
Unpleasant and extremely painful manifestations of ear diseases are classified by many features, one of which is the location of foci of infection.
Consider the possible types of otitis and examine in detail the symptoms of the middle ear.
Contents
- 1 Types of otitis
- 2 Classification of inflammatory processes
- 3 How is possible infection
- 4 Symptoms of otitis media of the middle ear
- 5 Stages of
Types of otitis
- External when inflammation is localized directly in the auditory canal. Most often, it is diffuse, when the whole surface of the passage is damaged or in the form of a furuncle, if some limited part is inflamed. Otitis externa is relatively easy to treat, since the discharge of secretions is not difficult, and access to the affected area is open.
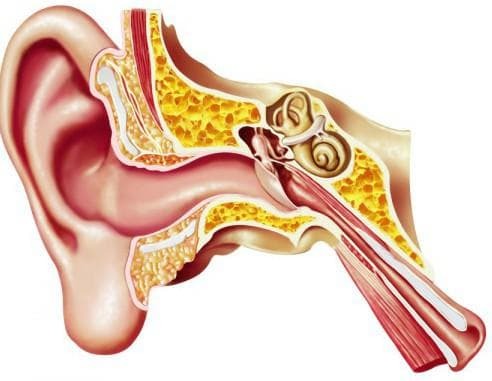
- Medium - develops in the next compartment of the hearing aid - the drum cavity. Its name, as it is easy to guess, is due to the location of the tympanic membrane, which will delay the outflow of purulent discharge, which will complicate the treatment. The average otitis counts in a variety of varieties, some of which will be discussed later. Treatment of otitis media involves a whole range of activities. Also, it is fraught with possible complications, so do not delay or neglect treatment.
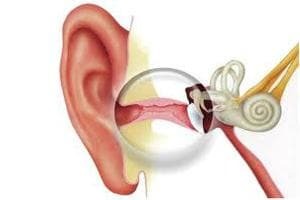
- Internal otitis or labyrinthitis is formed even further and is almost always a consequence of untreated or rapidly progressing otitis media. The characteristic signs of labyrinthitis will be dizziness and hearing loss. The pain sensations are slightly smoothed out, and they may disappear altogether, so this inflammation is so dangerous: the patient considers this sign a guaranteed cure and may stop treatment. That is why it is very important not to engage in self-medication, but to seek qualified help from a doctor - an otolaryngologist.
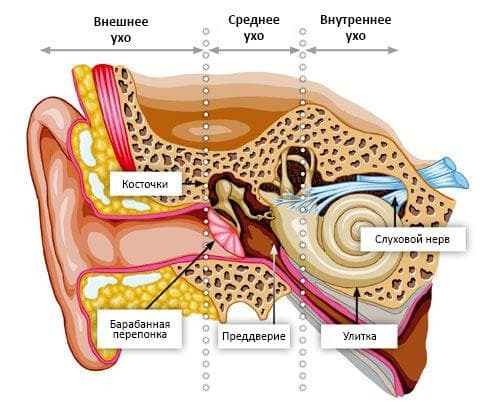
In the diagram - the structure of the ear
Causes of inflammation can have a different nature, so the main three groups of pathogens excrete otitis.
From this article you can find out how to effectively treat otitis media.
Classification of inflammatory processes
- Bacterial otitis media: caused most often by numerous representatives of the family of streptococcal and staphylococcal cultures. Often observed on the general background of the weakening of the organism after the diseases and during periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases. Treatment is carried out exclusively with the help of antibiotics, and an accurate characterization of the species will give an expanded smear of purulent discharge, if any.
- Viral otitis media: it develops due to ingestion of the influenza virus or herpes into the auditory cavity. In this case, special antiviral drugs and additional funds are prescribed. Often, viral otitis is a complication of SARS, so in the season of colds it is advisable to follow preventive measures. In case of illnesses, you can not tolerate influenza and SARS on your feet and refuse to take medication. A frequent reason is self-withdrawal of medications after first improvement during illness.
- Fungal nature of inflammation manifests itself when ingested fungus. The second name of fungal otitis is otomycosis. The main cause of the disease - non-compliance with basic rules of hygiene. Fungus enters the ear with unwashed hands, foreign objects and common diseases of the fungal organism. Often the disease is provoked by a dysbacteriosis after taking antibiotics or postoperative conditions. The treatment is carried out with special preparations of general and local action, additional immunostimulation of the organism is applied, as well as physiological procedures: washing the ear cavity and eliminating the external body of the fungus.
What are the signs of external otitis media can be indicated in this article.
The video describes the symptoms of inflammation of the middle ear:
What antibiotics for otitis is best used, you can learn from the article.
As you can see, there are a lot of "enemies" in our hearing aid, and most of them live quietly in our body and do not exert their harmful influence under unfavorable conditions.
The best prevention of ear inflammatory processes( as well as many other diseases) will be maintaining a high level of immunity and careful compliance with individual hygiene.
