You can be sure that nothing will ever happen to you. You can not read a lot of information and do not understand - what can happen and how can I help? Perhaps you are lazy and you do not want to spend your precious time on it - this is your personal desire and it has a right to exist. BUT exactly as long as it concerns only you.
If you become parents, you are responsible for your child, his health and safety. Your duty as a parent is to know how to be able to provide emergency medical care to your child in an emergency situation!
Contents of
- What is first aid, and how to understand when it is needed?
- What can happen to the child and how to help him?
- Features of the algorithm for providing emergency medical first-aid
- First aid for obstructive airways. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Backstrokes that combine with bumps in the chest
- Video: What to do if the baby chokes. Emergency methods
- Reception Gameplay. Subdiaphragmatic tremor in the abdomen
- Emergency treatment for children with bronchial asthma
- Algorithms for first aid for children with injuries
- First aid for children with bruises
- First aid for a child's head injury in a child
- First aid for a child with a stretching and fracture
- First aid for children with bleeding
- Firstemergency aid for nasal bleeding in children
- First aid for poisoning
- First emergency aid for a child with burns
- First aid for obmorozh
- First aid for a child with electric shock
- Emergency care for children with convulsions
- Helping a child with heat and sunstroke
- Emergency care for children with an anaphylactic shock
- Emergency first aid for children: advice andReviews
- Video: How to make artificial respiration for an adult and an infant?
 What is pre-medical care, and how to understand when it is needed?
What is pre-medical care, and how to understand when it is needed?
What is urgent first aid?
First aid is a complex of simple urgent measures aimed at saving a person's life, as well as preventing possible complications if there is an accident or disease.
Unfortunately, in your life you will often face the need to provide medical care to you or other people. And necessarily there will be a situation when the help will be necessary to render your child. It is possible that emergency care will be needed.
If anything happened to your child, you, like anyone who does not have medical education, first of all cause an "ambulance".Because medical care should be provided by people with appropriate education and permission to carry out the necessary manipulations.
They will assess the condition of the child and take the necessary measures. But the main question is WHEN?When will the ambulance arrive? When will the doctors help? And will not it be too late? You can not safely wait for them and see that the child's condition worsens. And after all, you have the opportunity to help here and now, only you need to know how!
 If the child's life is threatened something - then the situation is critical:
If the child's life is threatened something - then the situation is critical:
- the child is unconscious - does not react to touch and your words
- the child lacks breathing - the chest does not move, can not hear breathing, does not feel the breath on your cheek
- no pulseon the carotid, brachial, radial and femoral arteries
- pupils are dilated and do not respond to light
- skin is pale or with a bluish tinge
If the situation is critical, urgent measures must be taken!
What can happen to the child and how to help him?
From birth and up to 6 months, when the child turns over and stretches to all the handles, the following accidents happen:
- the child is injured in his crib or when he tries to get out of it
- children often fall from the changing table
- kids get burned about hot coffee or tea
- children are injured in accidents, tk.the child car seat is not properly operated or there is none at all.
Children from 6 months to a year already crawl and take the first steps:
- is injured by children's toys: they are cut on sharp edges, small details are swallowed
- are falling from a highchair
- beating on the sharp corners of furniture
- are gettingburns from cigarettes
- are injured when hot objects are caught, sharp knives or pieces of utensils
- fall out of a stroller or walkers
- are injured in car accidents
Children from one year to two, everywhere they go and are interested in everything:
- fall from the height that the
- climbed are poisoned by harmful substances that are eaten by the
- when they are injured in the study of their home: they overturn the cabinets, eat the medicine from the medicine cabinet
- sink or choke in the water: the
- tub, pool, pool,
- injuries are injured in car accidents

Mostinjuries the child gets at home, so your job is to provide him with a safe environment. All that a child can get, should be as safe as possible for him.
Of course, you can not remove everything - you need to teach the child that certain things can not be touched.
Features of the algorithm for providing emergency medical
- Evaluate the situation, understand what happened and what is the cause of the accident. This can be electric current, fire, fallen furniture or other objects.
- Call an ambulance, call for help.
- . Stop this cause, and always keep your safety - if something happens to you, you can not help the child.
- Try to remember howcan help the child, depending on the nature of the injury
- First aid: stop bleeding, do artificial respiration, indirect cardiac massage, apply bandage
- If you have the opportunity, how cano rather bring the child to a medical institution or wait for the "first aid"
- First-aid kit
 Tools and dressings that should be in your medicine cabinet:
Tools and dressings that should be in your medicine cabinet:
- scissors
- safety pin
- long tweezers
- disposable gloves
- disposable syringes of different volume
- liquid soap
- individual cooling package
- coolant
- bandages: - gauze of different widths, elastic - tubular bandage: №1.Finger, number 2.Hand, No. 3 Head
- adhesive plaster: - roll( tissue) - bactericidal( set-waterproof)
- individual dressing package
- medical dressing dressing
And such medicines :
- 1.5% iodine solution for scratching, cutting, wound edgesand tools
- antiseptic, the aerosol is most convenient only
- antibacterial ointment for burns and animal bites
- agent for burns, preferably aerosol
- oral rehydration agent
- activated carbon
- antipyreticin syrup for quick action and in candles for vomiting
- local antiallergic agent with insect bites, allergic reaction, contact with poisonous plants
- antiallergic agent inside, also plus drug and food allergy
- vasoconstrictor drops
- suppositories with glycerin
- antiseptic for eyes if-his horrible and with eye injuries
Emergency medicine for acute allergic reactions ( sold under the prescription):
- hormonal anti-inflammatory drug - dexamethasone( 2 ml <30kg of weight <3 ml)
- epinephrine( antiallergic): children under 6 years old - 0.15 ml, 6-12 years - 0.25 ml, over 12 years old - 0, 5 ml.
Also in the medicine cabinet should be the medications your family uses, if there are any chronic and other diseases.
