 Fibrinolytic agents( fibrinolytic agents, thrombolytics, plasminogen activator) are drugs that can dissolve intravascular thrombi and are used to treat arterial and venous thromboses, as well as for thrombus lysis in pulmonary embolism.
Fibrinolytic agents( fibrinolytic agents, thrombolytics, plasminogen activator) are drugs that can dissolve intravascular thrombi and are used to treat arterial and venous thromboses, as well as for thrombus lysis in pulmonary embolism.
In 1938, Streptokinase was obtained, and in 1940 the mechanism of its action was described. And only after 36 years, Russian cardiologist Evgeny Ivanovich Chazov published an article on intracoronary thrombus dissolution with the help of this remedy.
The discovery of this enzyme allowed to reduce the frequency of deaths in acute myocardial infarction up to 50%.
Since then, more advanced drugs have been synthesized. Modern plasminogen activators have fewer side effects, are more easily tolerated by patients and show better efficacy.
Classification of preparations of the
group The mechanism of action of fibrinolytics is of direct and indirect effect.
The first group includes pharmaceuticals that, when interacting with fibrin filaments, dissolve them. These drugs include fibrinolysin. This drug shows pharmacological activity both when ingested in humans, and "in vitro".Recently, in medicine, the drugs of this group are practically not appointed.
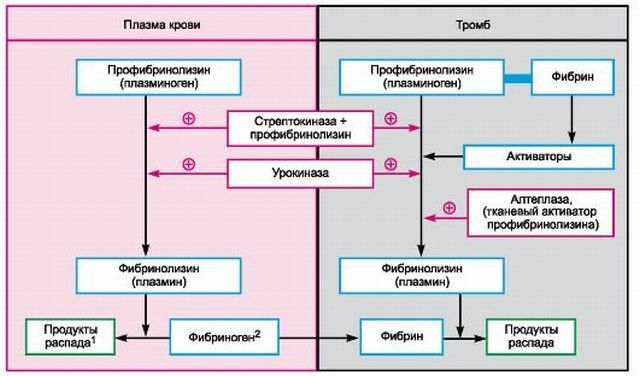
Indirect fibrinolytics( eg, Streptokinase, Urokinase) convert Profibrinolysin( plasminogen) to Fibrinolysin( plasmin), which has a therapeutic effect, namely dissolves the newly formed blood clot. This process is possible only in a living organism.
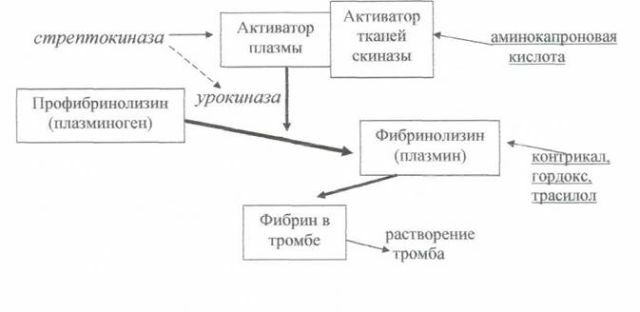
In addition, all plasminogen activators, depending on selectivity for fibrin, are divided into non-fibrin-specific( Streptokinase) and fibrin-specific agents( Prourokinase recombinant, Alteplase, Tenecteplase).
Non-fibrin-specific agents activate the fibrinolysin either bound or unbound to a thrombus, which results in depletion of the anticoagulant system and private hemorrhagic complications.
In direct-acting thrombolytic agents, efficacy is lower than that of preparations activating Profibrinolysin.
In domestic medicine, the following fibrinolytics of indirect action are used:
- Streptokinase;
- Alteplase;
- Tenecteplase;
- Prourokinase recombinant.
Features of application
All fibrinolytic agents are prescribed to dissolve fresh blood clots in thrombosis of blood vessels, different localization.
In addition, they are used for lysis of local blood clots in arteriovenous shunts and peripheral intravenous catheters.
When fibrinolytic drugs are prescribed for venous thrombosis in the first 48 hours in 70% of cases, thrombus dissolution is observed.
Even higher will be indicators if therapy is started for the first time 12 hours. In addition, in this case, the pharmacological effect will be better, in this case also less febrile and hemorrhagic complications are observed.
Plasminogen activators are prescribed for the following diseases:
- acute myocardial infarction;
- pulmonary embolism;
- unstable angina;
- thrombosis of the arteriovenous shunt;
- primary pulmonary hypertension;
- postpartum thromboembolism.
In phlebology, indications for the use of drugs are:
- thrombophlebitis;
- phlebothrombosis.
Side effects and contraindications
Contraindications to the use of drugs of this group are:
- various bleeding;
- hemorrhagic diathesis.
In addition to treatment with thrombolytic agents, it is worthwhile to abstain in a number of diseases:
- pulmonary tuberculosis in the acute stage;
- gastric and duodenal ulcer;
- inflammatory processes in the large intestine;
- acute pancreatitis;
- myocardial inflammation;
- radiation sickness;
- tumors of the central nervous system;
- status immediately after surgery, childbirth, spontaneous and induced abortion;
- recent biopsy of visceral organs;
- sepsis;
- diabetic retinopathy;
- arterial hypertension, when the upper pressure is more than 200, and the lower one is -110 mm.gt;Art.
