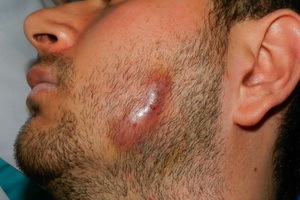
 Maxillofacial actinomycosis in humans develops as a result of damage to the radiant fungus. This microorganism is widespread in nature, it can also be found in the human body. The disease provokes a decrease in the immune capacity of the body.
Maxillofacial actinomycosis in humans develops as a result of damage to the radiant fungus. This microorganism is widespread in nature, it can also be found in the human body. The disease provokes a decrease in the immune capacity of the body.
A locally invasive infection that affects the maxillofacial area is called actinomycosis or radiate-fungal disease. This disease was named after the name of the pathogen - radiant fungi( actinomycetes).Pathology is characterized by the development of an intraosseous abscess.
Almost always the disease is caused by an anaerobic form of fungi. Since actinomycetes are present in large quantities in the environment( in soil, plants) and in the human body, it is commonly believed that the disease is endogenous( caused by the fungus living in the human body) or exogenous( the fungus penetrates the environment) nature.
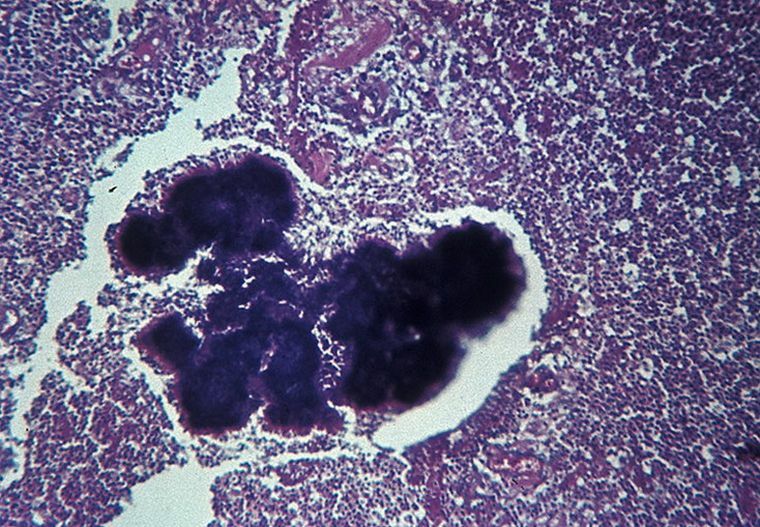
Actinomycetics photo close-up actinomycosis pathogens
Contents
- Causes and pathogenesis
- Features of development symptomatology depending on the form
- Diagnosis
- Treatment methods
- Preventative measures
- Consequences of the disease
Causes and pathogenesis of
The presence of pathogens in the human body is normal. With their help, a definite flora is formed in the mucous membranes of the eyes and oral cavity. With adverse factors, the fungus is able to parasitize in the intestine, in the lungs and in the mouth.
The pathogen is able to penetrate through lesions on the skin, through inhaled air. The main causes of the development of the disease include:
- carious cavities and infected prigesneve pockets;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules for oral and dental care;
- wounds and mucosal injuries;
- decreased immunity and the presence of a hotbed of chronic infection.
Contact path of infection is extremely rare. Most often the disease affects men living in large cities. 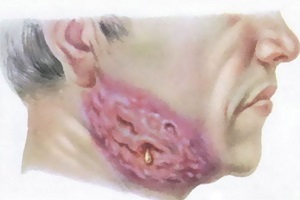
The disease causes Actinomyces israelii. Other anaerobic microorganisms can complicate the course of the disease. The infection spreads lymphogenous and hematogenous ways. A part of the micelle is transferred through the lymph.
When the actinomycete hits the human body in the first place, the disease does not develop. To develop the infectious process requires a secondary penetration of the pathogenic factor. After re-introduction of the radiant fungus, actinomycosis of the maxillofacial region develops. The latent period of the disease is from 1 to 3 weeks.
Features of development of symptoms depending on the form of
Actinomycosis can affect different organs of a person. According to the classification of the forms of the disease, the following are distinguished:
- cutaneous form , which is caused by secondary entry of the pathogen through wounds;
- abdominal - one of the most dangerous forms, the cause of which can be the introduction of the pathogen into the intestines, stomach, esophagus, - with fatal infection, the lethal outcome is 50% of the number of cases.
- lesions of bones and joints , this form is rare;
- stop disease ;
- disorders of the genitourinary system ;
- destruction of the central nervous system ;
- maxillofacial form is the most common( up to 90% of cases).
