- Paratraumatic( near-wound, post-traumatic) eczema - is localized mainly around injuries( burns, frostbite, etc.) and in places where purulent discharge is absent. On the affected areas of the skin, reddening appears, which is formed into pustules and vesicles. Then erosions occur in their place, which under the influence of purulent discharge and as a result of necrosis of the epidermis grow into depth and length. This process can be complicated by the development of multiple folliculitis.
- The true( idiopathic) eczema can last for many years with a wavy or continuous flow. Foci of inflammation in the form of small vesicles( vesicles) and serous papules( formation that rises above the skin) appear on any part of the body, but most often the dorsal sides of the hands and feet are affected. The main symptoms of the disease are itching, which can lead to sleep disturbances and neurotic disorders, as well as dry skin, flaking and cracks.
- Disgytrotic eczema develops over 2-3 weeks, in some cases - several months with a chronic recurrent course. On the skin between the fingers, palms, back surfaces of the hands, feet appear serous-filled bubbles in size from 2 to 5 mm, which gradually burst, and in their place erosions with suppuration and brown crusts are formed. Dyshidrosis eczema is accompanied by redness and severe itching.
- Atopic eczema is allergic and affects such areas of the body as the face, elbows and knees, ankles, forearms. Because of the inflammatory process, the affected skin looks scaly and very dry. Also, the symptoms of the disease are burning, itching, redness, the formation of blisters containing exudate. Atopic eczema can be accompanied by a violation of the intestinal tract and digestive disorders.
- Microbial( bacterial) eczema often occurs against the background of existing skin lesions. The foci of inflammation are clear and even with a prominent central region, which has a wet and reddened surface. On the entire area of the affected surface there is an accumulation of purulent crusts, causing itching. Depending on the type of microbial eczema, inflammation can appear on the face( in the area of the upper lip, chin), as well as around the wounds and injured skin areas.
- Mycotic( fungal) eczema is a combination of an allergic reaction and fungal skin damage caused by pathogens. Eczema is chronic and affects the skin of the shins, palms, feet, creases between the fingers. It appears with rounded rashes of pink or gray color, which cause the patient discomfort due to itching.
- Varicose( venous) eczema is a disease that occurs at the site of veins, due to prolonged blood stagnation. On sites where there is an expansion of veins, there is a strong itch and a change in skin color from red to violet.
- Seborrheic eczema is characterized by a chronic course and frequent relapses, manifested by eruptions that occur in places with a high content of sebaceous glands - the scalp, face in the eyebrows and nasolabial folds, interscapular area, chest, large folds. Symptoms of the disease are the formation of fatty crusts or scales, leading to the gluing of the hair. With severe itching and burning, a secondary infection can join. Seborrheic eczema is manifested in childhood, and afterwards it is periodically activated by a person throughout life.
- The coin-like( numular, plaque) eczema of is characterized by the appearance on the skin of highly itching generalized lesions of clear, rounded shape. In the period of exacerbations, the rash is itchy, the lesions are flaky and wet. The disease begins from the inner surface of the thighs, then the rash appears on the back of the palms and spreads to the trunk and legs.
- Tylotypic( horny) eczema is characterized by slow flow and exacerbations in the cold season, due to low humidity. Horny eczema is most often manifested on the hands( elbows, back of the hands) and fingers. Affected skin first acquires a thick stratum corneum, then there are bubble rashes and excessive peeling accompanying itching.
- Contact( professional) eczema is a sluggish inflammatory disease that develops during working activity due to exposure to toxic substances. Characterized by severe redness on the skin, swelling, the formation of papules and vesicles, accompanied by itching, burning and pain. This eczema affects open areas of the body, because they are in contact with irritants, which provoke its appearance.
- Allergic eczema - inflammation of the skin, which are of a neuro-allergic nature. Symptoms can be different, but mostly the disease creates discomfort in the form of itching, burning, dryness and redness of the epidermis. The disease affects any place of the human body, especially often rashes appear on the neck, hands, face, from the inside of the elbows, ankles and knees.
