Accomodation is the ability of the eye to focus on objects that are at different distances, while maintaining clear vision. Neglect of the rules of eye care, various diseases and age-related changes lead to disruption of the visual system, which affects the quality of human life.
- Mechanism of accommodation
- Measurement of
- Norms of
- Reasons for
- Types and symptoms of disorders
- Presbyopia( senile vision)
- Asthenia asthenia
- Weakness of accommodation
- Conventional excess supply of accommodation and spasm of accommodation( false myopia, tired eyes syndrome)
- Paresis and paralysis of accommodation( cycloplegia)
- Threats
- Treatment
- Drops
- Vitamins and minerals
- Points
- Lenses
- Laser correction
- Workout
- Appar
- Physiotherapy
- In children
- Prevention
Mechanism of accommodation
The quality of vision is determined by the ability of the eye to refract and conduct rays of light in such a way as to see equally well at close, medium and long distances. To change the angle of refraction of light allows the elasticity of the lens and the ciliary muscle( internal paired muscle of the eye) that regulate its tension and the zinn ligament( circular ligament supporting the lens).
- When considering an object in the distance, the ciliary muscle relaxes, and the zinnic ligament tenses, pulling the capsule of the lens and making it flat. In this case, the refractive power of the optical system of the eye decreases.
- Focusing on the subject near causes tension of the ciliary muscle and relaxation of the zinn ligament, which causes the lens to become convex, and the refractive power of the eye increases.
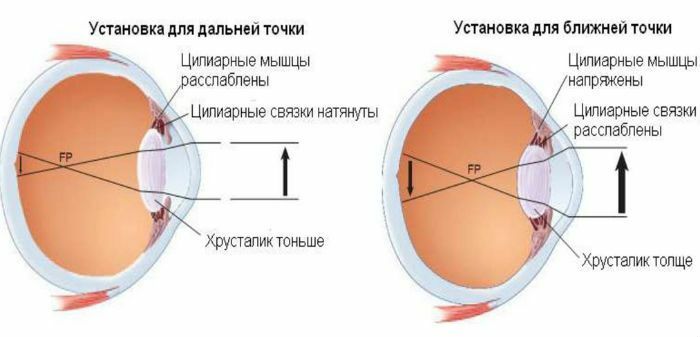
The accommodation process occurs automatically and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system: the parasympathetic department is responsible for the work of the ciliary muscle, the sympathetic for the cynic ligament.
to table of contents ^Measurement of
When checking the accommodative ability of the eyes, several parameters are used:
- Absolute accommodation - calculated for one eye when turned off from the view of the second.
- Relative accommodation - binocular vision( with two eyes), at which the accommodation process is accompanied by convergence( reduction of the visual axes of the eyes on the subject).With normal vision, accommodation and convergence occur in parallel and in concert.
- Functional peace of accommodation - a condition in which accommodative stimulus is absent, there is no need to involve ciliary muscles and cynic ligament, the view is directed into the distance.
- Area( length) of accommodation is the distance between the furthest clearest point( in a healthy person it lies at infinity) and the nearest point of clear vision( at a distance of 10 centimeters).Expressed in linear quantities.
- The volume( force, amplitude or width) of the accommodation is the difference in refraction( the refractive force of the optical system), which increases from the resting state to the maximum accommodation voltage, that is, when looking from the far point of clear vision to the near. The unit of measurement is diopter.
- The accommodation voltage is the negative part of the relative accommodation, the amount of accommodation spent to focus the eye on a particular object.
- The accommodation reserve is a positive part of the relative accommodation, a reserve of accommodation volume remaining after the eye stops at any fixation point. Normally, to work at close range, the accommodation reserve should be at least half the voltage( optimally - 33 centimeters), otherwise visual fatigue will quickly arise.
For the diagnosis of disturbances in accommodation, the following methods are used:
- Inspection of vision without glasses and with the selection of suitable glasses( lenses).
- Visometry - visual acuity assessment using special tables( Sivtseva, Golovina).
- The is a definition of the position of the near and far points of clarity for each eye with the use of special medical devices( optometrists or ccomodometers).
- Proximetry - calculation of the accommodation area using a special ruler and an object moving along it, as well as a spherical lens.
- Skiascopy - definition of the type and degree of refraction. It is held in a dark room with mirrors and a ski-scopic ruler with lenses.