First aid for airway obstruction. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
One of the most common causes of death in childhood is the overlap of the airways. When this happens, the child tries to draw in all the forces. If the child coughs, it means he choked on something and the airways are partially blocked. At the same time he can talk, cry and the main thing is to breathe.
To eliminate a foreign body, often quite enough cough and vomitive reflex, which will arise in the child. In this case, parents should not do anything, you can only hinder and harm, let the child try to cope. Just stay close and try to emotionally support the baby so that he does not start to panic, but calms down.
Do not get into the mouth of a child and do not try to get a foreign object to the touch - you can push it further!
When should I act?
- the child tries to grab the air
- the baby's skin starts to turn blue
- he loses consciousness
- on the child it is clear that he choked: open mouth, rounded eyes, increased salivation, and he is frightened
- older children show that they choked, holding on to the throat
If yousee the child one or more of the above signs - you need to act. There are two approaches that you can apply.
Back shots that combine with shocks in the chest
This approach is designed for children under one year.
Try to help the child first, do all the manipulations, and then call the ambulance. Simultaneously with the rescue activities, call for help, even if you are alone, maybe someone will hear and be able to call rescuers.
Compression of the chest. If after a blow on the back the child does not start to cry or cough, i.e.did not begin to breathe and the object has not yet come out, turn the child upside down, in the same position, head down, put it on your knee. Four times, press the chest in the center in place, on the finger below the middle between the nipples. Press down with two or three fingers, lowering the sternum by 4 cm and taking a break so that it returns to its original position. Do the first and second items in turn until the foreign object comes out, or until the child loses consciousness. In the second case, strikes on the back can not be done, you need to do an indirect heart massage.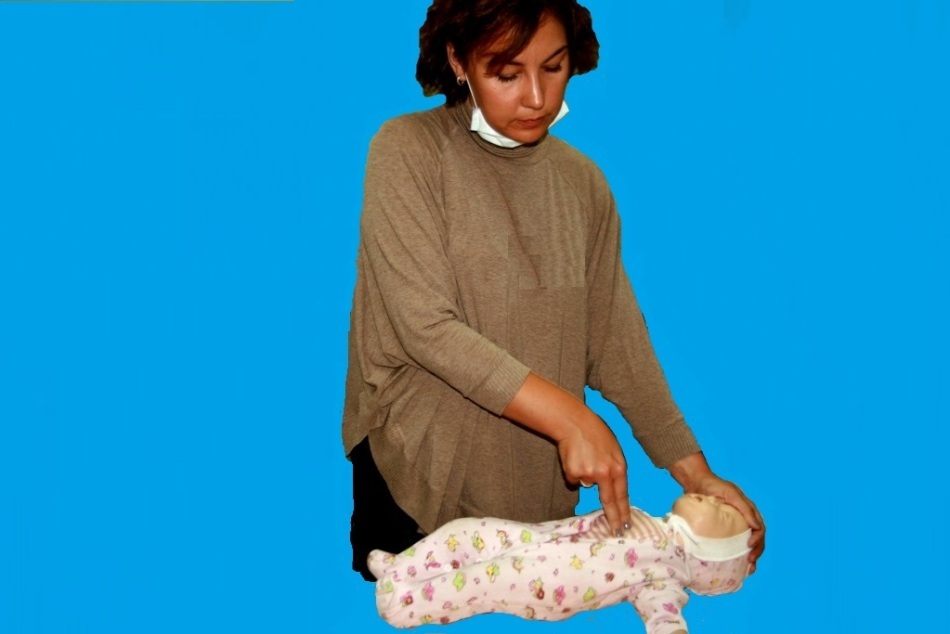  Look inside your mouth and find a foreign object. If the child is unconscious and you give him a heart massage for more than 30 seconds, look in his mouth and look for a foreign body. If you find it, get it.
Look inside your mouth and find a foreign object. If the child is unconscious and you give him a heart massage for more than 30 seconds, look in his mouth and look for a foreign body. If you find it, get it.
Breathing mouth to mouth. If your child still does not breathe, do artificial ventilation. To do this, make 2 expirations by mouth-to-mouth or mouth to nose and mouth. If the chest is lifted when the air is blown, then the airways are clean. Continue to do artificial respiration until the baby begins to breathe. In the event that the baby's chest does not lift with artificial ventilation, press your mouth to the child's mouth and make two more exhalations.
Repeat steps 2, 3 and 4 from the beginning. Alternate an indirect cardiac massage for 30 seconds with two exhalations of artificial respiration and mouth check before the arrival of physicians.
Video: What to do if the child chokes. Emergency techniques
If two minutes have passed, cardiopulmonary resuscitation does not help and no one has yet called rescuers, leave the child and call the ambulance.
Five hits on the back. Place the baby face down, so that his body lies on your forearm and tilt to keep his head below the trunk. Tap your palm between your shoulder blades - the strokes must be strong and fast.
