
The medical term "palpation" comes from the Latin "palpatio", which means "to feel."Palpation is an important method of physical examination of the internal organs of a person, which allows you to determine the properties of tissues, as well as to detect physiological changes in the body. The feeling of the liver is based on the mobility of the organ in the abdominal cavity during breathing. This method of clinical diagnosis is prescribed for patients with bile duct disease and liver pathologies.
- Liver palpation value
- Liver percussion
- Liver palpation
- Liver palpation technique
- Causes of liver enlargement
- Palpable liver properties
Palpation value of liver
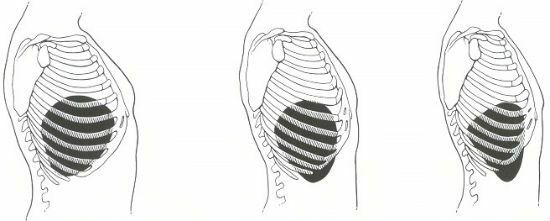
With a palpation of the liver, it is possible to determine:
- localization and the nature of the lower edge of the organ;
- morbidity of the organ;
- consistency and form of the liver;
- the location of the lower border of the organ with respect to the costal arch;
- surface features.
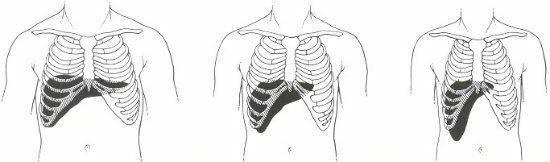
Percussion of liver
Before palpation, the patient is assessed by the percutaneous method. This procedure also allows you to determine the size of the organ being examined.
The liver is an airless organ and when it is tapping it produces a dull sound, and part of the liver, which is blocked by the lung, shortens the percussion sound. The doctor with the help of tapping determines:
- of the border and the height of hepatic dullness;
- upper and lower edge of the organ.
Percussion of the liver is performed by the method of Professor MG.Kurlova. In this case, the boundaries of the organ are fixed on three main lines:
- of the anterior median line;
- right mid-clavicular line;
- costal arch.
In medical practice, the definition of the lower border of the organ is important, since in most cases the change in liver size occurs downwards. With the help of percussion specialist determines how many centimeters the liver stands out from under the costal arch.
to table of contents ^Preparation for palpation of liver
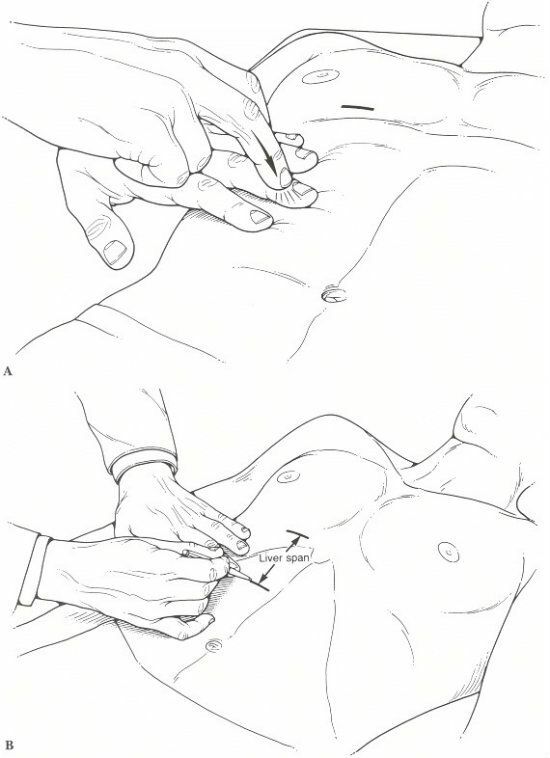
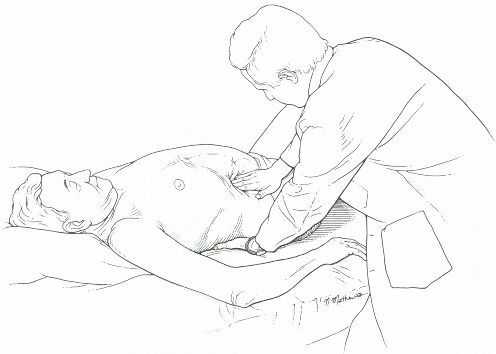
Palpation of the liver in medical institutions is most often performed according to the classical method of Professor VP.Obraztsova. This diagnostic measure should be carried out in a well-lit and warm office. Before probing:
- The doctor sits face to patient on the right side.
