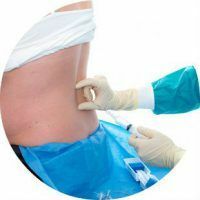
When performing spinal anesthesia in the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord, a local anesthetic solution is administered. This type of anesthesia was first described in 1899.With the advent of new drugs, the improvement of needles for puncture, the definition of possible complications and the adoption of measures to prevent them, the technique began to be used quite actively. Studies have proven the safety of spinal anesthesia for the body, which has caused its active spread.
How the
works After injecting the drug into the subarachnoid space, spinal anesthesia affects the spinal cord, causing it to blockade, thus providing long-term anesthesia for surgical interventions performed on the hip joint, lower extremities, perineum, lumbar spine and lower abdominal cavity.
The main advantages of spinal anesthesia are:
- Rapid onset of action.
- Strong anesthetic effect.
- Postoperative pain relief.
- Reducing the risk of complications such as pulmonary embolism, thrombosis.
- In addition, with spinal anesthesia, the load on the lungs and heart is much less than with other types of anesthesia( epidural, general, etc.).
Differences in spinal and epidural anesthesia
- Different cavities in the spine for anesthetic administration: epidural or subarachnoid space.
- The mechanism of action is different: in case of epidural anesthesia, the final parts of the nerves are blocked, with spinal cord blockade of the spinal cord.
- There is a difference in the rate of disappearance of pain and tactile sensitivity after the introduction of anesthetic.
- Needles for puncturing are different in thickness.
- Epidural anesthesia is more dangerous( a greater percentage of the risk of complications) than the spinal anesthesia.
Indications
- Endoscopic urological operations. Preservation of consciousness allows you to monitor the patient's condition, which has the ability to report pain that occurred during the operation.
- Operations on the rectum - the implementation of such interventions involves the finding of a patient on the stomach. The disadvantages include the difficulties of transferring to general anesthesia, since any actions on the airways in this state are very risky.
- Manipulation on the hip joint. Studies have shown that in elderly patients with fracture of the neck of the hip, blood loss during intervention decreases, and in the rehabilitation period, delirium and confusion are less common. In addition, the risk of thrombosis is reduced.
- Obstetrics. In this case, spinal anesthesia has a number of advantages - ease of use, stable blockade, low consumption of anesthetic, due to which it gets to the fetus in the minimum amount. The blockade is used during childbirth, vacuum extraction or application of forceps, episiotomy. Anesthesia is often used for caesarean section, even if the operation is performed in emergency cases, the necessary condition is to maintain blood pressure at a high level.
- Recently, spinal anesthesia is suggested for use in pediatric surgery. In preterm infants who need surgery, after general anesthesia, the risk of developing apnea increases, and an anesthesia of this type reduces it. Proved its safety and effectiveness in the conduct of newborn interventions in the groin, the genitourinary organs and lower extremities.
Contraindications
Allocate absolute and conditional contraindications to this type of anesthesia. The first ones are:
- Failure of the patient.
- Bacteremia.
- Severe hypovolemia.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Infection of the skin at the site of the puncture.
Among the relative contraindications are the following:
- Peripheral neuropathies.
- Back pain.
- Previously transferred operations on the spinal cord and spine.
- Treatment with aspirin and heparin.
- Emotional instability of the patient and absence of contact with it.
- Disagreement of the surgeon.
Preparation for surgery involves obtaining consent from the patient, conducting laboratory tests, prescribing premedication.
Consequences of
Pronounced hypotension is a frequent consequence of the use of spinal anesthesia. It is the result of the influence of an anesthetic on the roots of the spinal cord. As a result, there are two types of reactions that can lead to cardiac arrest. The first is characterized by a decrease in heart rate and pressure, discomfort in the abdomen, accompanied by nausea or vomiting. The second type of reaction - pronounced tachycardia, mild cyanosis, pallor.
Other consequences after anesthesia:
- Headache.
- Urinary retention, more common in men.
- Pain at the injection site on the back.
- Arrhythmia.
- Arterial hypertension or asystole.
- Disturbances of breathing, up to its complete cessation, can occur when an anesthetic arrives above the third thoracic segment of the spinal cord.
- Meningitis is the most dangerous complication that develops due to a sterility disorder.
The use of spinal anesthesia is dangerous for patients with hypovolemia( decreased vascular tone), since it is possible to reduce venous return, cardiac output and pressure. Often, patients experience such adverse reactions as anesthesia, such as pain in the back or head. Their development is associated with the technique of performing a lumbar puncture. As a rule, pain is present constantly, the intensity decreases in the prone position and is strengthened if the patient sits or stands.
Another complication is adhesive arachnoiditis, which develops gradually. Weakness and loss of sensitivity in the lower extremities are the main clinical signs of this condition. They appear after some time after performing anesthesia and can cause complete paralysis. During the procedure, it is possible to infect the subarachnoid space. This is especially dangerous when the needle touches the infected tissue.
The cause of neurological complications during anesthesia may be trauma, ischemia or hematoma. Ischemia occurs as a result of prolonged hypotension or unreasonable use of sympathomimetics. Trauma can be obtained from a spinal needle or after an intranural injection. Recent studies have revealed previously unknown complications of anesthesia: visual impairment and scotoma development, hair loss, unexpected delayed circulatory arrest. The disadvantages of anesthesia include the ability to damage the spinal cord.
Drugs
For spinal anesthesia the following remedies are used:
- Procain is a preparation that provides a short-term powerful blockade. It is characterized by a rapid start and a short action( 40-60 minutes).Adding vasoconstrictors( epinephrine or norepinephrine) can increase the duration and intensity of the action.
- Tetracaine is a popular anesthetic used for spinal anesthesia. It has an average speed of onset of the effect and provides a prolonged blockade. The duration of the action can be increased by adding vasoconstrictors.
- Lidocaine is an amide that provides a short-term, powerful blockade.
- Bupivacaine is a solution that is characterized by a somewhat delayed onset of action and a lasting effect. There is no need to add vasoconstrictors, since they do not affect the duration of the blockade.
Technique for carrying out
To perform the puncture, the patient should take a posture lying on his side or sitting. The choice of the necessary position is carried out by the doctor. To safely and quickly perform anesthesia, it is recommended not to move during the procedure. At the injection site, the doctor, using a syringe and a thin needle, subcutaneously injects the required amount of a local anesthetic for analgesia. After this, a special needle designed for spinal anesthesia, produces a puncture of the skin.
If necessary, the doctor can cause a sleep-like condition, additionally introducing a sedative into a vein.6-8 hours before the operation it is forbidden to eat or drink anything. It is necessary to remove removable contact lenses and removable dentures, be sure to warn the doctor about the presence of eye prostheses. Do not apply makeup and do not manicure before the operation. Remove all rings, earrings, other ornaments.
Non-observance of these rules significantly increases the risk of complications. Anesthesiologist should be informed about all the operations, injuries, chronic diseases, allergic reactions, intolerance of medicines, medicines used. This information can be useful for preventing the consequences of anesthesia. Before operation it is desirable to have a good rest, take a walk in the fresh air, sleep and not be nervous.