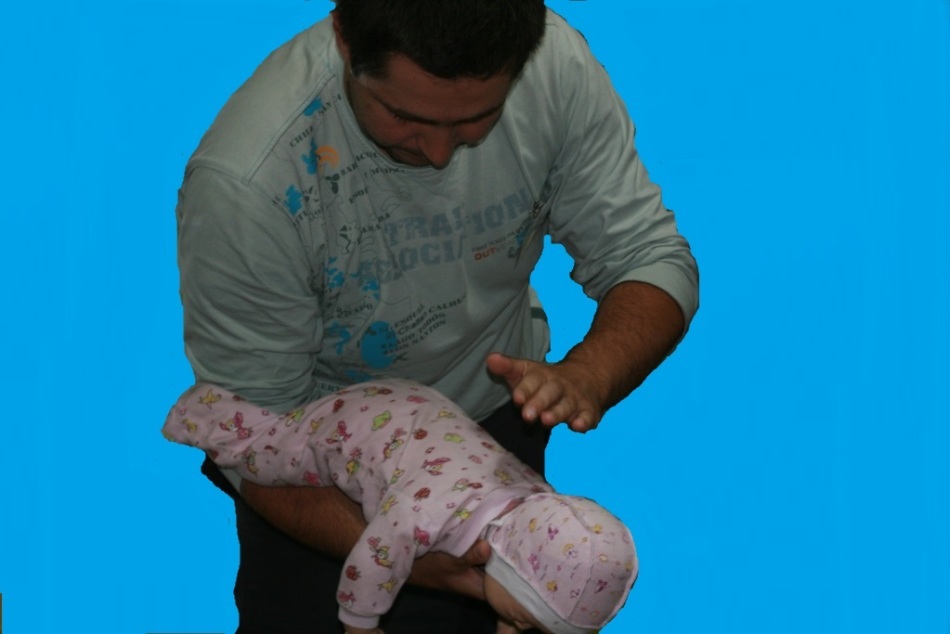 Reception Gameplay. Subdiaphragmatic thrust in the abdomen
Reception Gameplay. Subdiaphragmatic thrust in the abdomen
This method is performed with children older than a year.
It can be done only if the child is in the consciousness of .Approach him from behind, grasp your waist. One hand squeeze into a fist and with your thumb to yourself put a fist on the baby's belly just above the navel. Squeeze the fist with the second hand and press sharply into the depths and up the abdomen, repeat such tremors 6-10 times. Carefully ensure that your hands do not touch the baby's ribs and sternum. Continue the resuscitation until the foreign object comes out or until the child loses consciousness. In the second case, carry out cardiopulmonary resuscitation described in the previous section: indirect cardiac massage and artificial respiration.
 Emergency care for children with bronchial asthma
Emergency care for children with bronchial asthma
Bronchial asthma is now a fairly common disease in children. Exacerbation of this disease provokes
- untimely and wrong treatment
- contact with allergens
- cancellation or reduction of dosage of medicines
- bronchial infection
- acute respiratory disease
- emergence of serious source of environmental contamination
The main symptom of the disease is asthma attacks. Harbinger can be manifested by the sensation of itching, burning in the throat, paroxysmal coughing, sneezing.
In the midst of asthma observed:
- dry cough
- dyspnea
- inhalation short
- exhalation difficult to do, accompanied by wheezing
Asthma attacks are often removed by inhalation with a nebulizer. For this, the following bronchospasmolytic agents are used: Berodual and Ventolin.
These drugs are used in conjunction with mucolytic drugs - acetylcysteine, ambroxol, carbocysteine, which help children cough up phlegm, becausereduce its viscosity.
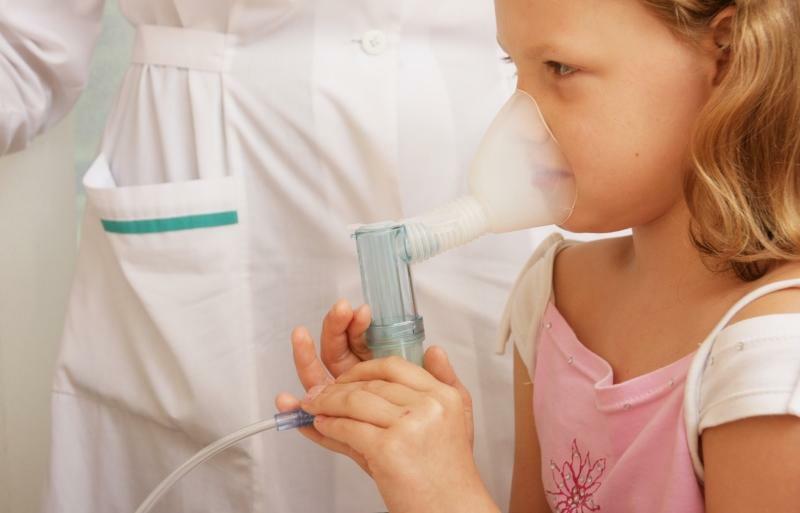

- Ventolin is available in nebulas of 2.5 ml. A single dose for a light attack is 0.02 ml for 1 kg of the child's weight, with an average of 0.03 ml / kg, with a heavy dose of 0.03 ml / kg every 20 minutes.
- Berodual is prescribed up to 6 years - 0.5 ml,from 6 to 14 years - 0,5-1 ml
- Ventolin and Berodual for inhalations are diluted in 2-4 ml of physiological solution
Children with severe asthma attacks should receive treatment in the hospital.
Algorithms of the first first aid for children with injuries
Trauma is considered damage to tissues and organs, which is caused by any environmental factors: physical, thermal, chemical, mechanical.
Injuries:
- of varying severity of damage to
- with and without bleeding
From these characteristics, what will be the first aid depends.
 The injury of the is such a trauma, in the event of which the integrity of the skin is not disturbed. Often a bruise occurs when a blunt object hits or falls.
The injury of the is such a trauma, in the event of which the integrity of the skin is not disturbed. Often a bruise occurs when a blunt object hits or falls.
Symptoms of injury:
- pain at injury site
- edema of this site
- skin discoloration
Although the injury seems frivolous, it can hide severe injuries to organs such as the spleen, brain, liver, kidneys. Therefore, after the injury, carefully observe the child, and if something is wrong, immediately contact the hospital.
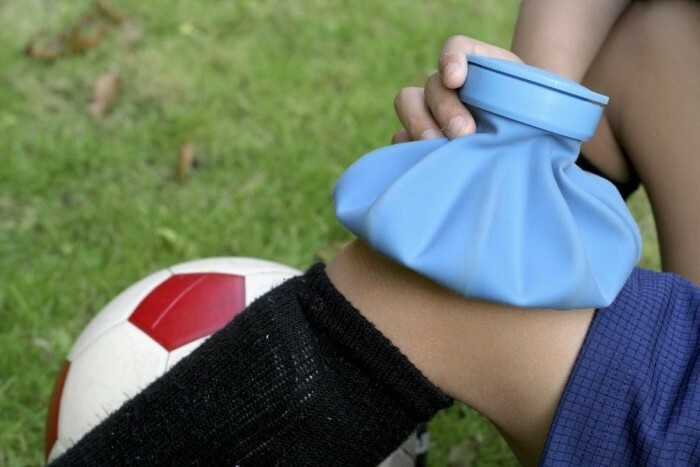 First aid.