Relative contraindications include:
- renal and hepatic insufficiency;
- menstrual bleeding;
- Hypermenorrhea;
- bronchial asthma;
- age is more than 75 years;
- several days after treatment with anticoagulants.
In addition, Creptokinase should be administered with caution in the recently transferred streptococcal infection.
When hemorrhage appears on the background of treatment with thrombolytic drugs, patients are prescribed antifibrinolytic agents.
Discontinue therapy only if bleeding threatens the life of the patient or the patient must be urgently operated.
In case of profuse hemorrhages, the patient may be prescribed aminocaproic acid, the administration of human fibrinogen or blood transfusion.
Of the side effects when using fibrinolytics can be observed:
- hectic temperature;
- headache;
- is an allergy, in the form of urticaria, face redness, itchy skin.
With the appearance of an allergic reaction, therapy is discontinued and, depending on the severity of the allergy, antihistamines or glucocorticoids are prescribed.
In elderly patients( over 75 years) during treatment, there is a high risk of cerebral hemorrhage, so before using fibrinolytics, you need to weigh the pros and cons.
List of popular fibrinolytics
In modern medicine, the following drugs are used:
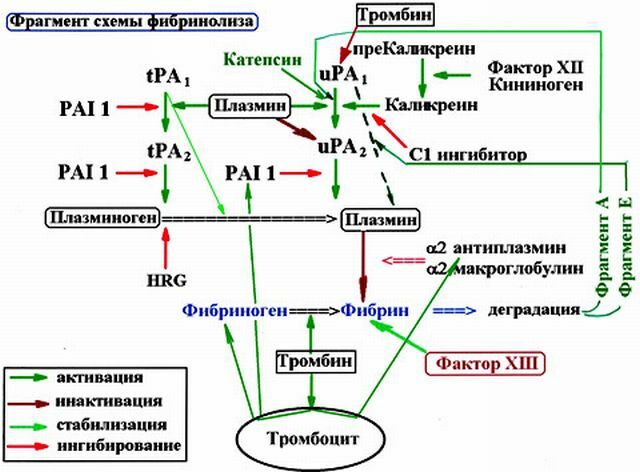
- Streptokinase is an enzyme that produces individual strains of β-hemolytic streptococci. Pharmaceutical
 industry produces a number of drugs on its basis: Streptase, Avelisin Brown, Tromboflux, and many others. Streptokinase catalyzes the conversion of fibrinolysin into fibrinolysin. Getting into the human body, part of streptokinase combines with antibodies and loses its pharmacological activity. In this case, the drug elimination period is only 20 minutes, whereas the half-life of the enzyme coupled to the profibrinolysin is 1 hour 20 minutes. Streptokinase is an antigen, therefore it causes the synthesis of antibodies, the amount of which increases with each new dose of the drug, as a result of which the pharmacological activity of the drug is reduced. As a rule, after 5 days of treatment, it is no longer useful to administer the medication, since it almost completely binds to antibodies. Also increases the production of antibodies streptococcal infection, which preceded thrombosis.
industry produces a number of drugs on its basis: Streptase, Avelisin Brown, Tromboflux, and many others. Streptokinase catalyzes the conversion of fibrinolysin into fibrinolysin. Getting into the human body, part of streptokinase combines with antibodies and loses its pharmacological activity. In this case, the drug elimination period is only 20 minutes, whereas the half-life of the enzyme coupled to the profibrinolysin is 1 hour 20 minutes. Streptokinase is an antigen, therefore it causes the synthesis of antibodies, the amount of which increases with each new dose of the drug, as a result of which the pharmacological activity of the drug is reduced. As a rule, after 5 days of treatment, it is no longer useful to administer the medication, since it almost completely binds to antibodies. Also increases the production of antibodies streptococcal infection, which preceded thrombosis. - Urokinase is an enzyme that is derived from human urine and kidney cells from the human embryo. It also activates plasminogen, it turns into plasmin, which causes the lysis of blood clots. Urokinase interacts with both plasmogen associated with the thrombus, and with what circulates freely in the blood. Therefore, when it is used in the same way as when using Streptokinase, there is a high risk of bleeding. For IV injections, the half-life of the drug is only 9-16 minutes. Almost never causes allergies, and antibodies are not formed to it.
- The tissue plasminogen activator is a proteolytic enzyme that resembles the plasminogen activator produced by the vascular endothelium. For medical purposes, Alteplase is used - a recombinant molecule of a tissue plasminogen activator, obtained by genetic engineering. The drug shows pharmacological activity only in the presence of fibrin. The half-life of the drug is only about 5 minutes. Unlike Streptokinase is not an immunogen, it can destroy long-term existing thrombi and the therapeutic effect of it is stronger. With the replacement of several amino acids in the Alteplase molecule, a new preparation of Tenecteplase was obtained, which is characterized by greater fibrin-specificity and a half-life period( about 20 minutes).
- Prourokinase recombinant .Its thrombolytic properties are similar to the tissue activator of plasminogen. It in the presence of a thrombus interacts with plasmogen, turns it into plasmin, which forms a more active double-stranded Urokinase molecule from the single-stranded Prourokinase molecule.
Because of the short half-life, fibrinolytics are injected intravenously drip or spray slowly for a quarter of an hour.
Thanks to the application of fibrinolytic therapy, millions of lives have been saved. Therefore, with the slightest suspicion of having a blood clot in the body, it is necessary to go to the hospital as soon as possible and begin treatment.
