doses and in the shortest possible time. Cancel the medicine gradually. But how to use dexamethasone in children with laryngitis is described in great detail in this article.
Dexamethasone is administered intravenously and intramuscularly - 0.5-2.4 mg per day in 2 divided doses.
Dexamethasone for Injection
- For the same purpose, prednisolone or beclamethasone dipropionate is used. The dose does not exceed 30-40 mg in knocking, is administered intravenously by a drop route. Used to relieve acute severe inflammation.
Injections of antibiotics, and other drugs are prescribed for nosocomial, that is, microbial origin, acute ailments. Appointment of them for non-severe forms of the disease is inexpedient and fraught with consequences.
And here is how to treat a genyantritis without a puncture and by what means, this article will help to understand.
Which antibiotics for sinusitis and sinusitis are the best and most effective, is described in this article.
Reviews
- Helena, 32 years old, St. Petersburg: "Several times he treated sinusitis, and for a long time. As it turned out, the pathogen was insensitive to amoxicillin, and I was persistently appointed by various ENT doctors. We prescribed clarithromycin, and it went well. "
- Tatiana, 28, Arkhangelsk: "Twice I changed antibiotics during treatment. We searched by experience: 3 days no change, another is appointed. And the genyantritis was heavy, purulent. In the end, they pierced Linkomycin. "
- Alexander, 31, Kaspiysk: "Acute sinusitis suffered in the past year. A dreadful headache, one can not breathe a nose, and when the temperature has risen, it was necessary and to lie down in a hospital. Antibiotics pricked the first 4 days - amoxicillin. A hot shot was made from the inflammation. For 10 days, all has passed. "
- Veronica, 26 years old, Lipetsk: "I have been sick with my sinusitis since childhood, pierced several times. I used sprays, pills, and injections. The injections help faster. I was prescribed gentamicin. For 5 days, everything passed, and it was not necessary to pierce. "
Antibiotics for sinusitis are prescribed in cases when the disease is caused by pathogenic bacteria. Injection is the most effective form of drug administration, but also because it is also the most dangerous, since possible side effects in this case are more pronounced.