First aid.
- Provide the child and the damaged place with peace. Try to talk with the baby calmly so that he calms down and relaxes
- Apply cold to the damaged area - this will reduce pain, reduce swelling and stop the hemorrhage in the tissues. Do not press hard;it will intensify the pain on the contrary. Hold for at least half an hour, if necessary, wait 10 minutes and repeat the procedure.
- If the hand or foot is injured, place it slightly above the child's body.
- If you do not observe signs of fracture, i.e.trauma is not serious, you can not resort to medical care
- However, always watch your child for a while.
- If you still suspect a fracture, injury to the internal organs or the brain, contact an
- specialist immediately. When providing emergency care for injuries, do not massage or rub the damaged area of the
. First aid for children with bruises
Scratch is adamage to the top layer of the skin in a linear form. Scratches usually appear from branches of trees, shrubs, pets.
A scratch of - damage to a larger area and is often on the knees and elbows after falling.
cuts are a stronger and deeper damage that damages all layers of the skin and can affect soft tissues.
The injuries damage the skin, soft tissues and can touch the muscle.
For the above injuries, the following first aid should be provided:
- clean the wound, rinse it under running water, preferably with baby soap
- treat the wound with hydrogen peroxide, do not use iodine
- if there is bleeding, stop it by applying a pressure bandage
- if bleedingnot strong and quickly stopped, treat the wound with a water-based antiseptic
- if bleeding is severe, apply a tourniquet and take the child to the hospital
- if you think the wound is serious and you will needapply seams, do not hesitate, consult a doctor.after 8 hours the wound will be infected and it can not be sewn
- if there is a foreign object in the wound, do not remove it, it can provoke bleeding, apply a bandage and contact a specialist
- for a bruise, apply cold and hold for up to half an hour.
 First aid in case of head injurychild
First aid in case of head injurychild
It is very important here to be able to distinguish between skull injuries and brain damage. The skull of a child works like a helmet for the brain, and he covers with the skin, which is often traumatized. The scalp contains a lot of blood vessels, so when the injuries go so badly the blood flows and the cones grow quickly, but do not worry much, apply ice and they will quickly pass.
The main danger in the child's head injuries is brain damage.
It is of two kinds:
- concussion
- bleeding
Pay special attention to the chipped wounds of the baby's head. Outwardly, they do not look serious, but they can damage the skull and cause inflammation of the brain.
 If your child has unconsciousness, check breathing. Not breathing? Do cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Breathing? Good. Look at the color of his skin, his lips are not blue? If not, lay it flat and call the doctors. If it seems to you that the neck may be damaged, do not touch the baby, do not change its position - this should be done by qualified medical staff. If a child has convulsions, watch his breathing path so that he does not interfere with breathing.
If your child has unconsciousness, check breathing. Not breathing? Do cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Breathing? Good. Look at the color of his skin, his lips are not blue? If not, lay it flat and call the doctors. If it seems to you that the neck may be damaged, do not touch the baby, do not change its position - this should be done by qualified medical staff. If a child has convulsions, watch his breathing path so that he does not interfere with breathing.
If the child is conscious, behaves normally, as before the fall, observe him and attach ice to the damaged area.
If your maternal intuition suggests something is wrong, consult a doctor. It is better to be safe here than to miss the moment when you can help without consequences. What to look for and when to go to the hospital:
- child is disoriented, loses balance
- can not wake up
- strangely breathes during sleep
- eyes mow or pupils are differently expanded
- is present vomiting
- skin turns pale
- from the ears goes blood or other liquid
- convulsions are present
First aid to the child with stretching andfracture
Fracture of the bones can be determined by severe pain, the presence of a tumor, restriction of mobility, the unnatural position of the fractured limb. In young children, so-called fractures often occur. At the same time the child can limp and can not stand on a sore leg.
Your actions:
- apply cold
- raise the injured limb slightly higher, place it on the
- pillow, fix the place of the injury, becausechildren can be uncontrollable because of pain and, moving, do themselves even more harm
- deliver the child to the hospital or call an ambulance
 For fixing the limb, a tire is best suited, instead you can use a stick, a rod, a board, a cane, an umbrellaetc. The tire should be applied to the limb and fixed so as to immobilize the next 2 joints on both sides of the fracture. If the fracture is open, do not press the tire towards him at all.
For fixing the limb, a tire is best suited, instead you can use a stick, a rod, a board, a cane, an umbrellaetc. The tire should be applied to the limb and fixed so as to immobilize the next 2 joints on both sides of the fracture. If the fracture is open, do not press the tire towards him at all.
First aid for children with bleeding
Children, as well as adults, have internal and external bleeding. By itself, bleeding, in addition to losing blood, is still dangerous for infection, so it must be stopped quickly. To do this, you first need to determine its intensity:
- with minor bleeding, you need to rinse the wound and apply a bandage
- with more severe bleeding - apply a pressure bandage
- with very heavy bleeding when the blood beats with a "fountain" - it is necessary to apply a tourniquet
If the lesions are small wound to the childIt should be washed with water and disinfected, for example, with hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, miramistin. Do not use iodine in any case.it will burn the damaged tissue, it is applied only to the edges of the wound in order to avoid infection.