- Wetting( wet) eczema is characterized by the appearance on the affected skin of redness, swelling and rash in the form of vesicles and serous papules. Sypnye elements are opened and transformed into point wetting erosions, thus there is an itch and a burning sensation.
- Anal eczema has a neuro-allergic origin, occurs in response to the action of external and internal stimuli. Accompanying the disease is deterioration of well-being and chronic fatigue. Symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, headache, rashes in the form of small bubbles filled with fluid are also observed.
- Kaposi's herpetic eczema most often develops in children under 2 years old. The main symptom of the disease are rashes, localized on the face, neck, scalp, in the auricles and behind-the-neck folds, on the hands, buttocks and the rear surface of the feet. During this period, the child's state of health worsens, lethargy, drowsiness, and body temperature may increase.
- Edged( epidermophytosis inguinal) eczema is a fungal disease characterized by the defeat of large folds of the skin( in the groin, between the buttocks, under the mammary glands).Manifestations can also appear on the trunk, palms, penis and scalp. Foci are pink scaly patches of rounded shape. After opening the vesicles, pustules are formed, then crusts and scales.
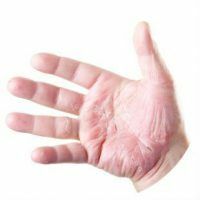
Eczema is a skin disease characterized by the appearance of such symptoms as rashes, itching, redness of the skin and peeling. Most often the disease affects the face, hands and feet. The disease is chronic, which occurs with periods of exacerbation and remission.
- reasons
- main symptoms
- Types Consequences Treatment
- Diet
- have
- children during pregnancy
- Treatment folk remedies
reasons
provoke appearance of eczema:
- Hereditary predisposition to the emergence of allergies.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines.
- Immune disorders.
- Liver diseases.
- Mycosis of the foot.
- Atopic dermatitis and exudative diathesis in children.
- Nervous shock and stress, mental breakdown.
- Work in the pharmaceutical and food industries, metallurgical and chemical enterprises.
- Vegetosovascular dystonia.
The main symptoms of
The manifestations of eczema vary depending on the type of disease and the stage of development of the inflammatory process on the affected area of the skin. However, the main symptoms characteristic of all species of specimens are:
- Appearance of the skin of areas of limited inflammation, with redness and roughness.
- The appearance of various kinds of rashes on the face, legs, hands, abdomen and other parts of the body.
- Constant or temporary itching.
- When the microbubbles are opened, painful cracks and ulcers develop.
- Dryness and thickening of the affected area.
Also, with eczema of any kind during periods of exacerbation, many people experience an increase in body temperature.
to contents ^Kinds of
Depending on the course and symptoms, the disease is divided into the following types:
to contents ^Consequences of
Also, eczema can cause erythroderma - a vast inflammation that affects almost the entire skin of the body. It is also treated only under the supervision of an experienced doctor in a hospital.
If eczema is ignored and not treated, then the inflammatory process is not limited to the skin and can go to allergic rhinitis, which leads to the appearance of bronchial asthma. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of eczema, it is necessary to visit a dermatologist and undergo the necessary treatment.
to the table of contents ^Treatment of
Eczema requires complex treatment. When symptoms appear, they first of all eliminate the cause that triggered the development of the disease. The following can be prescribed:
- Hyposensitizers: intravenous calcium chloride and intramuscular calcium gluconate, sodium thiosulfate and magnesium sulfate.
- Antihistamines: Dimedrol, Diazolin, Zaditen, Pipolphen, Suprastin, Tavegil, Telfast, Cimetidine or other
- Severe form of eczema prescribes the administration of corticosteroid hormones: Prednisolone.
- Immunocorrectors: Decaris, Methyluracil, Pentoxyl, Tactivine.
- During the acute period, diuretics( Hemodesis) and vitamins of group B.