- Ergography - assessment of the endurance, performance and fatigue of the ciliary( ciliary) muscle under visual loading through graphic images( ergograms).
- Automatic refractometry - examination of the refraction of the eye( determining the ideal image point relative to the retina) using a special medical device( automatic refractometer).
- Ophthalmometry is a measurement of the radii of curvature and refractive force of the cornea using an ophthalmometer instrument.
- Pachymetry - ultrasound or optical detection of the thickness of the cornea of the eye.
- Echobiometry( A-scan) - ultrasound examination of eye sizes. Allows to reveal pathologies of an eyeground, a cornea, a lens, a retina, probability of a myopia.
- Biomicroscopy is a method of examining the media and tissues of the eye by means of a slit lamp( special ophthalmic microscope).
Standards
The accommodative ability of the eye decreases with age.
Approximate age norms of absolute accommodation in diopters:
- 10 years - 12-14;
- 16 years - 10-14;
- 20 years - 9-13;
- 25 years - 8-12;
- 30 years - 6-10;
- 35 years-5-9;
- 40 years - 3-8;
- 45 years - 2-6;
- 50 years - 1-3;
- 55 years - 0,75-1,75;
- 60 years - 0,5-1,5.
Approximate relative stock requirements in diopters according to age:
- 7-9 years - 3;
- 10-12 years - 4;
- 13-20 years - 5;
- 13-20 years - 5;
- 21-25 years - 4;
- 26-30 years - 3;
- 31-35 years old - 2;
- 36-40 years - 1;
- 41-45 years - 0.
Reasons for
The deterioration of accommodation occurs for several reasons:
- Age changes - the gradual loss of the lens elasticity and curvature( the ability to change shape), its compaction, weakening of the ciliary muscle.
- Atrophy of ciliary muscle fibers due to increased intraocular pressure( eg glaucoma).
- Inflammatory processes, tumors, hemorrhages in the orbit.
- Defeat of meninges: neoplasms, meningitis, tuberculosis.
- Weakness of the muscles of the back and neck, violation of blood supply to the cervical spine caused by insufficient physical activity. Injuries or surgery on the eyes.
- Infectious and neurological diseases.
- Poisoning with drugs or toxins.
- Incorrect nutrition, insufficient intake of vitamins, protein and fats.
- Metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus.
- Non-observance of the work and rest regime, excessive strain on the eyes - long stay at the computer monitor, TV, incorrect position during reading.
- Hypokinesia of accommodative apparatus - the emergence of modern optical devices, when using which eliminates the need for the accommodation device, the balance between accommodations and convergence is disturbed, the binocular interaction between the eyes is weakened.
loading. ..
to contents ^
Types and symptoms of disorders
The pathologies of accommodation are divided into age( presbyopia) and acquired.
to contents ^Presbyopia( senile vision)
Occurs with age, characteristic symptoms in people with normal vision are noticeable after 40-45 years, with farsightedness( hypermetropia) deterioration occurs earlier, with myopia( myopia) - later.
Symptoms:
- strain of vision;
- rapid visual fatigue while reading;
- distance the nearest point of clarity, that is, the inability to read the fine print or view small objects at close range, to focus them away from the eyes;
- blurs letters when viewed near;
- blurred vision( short-lived) when translating the view between near and far objects;
- reduced vision in dim lighting and reduced symptoms in bright sunlight.
Astenopia asthenia
Characterized by increased eye fatigue due to prolonged activity near( reading, working at the computer) and is caused by weakness or overstrain of the ciliary muscle. Asthenopia is not considered a disease, but it can develop into a serious pathology. About half of PC users face this phenomenon.
Symptoms:
- doubling objects, blurry image;
- appearance of a veil before the eyes;
- thread, pain, burning sensation in the eyes, lacrimation;
- changing the shapes and sizes of objects of observation( for example, letters in the text);
- Inflammation of the eye mucosa;
- headache.
Weakness of accommodation
The state of insufficient or unstable accommodation, existing for a long time, appears gradually.
Symptoms:
- low head incline, incorrect posture during writing and reading;
- fatigue, discomfort in the eyes;
- headaches;
- decrease in accommodation volume by half( in comparison with the age norm) by removing the nearest and approaching the further point of clear vision.
Habitually excessive accommodation voltage( PINA) and accommodation spasm( false myopia, tired eye syndrome)
PINA is an existing long-term excess tonus of accommodation, in which the ciliary muscle remains tense even after the termination of the load( for example,into the distance).At PINA, the most corrected visual acuity( in glasses) does not decrease and is 1.0( 100%).Such a violation is most often manifested in children of school age and students who are forced to do much.