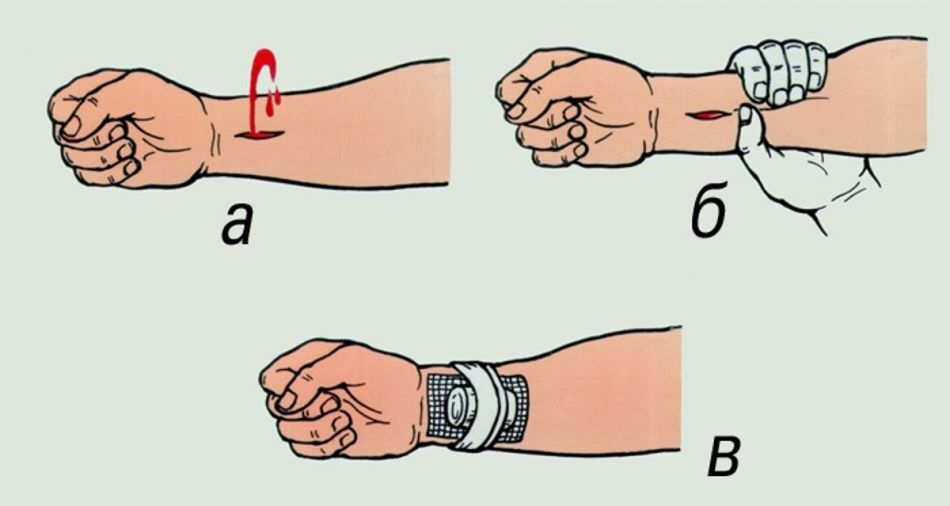
- In case of severe bleeding, there is a risk of blood loss, therefore it is necessary to apply a tight bandage
- . In case the bleeding continues, put another one or two
- on top Normally, more than three bandages are not required. Do not remove the bandage and keep on the baby until the doctor comes
- If the blood goes "fountain", immediately apply the tourniquet
- Before this, tighten the artery by strongly pressing on her finger if the child is not 2 years old, if the child is older - press the fist
- The harness is superimposed eitheron the upper third of the hand, if the arm is injured, or on the inguinal fold on the leg, if the wound on the leg
The tourniquet is always tied up above the wound, under it there should be a thin cloth or clothing. If you did everything right, the bleeding will stop immediately.
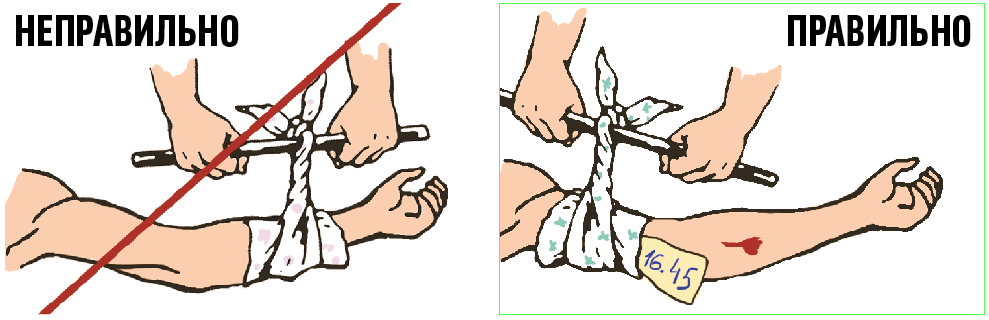 Harness hold on the body for up to 30 minutes in the winter and up to 60 minutes in the summer. If this is not enough, remove it for a couple of minutes and put it back a little higher than the last time. Do not forget to notice the time, the doctor will ask him.
Harness hold on the body for up to 30 minutes in the winter and up to 60 minutes in the summer. If this is not enough, remove it for a couple of minutes and put it back a little higher than the last time. Do not forget to notice the time, the doctor will ask him.
In case of bleeding, DO NOT
- remove foreign object from wound, if any, it must be fixed and covered with something
- remove bandage soaked with blood
- touching open wound not in sterile gloves
- tourniquet used only when blood goes "fountain"
First emergency aid for nasal bleeding in children
If the child is bleeding from the nose, seat him, tilt his head slightly forward and squeeze the wings of the nose so that the blood no longer flows. You can put a cold on the bridge of the nose.
When the blood goes with your nose it is forbidden to throw your head back, asThe blood will flow into the esophagus and possibly cause vomiting.
Do not use cotton, becauseit will stick to the vessels in the nose and when you remove it, you can damage them and the bleeding will begin anew. Usually it takes about 10-15 minutes to stop the blood.
 If this does not happen, contact your doctor immediately, continue to pinch your nose and apply cold to the bridge of the nose.
If this does not happen, contact your doctor immediately, continue to pinch your nose and apply cold to the bridge of the nose.
First Aid for Poisoning
Poisoning is the ingestion of harmful substances into the body of a child. They can be swallowed, received through the respiratory tract or with skin contact.
Often, poisoning is accompanied only by a stomach disorder, but there are also quite serious cases, up to a lethal outcome.
 If you saw that your child ate something poisonous, immediately call for an "ambulance."Rescuers need to quickly provide the following information:
If you saw that your child ate something poisonous, immediately call for an "ambulance."Rescuers need to quickly provide the following information:
- what it was for the poison, how much was ingested by
- when it happened, right up to the minute
- your child's age and weight
- what symptoms appeared
On the phone you will be consulted and will tell you what to do before you arrivedoctors.
Not all poisons are emitted with vomiting, and some can harm the esophagus, so do not induce vomiting yourself on the baby yourself.
Do not allow a child to tear if the following substances have been taken into the body:
- different polishes
- Petroleum products: gasoline, turpentine, gasoline, kerosene
- chemicals such as acid, alkali, cleaning agent
- such detergents as bleach or ammonia
Usually experts recommend in such cases to drink a lot of water or a cup of milk. But medical workers must tell you about it.