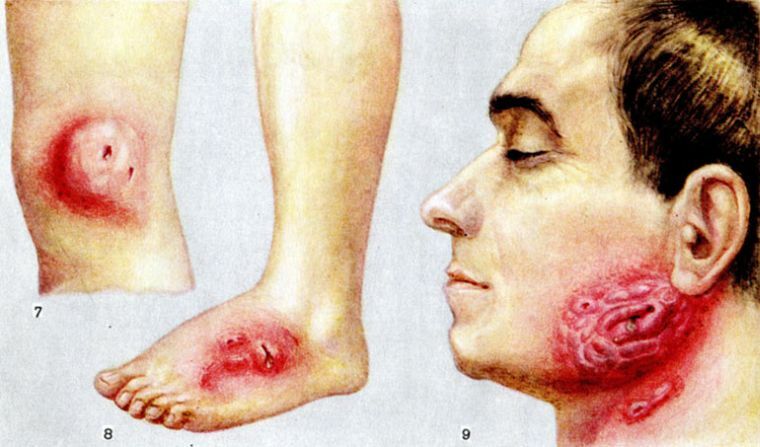
The following symptoms are typical for maxillofacial actinomycosis depending on the form of the disease:
- Cutaneous .The formation of subcutaneous seals, which are initially painless, and then opened and pass into fistulas. Skin is painted in a bluish-purple color.
- Cervical and maxillofacial forms. Characteristic symptoms: the formation of cushions on the neck, the defeat of the masticatory muscles. The infection spreads to the larynx, tonsils, mucous eyes and mouth, trachea, cheeks. On the face there are wet sores with purulent secretions. The asymmetry of the face is noted.
Actinomycosis of the maxillofacial region is classified by the localization of the actinomycete. The clinical picture thus has some differences:
- When the subcutaneous fat layer is affected, the infection is considered subcutaneous .It can progress against a background of abscess, phlegmon, and also defeat of lymph nodes. The course of the disease is calm and prolonged. In patients there is a slight increase in body temperature, there are no complaints of soreness. Such damage occurs due to trauma to the mucosa and is not common.
- When lesions of submucosal , the causes and manifestations are the same, but the pain intensifies with lower jaw movement and swallowing. In the place of the hearth, an infiltrate accumulates. It is possible to spread the infection to neighboring tissues, as evidenced by puffiness.
- The odontogenic granuloma , caused by radiant fungi, is asymptomatic. The lesion focuses on the bone tissue of the jaw. Without timely therapy, a fistula is formed on the mucosa.
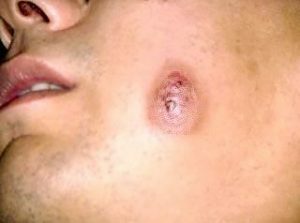
- The subcutaneous-muscular is one of the most common forms of the disease. The introduction of the pathogen occurs in the subcutaneous layer and spreads subsequently to the jawbone. The disease is characterized by acute onset and hyperthermia, the patient complains of movement restrictions, pain. When the doctor examines a deep infiltration. The place of introduction of the pathogen is swollen, the integuments in the place of the lesion of the bluish shade. Later, the skin in the site of the infection is perforated, and a purulent liquid with fungus drusen in the form of whitish grains begins to form.
- With exudative periostitis , the cause of which is the introduction of radiant fungus into the tooth( most often the lower jaw suffers), the infection extends to the periosteum. This condition differentiates with periostitis. But with it there is no pain when percussion of the affected tooth. After removal of the tooth, pus may not stand out, often extensive granulations are found.
- In the case of productive periostitis , a thickening of the periosteum is noted. Such pathologies are more common in childhood and adolescence. Bony growths can be detected using X-ray studies. They are localized along the edge of the body of the lower jaw and have a loose structure.
- Pain sensations that occur periodically but without changes in the mucous membranes are characteristic of the intraosseous gum. With an intraosseous abscess other than painful sensations, there is a restriction of jaw movements, swelling of the mucous membranes above the focus of infection, a feeling of numbness in the lips.
- Slowly developing tenderness and gradually developing hyperthermia are characteristic for actinomycosis of the lymph nodes. The clinic is similar to manifestations of adenophlegmonia.
- With , hyperplastic lymphadenitis signs differentiate with tumors.