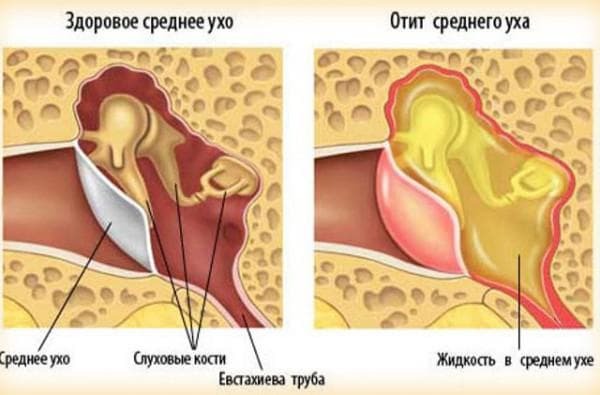
How the possible infection occurs
- Water entering the auditory meatus .Usually this requires another provoking factor - damage to the skin of the inner surface of the ear canal. This can be scratches and microcracks caused by sloppy cleaning or foreign objects.
- Complication after a previous disease. This is especially pronounced in childhood, but it can also disturb an adult. The most common side effects appear after other ENT diseases: sinusitis, sinusitis, angina, bronchitis.
- Contact with foreign object in the ear .Children often accidentally shove small parts into the nose or ear. Self-extracting is fraught with damage to the drum septum, so it's better to seek qualified help. In adults, a foreign object can be accidentally caught, for example, during a strong wind or a specific job. Extract it yourself also can not fail, so medical advice is recommended.
How does acute catarrhal otitis look like, you can learn from the article.
Specificity of pediatric otitis will be quite simple diagnosis and treatment. The main requirement is the inadmissibility of self-medication by folk remedies and the independent prescription of medications on the principle: someone helped.
The video describes the symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the middle ear:
What are the drops for otitis in adults that are best used, is indicated in the article.
Symptoms of otitis media of the middle ear
- Sharp or shooting pain in the ear .Older children can independently identify a symptom, and in the case of infancy, the disease gives a sharp change in behavior. The kid reaches for the ear, cries and refuses to eat and pacifier. An accurate diagnosis can be made only by a doctor, and the task of parents is to provide timely advice and ensure treatment.
- Discharge from the ear canal ( optional).Any discharge from the ear should alert the parents, even if it is a matter of conventional sulfur, only in larger quantities.
- Often observed, the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the auricle .With an average otitis discharge from the ear may not be, but the smell will appear.
- The temperature rise of in children can be caused by a variety of reasons, but if the above symptoms are present, then this is a serious reason to suspect otitis.
How to remove sulfur fuses in the ears, you can find out by reading the article.
In children, the disease is quite common, but it passes relatively quickly. It is important to know that the faster you contact a doctor, the greater the chances of getting rid of antibiotics and complex treatment. Emergency methods will be antipyretic drugs and analgesic turundochki with boric alcohol or special ear drops. Apply them only a short time to ease the pain, and not use for self-treatment.
On the video - symptoms of middle ear inflammation in the infant:
What antibiotics are used for otitis media in children are indicated in the article.
Warmings of the ear canal cause a temporary sense of relief, but without prior consultation and finding out the nature of otitis media can be extremely dangerous. The patient should be protected from drafts and low temperatures, but independent heating can trigger the progress of the disease and the transition of catarrhal otitis to the purulent stage.
In adults, the symptoms of otitis are identical to manifestations of the disease in children. First of all there is a sharp pain in the ear area, the simplest diagnosis: a little pressure on the outer ledge near the ear canal. If there is a sharp pain syndrome, then it's in the otitis. Treatment of adult patients occurs depending on the pathogens of infection and the symptoms that appear. Often in order to cure otitis, it is necessary to remove the infection of the nasopharynx or tonsillitis.
How is home treatment for ear inflammation, you can learn from this article.
Stages of
The disease is characterized not only by the above symptoms, but also by three stages of development.
- The acute form of of catarrhal otitis is extremely painful. Unpleasant sensations intensify towards evening, causing unbearable discomfort. Sharp movements of the head, coughing and sneezing provoke shooting pain, giving away to the field of the temple or teeth. The hearing decreases and the temperature rises.
- Purulent form of otitis follows immediately after catarrhal. Allocations of pus accumulate in the cavity behind the tympanic membrane. Often to remove excreta, the doctor produces a small puncture of the tympanic membrane. If this is not done, it can break through on its own.
The treatment of inflamed adenoids in children is indicated in the article.
The video describes the acute form of otitis:
The process of regeneration occurs after the destruction of infection and complex treatment. Purulent discharge is removed naturally, the internal surface is gradually restored, as is the damage to the tympanic membrane. The final manifestations of otitis occur after about 10 days in children and two to three weeks in adults. At the same time, gradual restoration of hearing can be observed.
What folk remedies for the ingested ear are most often used, is indicated in this article.
Skip the occurrence of otitis media quite difficult: the disease itself will give a signal in the form of a strong shooting pain.
If you have any suspicions of otitis in any location, you should immediately call your doctor .Timely treatment significantly increases the chances of getting rid of otitis without the use of antibiotics and strong medications. Otitis in children and adults has the same nature and symptoms. Children's ear diseases develop more rapidly, but also go much faster. Prophylaxis of otitis of different complexity will consist in hardening and vitaminization of organisms, timely treatment of infectious diseases of different localization.