In addition, external therapy is mandatory for the treatment of the disease. At the initial stage of the disease the doctor prescribes non-hormonal ointments from eczema:
- indomethacin;
- carofilenic;
- with silver nitrate;
- boron-naftalannaya.
If eczema is accompanied by infectious, fungal or bacterial diseases, a cream or tablets is prescribed to treat Losterin and Exodermil. Strong antifungal effect has Skin-cap. A common remedy for eczema on the hands is a zinc-based ointment.
In severe and acute stages of eczema, hormonal ointments are prescribed. The following types of such agents are divided by the degree of impact on the disease:
- With a weak action: Fluorocinolone acetonide 0.0025%.
- With moderate: Afloderm, Dexamethasone 0.05%, Hydrocortisone, Cinnatort.
- With strong: Apulein, Advantan, Sinalar.
- With the highest: Dermovate, Galcinonide.
After the opening of the blisters for the treatment of the surface of the skin, Castellani liquid( Fukortzin) is prescribed.
to table of contents ^Diet
Some products can cause an exacerbation of eczema:
- fried fish;
- chocolate;
- citrus fruits;
- strawberry;
- nuts;
- other products that have a high allergenic ability.
If the first signs of eczema occur, all these products must be excluded from the diet. In this disease, the type of culinary processing of products is of great importance. For example, boiled meat for a person may not be allergenic, but here the fried will provoke the appearance of rash and itching. It concerns both smoked products and natural milk, which have a rather high risk of becoming an allergen.
The children of
The first symptoms of childhood eczema often make themselves felt already in the first months of lifethe kid. Eczema in children is manifested in the form of small red spots on the face( cheeks and chin), and its signs can be noted on the wrists of the hands, neck, elbows, feet, knees and even on the eyelids.
Skin on the affected areas coarsens, and reddened specks gradually increase in size, swell and then transform into small vesicles. After the opening in place of the bubbles there are erosive foci. Such rashes are often accompanied by severe itching and burning. The child at the same time restlessly sleeps, becomes tearful, he may lose his appetite.
In case of combing eczematous spots, the affected areas become wet, crusted and flaky. Later, an infection can join and the possibility of purulent complications is not ruled out. To prevent this, it is necessary at the first manifestations of childhood eczema to immediately seek help from a specialist.
to the table of contents ^In pregnancy
Symptoms of eczema are individual for every pregnant woman. It can be:
- Severe hyperemia of the skin or slight reddening of some parts of the body( abdomen, arms, neck, chest).
- Severe itching and flaking.
- Complications in the form of infection of affected tissues may develop.
Treatment of eczema in a pregnant woman is complicated by a limited choice of medicines, for example, it is forbidden to use hormonal drugs, etc. Therefore, to effectively solve this problem, it is necessary to carry out complex treatment with the participation of a dermatologist and gynecologist.
to table of contents ^Treating folk remedies
- Sea buckthorn oil for the treatment of eczema should be taken orally at 1.5-2 ml per day and externally used as a 5% ointment. The oil promotes resorption of infiltrates, reduces pain, swelling and burning, and stops peeling.
- Healing ointment from 2 tbsp.l.birch tar, 5 ml of melted beeswax and vinegar, as well as 10 ml of vegetable oil, honey and purified sulfur. All put in a container, pour hot water and simmer for 15-20 minutes. Then cool and apply a thin layer on the affected areas of eczema skin.
- Tea tree oil with eczema is applied in the form of rubbing. A few drops of oil must be applied to the affected areas and rubbed - this will reduce inflammation, as well as stop the spread of infection.
- Kalina and currant with eczema are used in the form of decoction. For its preparation, the leaves of medicinal plants in a proportion of 1: 1 pour boiling water, add a small handful of fruits of the viburnum and leave for 25-30 minutes. Next, in a ready-made broth, get wet cotton cloth and attach to the skin.
- Tincture of celandine for the treatment of eczema is prepared as follows: 4 tbsp.l.chopped herbs celandine pour hot water and boil for 5 minutes and then let it brew for 8 hours. Ready to infuse and apply infusion for trays.