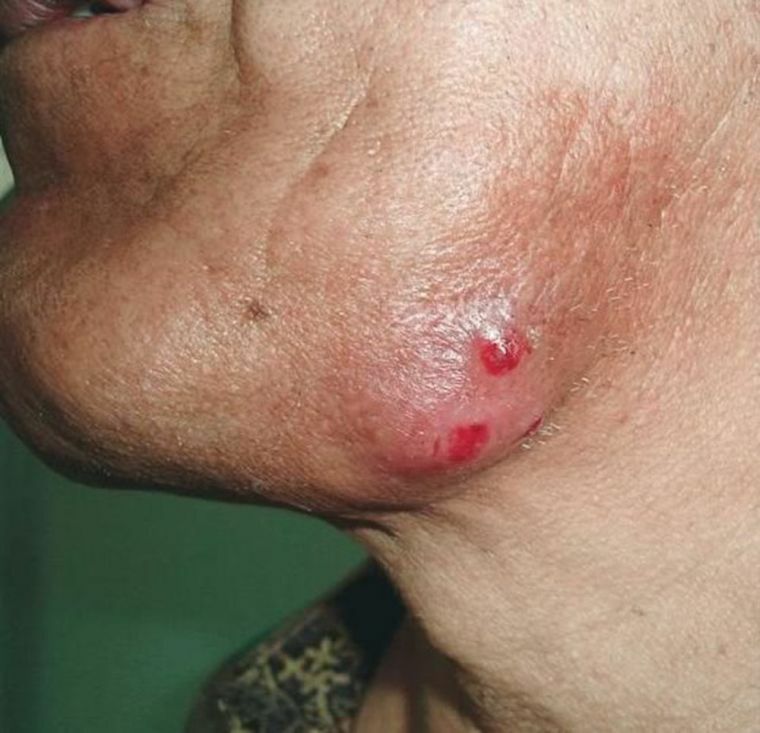
Diagnosis of
The disease is differentiated with phlegmon, abscess, periostitis and tumor processes of various etiologies. It is necessary to conduct research on diseases such as syphilis and tuberculosis, for which such symptoms can be characteristic.
 The complexity of diagnosis is that such clinical manifestations are characteristic of inflammatory and neoplastic diseases.
The complexity of diagnosis is that such clinical manifestations are characteristic of inflammatory and neoplastic diseases.
The difference is that actinomycosis has a sluggish character. The disease lasts with periodic exacerbations. The inefficiency of anti-inflammatory therapy indicates a disease caused by actinomycetes. To diagnose actinomycosis, x-rays and microbiological analyzes are prescribed.
Treatment Methods
Cardinal methods of treatment: removal of teeth that provoked infection, granulomectomy, removal of nodules of periosteum with subsequent drainage. In addition to surgical methods, therapy aimed at suppressing the vital activity of the radiation mushroom is used. For these purposes, patients are prescribed Actinolysate. 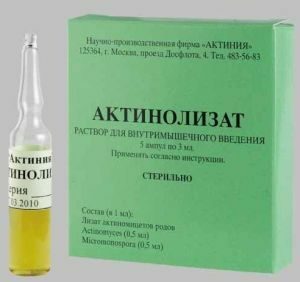
An important role in the treatment is given to the course of therapy to strengthen the body's immune forces. Widely used methods of physiotherapy, including laser exposure, iontophoresis with drugs and treatment with ultrasonic waves.
Treatment of actinomycosis should be carried out in a comprehensive manner. The leading role is played by the removal of the focus of infection and affected tissues.
For the removal of intoxication, infusion therapy is performed. And as a fortifying agent prescribed vitamin complexes. In the postoperative period, antibiotic therapies are prescribed.
Preventative measures
To prevent disease, timely sanitation of the oral cavity, compliance with personal hygiene rules is important. To avoid infection with fungi, it is necessary to strengthen immunity and prevent the presence of foci of infection.
Any infection can provoke a secondary injection of actinomycetes and lead to a relapse of the disease.
The cause of infection can also be residual effects after the infection, if the patient's medical instructions were not properly performed.
Consequences of
disease Timely treatment started guarantees a positive prognosis. In some cases, after a certain period after the therapy, antibacterial courses are repeated.
Despite the sluggish nature of the disease, actinomycosis can lead to serious complications. Radiant fungus is able to penetrate into the small and large circle of blood circulation, which leads to metastasis of the foci. Complication can result in sepsis of hematogenous or lymphogenous etiology.
Complications occur when the treatment is delayed and the disease is of a duration. Severe forms of infection, in which several lesions are diagnosed, can provoke generalization of the process and the spread of infection to other organs.

It is especially dangerous to introduce foci of infection into the chest, brain and intestines. Metastasis of foci of radiant fungus can lead to death.
Actinomycosis is a pathological process with a weakly expressed clinical picture in the initial stages. In order to avoid this infectious disease, it is necessary to follow preventive measures. In case of changes on mucous membranes, consult a doctor. Self-medication can be not only useless, but also dangerous.