The accommodation spasm is also a spasmodic contraction of the ciliary muscle, which continues under conditions where focusing is not required near. However, unlike Pina, spasm causes a decrease in the most corrected visual acuity to 0.7-0.9.
Symptoms of these disorders:
- deterioration of visual acuity in the distance;
- double vision;
- rapid eye fatigue during visual work near;
- feeling of pain and burning in the eyes;
- pain in the eyeballs, temporal and frontal areas;
- redness of the eyes;
- lacrimation;
- occurrence of excessive irritability and fatigue;
- volume of accommodation with spasm is difficult to determine - the distant point of clear vision almost merges with the near, and the accommodation area extends only by 2-3 centimeters;
- at PINA, the nearest point of clear vision is distant, and the accommodation volume is about 2 times lower than normal.
Spasm develops quickly enough and becomes the reason of the reference to the oculist. Pina appears gradually, periods of clear and poor vision in the distance change each other, persistent deterioration of vision occurs imperceptibly and in most cases is detected accidentally, during a physical examination.
to table of contents ^Paresis and paralysis of accommodation( cycloplegia)
Characterized by the inability to view small objects at close range due to blockade of contractions of the ciliary muscle.
Paresis can be:
- central - due to heavy metal poisoning, infectious diseases, diabetes mellitus;
- peripheral as a result of taking M-cholinolytics.
Paralysis is provoked by infectious diseases, injuries, oculomotor or trigeminal nerve damage, as well as a number of pharmacological preparations.The manifestations of the violations are:
- blurry( blurring) of the near vision - the hand with the text with the standard font has to be removed further from the eyes;
- difficulties in writing - a person does not see the letters that he writes;
- inability to view text when the head is tilted, reading with one eye;
- squint if necessary to consider the object near;
- frequent closures, redness of eyelids and conjunctiva;
- rubbing of eyes, sensation of itching, burning, foreign object;
- headache after visual exertion;
- diplopia( image doubling);
- mydriasis( dilated pupil);
- impossibility to determine the amount of accommodation - the near point of clear vision merges with the distant one.
Pathologies develop rapidly and can affect one or both eyes.
to contents ^Threats to
Spasms, paresis and paralysis of accommodation can indicate serious illnesses - craniocerebral trauma, brain tumors, circulatory disorders, infectious or neurological lesions.
Ignoring such violations as weakness of accommodation or PIN can lead to serious consequences:
- vision impairment by 1-3 diopters, and sometimes more;
- constant burning sensation, foreign body in the eyes, their redness;
- pain in the eyes and head;
- deterioration of state of health, increased fatigue.
In the absence of therapy, such changes become permanent.
Read also what is cataract, why it develops and how to treat the disease in children and adults. Http://woman-l.ru/katarakta-prichiny-simptomy-lechenie-i-profilaktika/to the table of contents ^Treatment
Assumes a comprehensiveapproach and is assigned according to the type of pathology:
to the table of contents ^Drops
In cases of accommodation disorders, cycloplegic and mydriatic preparations are used - they allow to relax the ciliary muscles( for example, with spasm), increase the contractility of these muscles( with PINA), widen the pupil,take awayit mobility eye( Atropine, Digofton, Irifrin, Mezaton, Taufon, Tsiklomed).
to contents ^Vitamins and minerals
The balance of these substances has a stimulating effect on accommodation:
- calcium and vitamin D3 improve neuromuscular conduction, relaxation and contraction of the ciliary muscle;
- antioxidants( anthocyanosides of bilberry extract, beta-carotene, vitamins C and E, dikvertin, lutein, selenium, zinc) improve blood properties, strengthen blood vessels and increase blood flow in the retina.
Points
Correction involves the permanent or periodic wearing of glasses selected by an ophthalmologist in accordance with the type and degree of refraction:
- Monofocal glasses for near - used for presbyopia or accommodation weakness, as well as for temporary correction for paresis. The advantage of the method is its simplicity of manufacture, good result, low cost. The disadvantage is the limitation of the zone of clear vision by the area near, and when looking at some distance further the glasses have to be removed or viewed above them.