The first emergency aid for a child with burns
 There are several degrees of severity of burns that depend on the soreness and the amount of tissue damage:
There are several degrees of severity of burns that depend on the soreness and the amount of tissue damage:
- first degree burns are manifested by the reddening of the skin, do not hurt much and to remove it you need to hold the damaged area in cold water, smear itantiseptic cream or aerosol and wait a little while
- second degree burns show blisters and rejection of the damaged skin layer and strongly hurt
- Auger of the third degree affects the rather deep layers of the skin
 Your actions:
Your actions:
- If the clothes burn, extinguish it with something like a blanket or other clothing.
- . Quickly remove clothing hot from fire or boiling water, do not burn the baby in another place, cut it if
- is required. Evaluate how serious everything is
- Place the damaged area in cold water for at least 20 minutes. Do not use ice, it will hurt the sick skin even more. Do not smear the burn with oil or other fat
- If there are blisters, the skin is white or black, anoint it with antiseptic and cover with a clean cloth or bandage, do not press hard. Take the child to the hospital or call an emergency room.
- Give the child an antipyretic
With electric burns, needs emergency medical care and, more often than not, resuscitation of the victim. They are dangerous for violating the rhythm of the heartbeat.
 With chemical burns , remove neatly damaged clothing from the child, replace the burn with cold water. If this substance has got into the body, see the section First Aid for Poisoning. If the substance gets into the eyes, rinse them immediately under running water for 20 minutes.
With chemical burns , remove neatly damaged clothing from the child, replace the burn with cold water. If this substance has got into the body, see the section First Aid for Poisoning. If the substance gets into the eyes, rinse them immediately under running water for 20 minutes.
With sunburns , cool the damaged area with cold compresses or water, anoint ointment from burns, for example, Panthenol.
First aid for frostbite in the child's cheeks, face, hands and feet
Frostbite in children happens due to low temperatures( enough and -10 ° C), resulting in damage to parts of the body or even die tissues.
There are several degrees of frostbite:
- The first degree of - the damaged area turns pale, and if its heat becomes red and swells. The necrosis does not occur and after a week everything passes
- . The second degree is - the damaged area is pale, there is no sensitivity, blisters appear, itching and pain appear. Recovery takes up to two weeks
- The third degree is - the vesicles on the affected area are bloody, there is no sensitivity, severe pain. Skin cells die, scars form. After 2-3 weeks the damaged tissue is rejected
- The fourth degree of is frost-bitten skin of blue color and has a marble color. If you warm up, there are swelling, there are no blisters, there is no sensitivity. Defects of the joints, bones, soft tissue necrosis
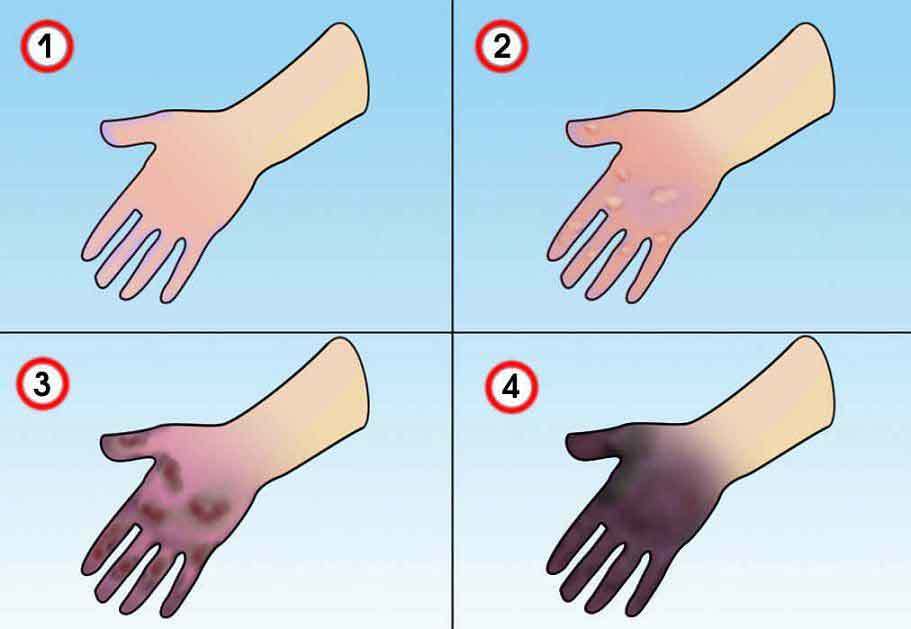 The main measures for frostbite:
The main measures for frostbite:
- take the child to heat
- undress
- assess the degree of frostbite, if damage of the second, third or fourth degree - immediately call an "ambulance"
- with first degree frostbite warm updamaged areas, you can make baths with potassium permanganate or furatsilinom, first make them with a temperature of about 25 ° C and in half an hour bring to 37-39 ° C
- can warm the frostbitten skin with breathing,wipe it lightly with a natural warm cloth, then wrap it with a cotton-gauze dressing
- with frostbite of the second, third and fourth degree , while waiting for the doctors, apply a bandage that keeps the heat, it is made of such layers: gauze + cotton + another layergauze +
- film, fix the damaged area by applying cardboard on top of the bandage, wrap it in wool, let the child drink hot and let it take analgin
REMEMBER: In case of frostbites, rapid heating and grinding with snow is strictly prohibited. In case of severe damage, do not rub oil, grease or alcohol!
 Frostbite of the cheeks is characterized by pale skin color, on which there are red spots and swelling. In a couple of days, the color may change to cyanotic, which then turns green and yellow. Apply ointment to frostbitten cheeks, for example, rescuer, bepanthene or traumel. If you go out with the baby in the cold, be sure to lubricate your face with a special cream that protects against frost.
Frostbite of the cheeks is characterized by pale skin color, on which there are red spots and swelling. In a couple of days, the color may change to cyanotic, which then turns green and yellow. Apply ointment to frostbitten cheeks, for example, rescuer, bepanthene or traumel. If you go out with the baby in the cold, be sure to lubricate your face with a special cream that protects against frost.