- The patient lies on his back with a slightly raised head. The legs are in a straightened or semi-bent position.
- The patient's hands are on the chest to limit her mobility.
Technique for performing palpation of the liver
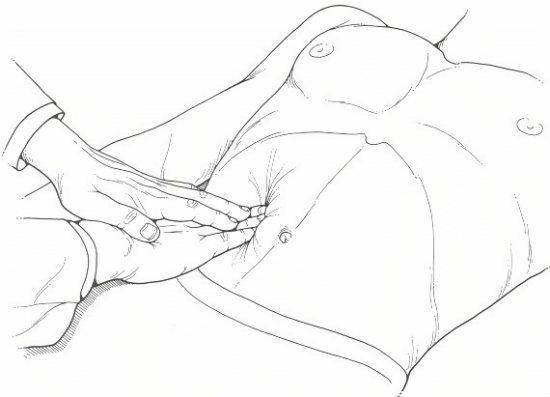
The palpation technique is based on VP.Obraztsov is the concept of the formation of a "pocket".In the process of inspiration, the falling liver enters it, and then at the exhalation height it slips out of the "pocket".The technique of palpation of the liver includes the following stages:
- Preparation. The doctor puts a flat right hand with half-bent fingers on a part of the patient's abdomen, where the lower limit of the organ was previously determined by the method of tapping. The left hand fixes the right side of the chest. His thumb is in front on the costal arch, and the other fingers are located behind.
- Conduction of palpation. The doctor with his right hand, when exhaling, moves his skin down and smoothly immerses his fingertips into the abdominal cavity, forming a skin fold - a "pocket".Then the doctor asks the patient to take a deep breath, during which the lower edge of the organ drops into an artificial pocket and bypasses the fingers. If the lower edge of the organ could not be palpated, the manipulation is repeated. In this case, the doctor moves the tips of his fingers upward to the costal arch by 2 cm. The liver is examined several times. If a lot of fluid has accumulated in the liver, palpation is performed by an impulsive method. A doctor with two, three or four fingers of the right hand, causes short, jerky strokes from below upwards along the front abdominal wall. This manipulation lasts until the discovery of a dense body - the liver.
- Completion of the liver. After palpation, the doctor treats the hands with an antiseptic and evaluates the results of the diagnosis: the sensitivity, shape and density of the liver, as well as the presence of irregularities on its surface.
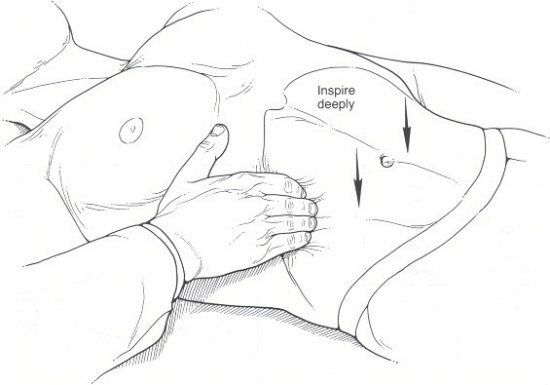
In a healthy person, the liver is not palpable. To probe the organ is possible only when it is lowered or enlarged.
to the table of contents ^Causes of liver enlargement
Significant liver enlargement is characteristic in the following diseases:
- liver cancer;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- chronic liver disease;
- of right ventricular heart failure;
- anemia;
- leukemia;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- disorders of bile outflow;
- chronic infections.
Properties of palpable liver
The healthy margin of the liver is soft and even, and its surface is smooth. Palpation is painless.
Smooth surface of the liver is typical for cirrhosis, congestive liver and hepatitis, and the granular surface of the body - with syphilis, abscess, atrophic cirrhosis. With oncological diseases, the lower edge of the liver is thickened, hard and uneven.
The pain of the liver is observed when it is stretched or inflamed.
In the diagnosis of the liver, the dynamics of changes in organ size matters. A sharp increase in liver size is characteristic of cancer and fatty degeneration, and a decrease in acute hepatitis and cirrhosis.