- Alternating monolateral weak-myopic defocusing( alternating anisocorrection) - use of 2 pairs of glasses to wear every other day. In glasses, a defocus is created for each eye. The method is recommended for children with a small myopia when a weakness of accommodation is detected. Advantages - high visual acuity in the distance with reduced load on accommodation, simplicity of selection, reasonable price. The disadvantage is a slight violation of the refractive-accommodative balance.
- Monofocal monofilament monofocal glasses - designed for people with myopic anisometropia( refractive error, the degree of which differs for each eye), who previously worn glasses with hypocorrection. In these glasses one eye is adjusted for sight near, another - for a distance.
- Bifocal glasses , in which the upper part of the lens is used to correct the vision in the distance, the bottom - for near. Are intended for presbyopes and persons with a weakness of accommodation, including children. When moving from the top of the lens to the lower refraction, it changes in a jumplike manner.
- Progressive glasses - provide high quality of vision at different distances. In them, the transition from the top of the lens( for distance) to the lower part( for near) occurs smoothly. Advantages - the ability to have 1 pair of glasses for permanent wearing, clear vision, no jumps of the image. Among the shortcomings is the need to change the habitual behavior( tilt and turn of the head), distortion of the image when looking in the wrong zone of the lens.
- Monofocal glasses for nearness with degression - used to correct presbyopia. In them, the optical force of the lens smoothly varies from bottom to top.
- Points for support of accommodation - glasses with monofocal corrective lenses, slightly offloading accommodation when working near. Recommended for people with visual fatigue, young presbyopes, children at risk of developing myopia.
lenses As with wearing glasses, eye contact lens correction involves the use of the principle of monovision, as well as the use of bi-or multifocal lenses.
Depending on the structure of the lens there are:
- Simultaneous - working on the principle of simultaneous vision, when zones of clear vision at different distances are located in the pupil area. As a result, several different images are projected onto the retina, and the brain chooses the right one.
- Alternating - use the principle of alternate vision, as in bifocal and progressive glasses.
Laser correction
An alternative to eyeglasses and lenses is a change in the thickness of the cornea( the elimination of its irregularities and defects that lead to poor eyesight) with the help of laser beams, thereby increasing the refractive power of the eye and increasing the clarity of the image of objects.Indications:
- myopia from -1 to -13 diopters;
- farsightedness from +1 to +6 diopters;
- astigmatism from +/- 1 to +/- 4.
Modern methods of correction are safe and painless, allow to restore sight to patients 18-45 years old.
to contents ^Training
To remove the spasm of accommodation helps special gymnastics for the eyes. They can also be used to prevent violations.At home:
- Close the eyes and slowly move the pupils from side to side, from top to bottom, diagonally, along the circumference, to describe eight. It is recommended to perform as often as possible with visual exertion.
- Blink tightly for a few seconds, then quickly blink for 30 seconds. Can be used repeatedly when doing work on the computer.
- Draw a point on the windowpane( you can mentally), slowly translate the view from this point to distant objects outside the window, and then to the tip of your nose. Exercise 1-2 times a day for 3-7 minutes. If the patient was prescribed glasses for distance, they should be trained in them.
Inpatient:
- Training on Avetisov-Matz. Supposes reading for several minutes in different lenses - from the maximum possible load to the minimum.
- Method of optical micro-fogging by Dashevsky. Used to treat PNA, separately for each eye. Adjusting the vision to 1.0 with glasses, add to them, and then remove the lens +0.25 diopters, training the eye to move from a small mist to an automatic restoration of visual acuity to 1.0.By the same principle, then reduce the number of negative diopters in glasses.
- Propagation method for Volkov-Kolesnikova. Used with a stable PIN, also based on the replacement of lenses - from positive to negative, with more to less power. In this case, the patient looks at the lines of the Sivtsev table for several minutes.
Apparatuses
For the elimination of accommodation disorders use special devices:
- Ophthalmic Exerciser-relaxator Vizotronik - has a relaxing effect on the ciliary muscle.
- Medical device for training eye accommodation Oxys - allows you to alternate the relaxation and tension of the ciliary muscle, changing the distance between the image of the object and the patient's eye from close to remote and back.
- Apprentice for accommodation training Brook - thanks to a multitude of light emitters, an object is formed on the lens of the device, which moves from a close distance to virtual infinity and in the opposite direction.
- MACDEL 09 device - provides low-intensity laser stimulation of the ciliary muscle. Non-contact exposure to infrared laser radiation enhances the metabolic activity of epithelial cells of the ciliary body.