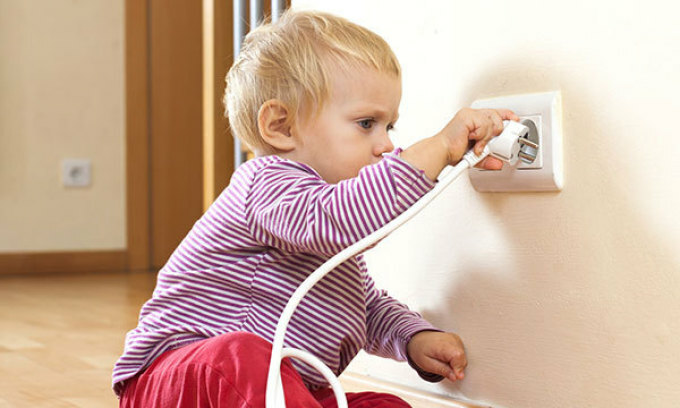
First aid for a child with electric shock
You probably have a bunch of electrical appliances at home that are potentially dangerous when there is a small researcher in the house.
If you still did not follow and the child reached the faulty wire or outlet, you immediately need to give him first aid:
- Disconnect the power source, if this is not possible, pull it away from the child or vice versa, depending on the situation. BUT do not do it with your bare hands, you too will be shocked and you will not be able to help the child! Use a stick, a mop, a folded newspaper, a rope, something rubber, in general in that it does not conduct electricity
- Check the baby for breath, look at the color of his skin, whether he has a reaction to external stimuli
- If there is no breath, there is noheartbeat, urgently begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation( description is in the appropriate section)
- Call for help
- Do not move the child. Exposure to electric shocks could damage the spine of the

- . If the child is conscious and breathing, check the electric shock site, the skin may have burned and the burn should be done.
- Contact your pediatrician. The electric current can damage the internal organs and the child must definitely inspect the doctor
. TIP: To eliminate the current source, you can cut all the electricity in the house by disconnecting the fuses on the meter. This is the most effective way, but only if you know where this counter is located.
Provide the child with a safe area for research:
- all outlets are protected from children
- repair or discard all broken electrical appliances
- replace peeled wires with new
- do not climb the toaster into the toaster and put wooden tongs near the toaster, just in case.
Emergency carecramps in children
In the brain sometimes there are electric discharges of pathological origin, which become causes of seizures.
The child during convulsions can:
- fall on the floor
- roll on the floor
- foam is formed at the mouth
- roll up the eyes
- bite the tongue
- temporarily lose consciousness
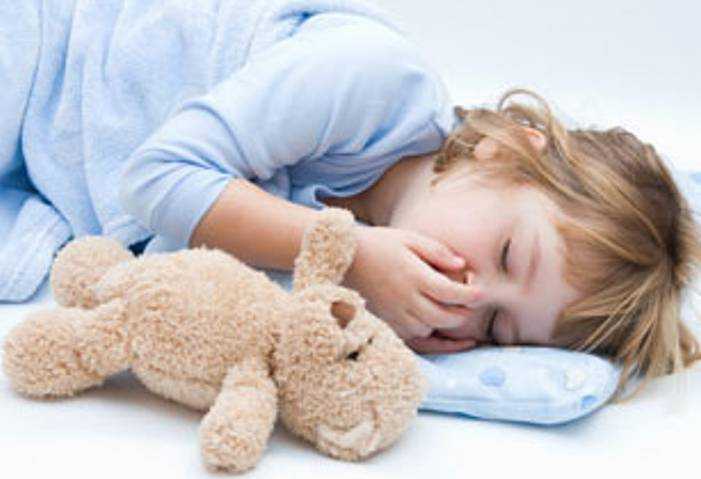 The task of the parents is to ensure that the breathing of the child does not interfere, for example, the tongue or tongue.
The task of the parents is to ensure that the breathing of the child does not interfere, for example, the tongue or tongue.
Often, convulsions occur with an increase in body temperature in a child. Attacks quickly pass and most often do not harm the body.
What should be done during the child's seizures:
- lay it on the floor, turn the face to the side or down, so that the discharge and tongue do not block the airway
- do not put anything into the child's mouth, no food and drink, neither during an attack, norsome time after it
- do not hold back the cramps
- do not worry if the lips are of normal color, then the baby is breathing and everything will be fine
- if the lips are still blue and there is no breath, clear the pharynx and do mouth-to-mouth resuscitation
- to avoidbruises about the mebь, clear the space around the
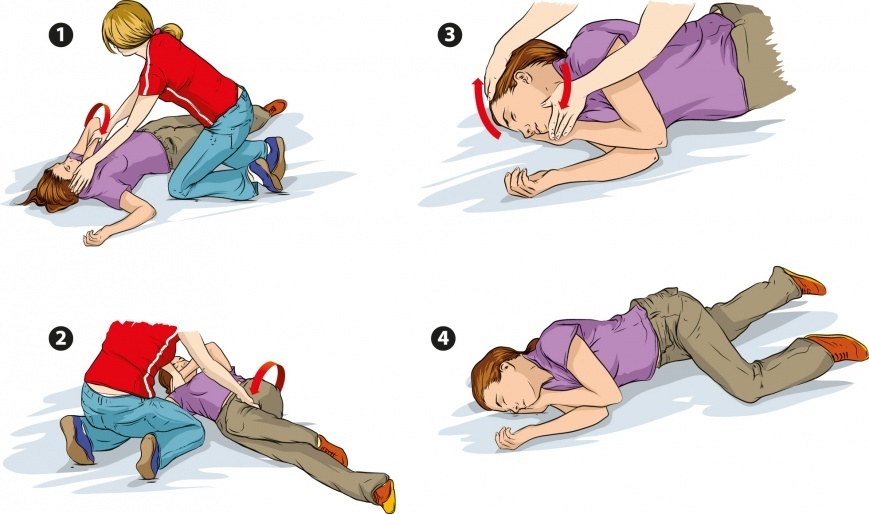
- Seizures may have a second wave to prevent it from putting the antipyretic candle, strip the baby, wipe with warm water to lower the body temperature
- After the attacks, the children usually fall asleep
- If your baby's convulsions did not start from the heat,urgently call for emergency help.
Helping the child with heat and sunstroke
Thermoregulation in children does not work like in adults, so children often overheat. Heat can provoke a child's heat or sunstroke.

REMEMBER: Symptoms of heat stroke in children appear later than internal changes in the body, so noticing them needs to act very quickly!
- Symptoms of heat stroke:
- increases body temperature
- skin is dry and hot
- baby almost does not sweat
- pulse and breathing quickens
- possible hallucinations, seizures, nonsense, impaired coordination, and even unconsciousness
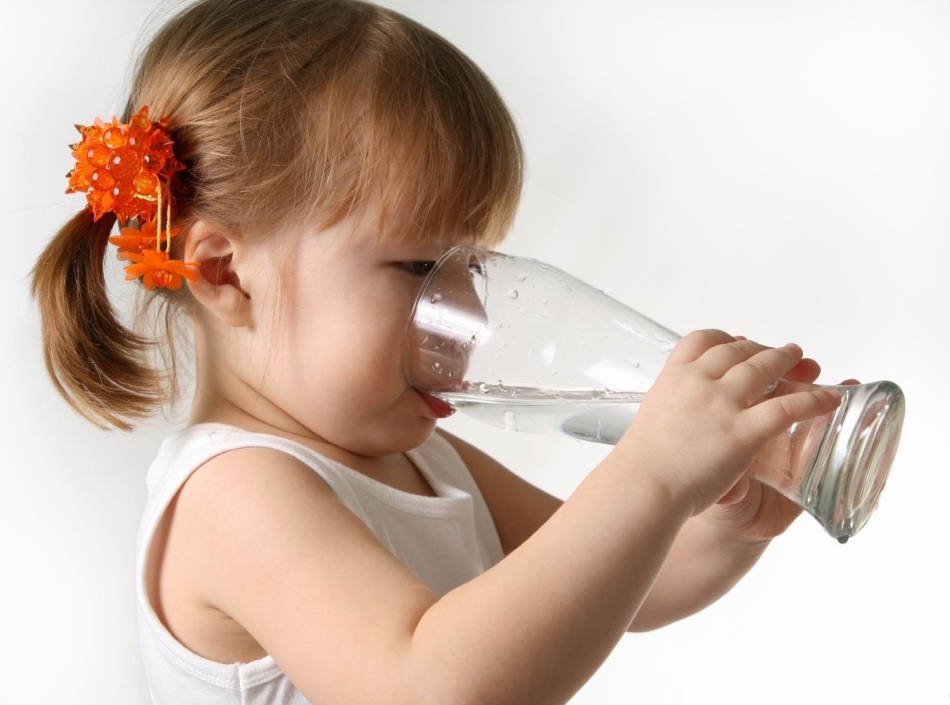 You must help your child immediately :
You must help your child immediately : - reduce body temperature and cool it - make a cool bath or wrap the baby with a wet cool sheet
- water your baby, often and gradually, with teaspoons, so as not to provoke vomiting and strongerie dehydration
- as quickly as possible to call an emergency room or take him to the hospital.
Emergency care for children with anaphylactic shock
 Anaphylactic shock is an allergic reaction, which most often occurs when a child is given medication or with insect bites. This reaction develops very quickly and strongly manifests itself. Anaphylactic shock suddenly begins - the child pales, turns blue, shows anxiety and fear, dyspnea appears, vomiting, the appearance of itching and rash. The child begins to gasp, cough, there is pain in the region of the heart and a headache. There is a sharp drop in blood pressure and the child loses consciousness, there are convulsions, there is a possibility of a lethal outcome.
Anaphylactic shock is an allergic reaction, which most often occurs when a child is given medication or with insect bites. This reaction develops very quickly and strongly manifests itself. Anaphylactic shock suddenly begins - the child pales, turns blue, shows anxiety and fear, dyspnea appears, vomiting, the appearance of itching and rash. The child begins to gasp, cough, there is pain in the region of the heart and a headache. There is a sharp drop in blood pressure and the child loses consciousness, there are convulsions, there is a possibility of a lethal outcome. First aid. Immediately place the child horizontally on the back, lift the legs up and place something. Head to the side, lower jaw extend and watch so that the tongue does not sink and the child does not choke with vomit.
If the allergen is injected:
- , immediately stop the injection of the allergen
- , make several injections around the site of injection of 0.1% rH adrenaline at a dosage of 0.05-0.1 ml for each year of life, but not more than 1ml
- , apply iceto the injection site of
- , apply a tourniquet above this place and hold for 30 minutes
If the allergen is buried in the nose or eyes, rinse them immediately under running water.
If the allergen has been eaten, immediately wash the stomach to the child if it is possible to do so in his condition.
In the last two cases, you also need to inject 0.1% of adrenaline rn intramuscularly and in the muscles of the mouth cavity of the bottom of the mouth 3% of the prednisone solution at a dosage of 5 mg / kg of body weight.
It is necessary to give the child antihistamines:
- 1% rim dimedrol at a dosage of 0.05 ml / kg of weight, but not more than 0.5 ml for children for the year and 1 ml - older than the year
- 2% rr suprastin 0.1-0,15 ml / year of life
Open the windows to receive oxygen. Be sure to follow the pulse, blood pressure, breathing and call an ambulance!
 Emergency first aid for children: advice and feedback
Emergency first aid for children: advice and feedback According to statistics, one third of accidents occur with children at home, so the main task of parents is to ensure home security and prevent trouble.
We hope that after reading this article, you will be able to provide your child with first aid, if he needs it.
Take care of your children!
Video: To How to make artificial respiration for an adult and an infant?