- Laser speckle - hit of a scattered beam of laser helium-neon radiation on the retina of the eye causes a picture in the form of a set of randomly located spots of different sizes( speckle structure).At the same time, the work of the sensory apparatus of the eye improves, the tension of the accommodating apparatus decreases.
- Apparatus for vacuum ophthalmic massage( AVMO) or local barotherapy( pneumomassage).The use of air waves enhances peripheral circulation, reduces spasm of blood vessels, improves trophism of tissues.
- Ophthalmic electrostimulator( ESOF), magneto-acupuncture massager Zhezoton - affect the sensory and neuromuscular devices of the eye with weak impulses of electric current.
- Complex Ambliocor - provides video-bioelectric correction of activity of the cortical part of the visual analyzer. The patient looks through animated or feature films, with a worsening perception, the screen goes blank, and when it improves, it turns on. The method is based on the motivation to see as much as possible, while the brain stimulates the best vision.
Physiotherapy
The following methods are used to restore accommodation:
- Magnetotherapy and magnetophoresis - assume the influence of the magnetic field to improve the microcirculation and reactivity of blood vessels, normalize their elasticity and tone. When magnitophorese use drugs, the effect of which is enhanced by the apparatus.
- Electrophoresis - improves the penetration and action of medications with a DC source.
- Acupuncture is a method of acupuncture using silver needles injected into bioactive points of the body, including in the eye area. To remove painful sensations thus allows preliminary massage of points.
- Electroreflexotherapy - influence on acupuncture points by electric current. The common points are supplied with a current of negative polarity, at points in the eye area - positive.
- Massage neck and collar zone - improves blood circulation, it is recommended to conduct courses for 10 sessions 2 times a year.
In case of accommodation disorders caused by traumas, infectious, neurological or psychological lesions, the treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
to contents ^In children
One of the most common diseases in pediatric ophthalmology is accommodation spasm - according to statistics, they suffer about 15% of school-age children.
Violation is caused by visual fatigue, when the child spends a long time at the computer, tablet, phone, at the TV screen, and also reads, draws, works with small details( embroidery, weaving from beads).To determine the visual impairment, parents can by characteristic features:
- fatigue in visual work;
- frequent rubbing or squinting of eyes;
- headaches in a child;
- decline in school performance;
- degradation of image clarity at standard distance, diffuse or doubled picture when looking away.
This state can last several months and even years and is reversible up to a certain point. However, long-term uncorrected false nearsightedness may eventually become true. Therefore, early diagnosis of accommodation disorders and proper treatment are very important.
to contents ^Prevention
The main task of the accommodation system is the formation of a clear image on the retina in response to the appearance of diffuse contours as the object approaches the eye. The successful accomplishment of this task largely depends on the physiological state of the accommodative system, the following measures help to support it in the norm:
- Correct lighting. For visual loads, natural light is desirable, and the light should be distributed evenly. When using a table lamp, it must be placed on the left( for left-handers on the right), and also include general lighting.
- Correct position of the body. Optimum distance when working with close objects( book, tablet) - 35-40 centimeters. The computer needs to be installed opposite the person, just below eye level, the TV should be at a distance of 3-5 meters. Reading lying and tilting the head to the book are the main reasons for the development of myopia.
- Rest mode - with hard work you need to take breaks every 30-40 minutes and give your eyes a 5-minute rest.
- Gymnastics for the eyes of - even small children need to be taught to perform a simple set of exercises( blinking, looking from a distant object to a close one and vice versa, circular movements of closed eyes).
- Physical exercises - strengthen the body as a whole and vision in particular. Especially important are playing sports for children, in between training they need to actively move( run, jump, crouch, bend).Useful walks in the open air, swimming, neck and shoulder massage.
- Water procedures. To improve the blood circulation in the retina, contrast baths for the face help, you can wash yourself alternately with warm and cool water. When visiting swimming pools with chlorinated water, as well as open water bodies, special glasses should be used to protect the eyes from infections and disinfectants.
- Proper nutrition. The diet should be varied and balanced, including enough vitamins and minerals. Especially useful are green leafy vegetables( cabbage, spinach, sorrel), carrots, bell peppers, oranges, kiwi, dried fruits( raisins, dried apricots, prunes), nuts, beans, eggs, dairy products, sea fish.
- Adequate vision correction - involves the correct selection of glasses or contact lenses, taking into account individual characteristics of a person.
