 Disease known in medicine as calculous sialoadenitis, and the inhabitants call it salivary stone disease is quite common.
Disease known in medicine as calculous sialoadenitis, and the inhabitants call it salivary stone disease is quite common.
The main pathogenetic link is the formation of stones in the ducts of the salivary glands. Most often, the pathological process involves the submaxillary gland, and more specifically, its ducts. The ducts of the sublingual and parotid salivary glands are less often affected.
The disease is more common in children aged 7 to 12 years.
Content
- disease development mechanism
- Causes and risk factors
- Clinical picture
- Acute VS chronic
- disease diagnosis
- complex therapeutic measures
- Surgery
- Prevention calculouse sialoadenita
- Complications and prognosis
mechanism of
disease Formation of stones in the salivary glands occurs ifpresence of chronic sialoadenitis. Inflamed tissues of the gland create conditions for the disturbance of metabolic processes, as a result of which the density of saliva and the rate of its outflow change. Acute forms of the disease are rarely complicated by stone formation.

In the photo stones extracted from the salivary gland
The formation of a stone or compaction in the duct of the gland leads to a violation of the outflow of saliva. Compensatory mechanism is the expansion of the duct, but this mechanism only acts for a short time, and then closes the pathogenesis ring.
Due to prolonged stagnation of saliva in the enlarged duct, all conditions are created for its infection and the formation of an inflammatory infiltrate.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of the formation of stones in the ducts of the salivary glands is a prolonged stagnation of saliva. This condition occurs because of:
- dyskinesia of the ducts;
- inflammatory changes - sialadenitis;
- metabolic disturbances in the body( exchange of phosphorus and calcium);
- decrease in the protective properties of saliva;
- ingress into the foreign body.
A predisposing factor to the development of salivary stone disease is the presence of chronic diseases in the patient caused by a metabolic disorder in the body.
Features of the clinical picture
With the development of calculous sialoadenitis, the patient has a number of symptoms that cause him to consult a doctor:
- mouth pain while eating;
- dry mouth;
- difficulty opening the mouth;
- saliva becomes viscous and difficult to swallow;
- ear pain
 Symptoms of the disease develop gradually and are found in various combinations depending on the stage of the disease. At the initial stage, called asymptomatic, the patient only notes the occurrence of unpleasant sensations during meals.
Symptoms of the disease develop gradually and are found in various combinations depending on the stage of the disease. At the initial stage, called asymptomatic, the patient only notes the occurrence of unpleasant sensations during meals.
After 20 minutes after mechanical exposure, discomfort completely disappears and the person does not bother. Do not flatter yourself and pay no attention to what is happening. This stage is the first news of the formation of the pathological process. In the absence of treatment, it passes into the acute phase.
Acute VS chronic
Acute sialoadenitis develops suddenly, sometimes for several hours, manifests with acute pain, increased body temperature, general weakness and headache.
This process in most cases accompanies the development of an abscess or phlegmon. At the outlet of the duct of the salivary gland, swelling, redness and soreness increase.
Food intake is difficult due to the increase in soreness with any mechanical effect. On examination, in addition to subjective complaints, there is a gaping mouth of the duct of the salivary gland, dry mucous membrane, absence of saliva outflow, discharge of a small amount of pus from the hole.
When the disease is transferred to a chronic form, inflammatory phenomena disappear. There is a slight swelling, asymmetry of the glands develops, a slight increase in the size of the glandular tissue is formed.
When you massage the duct from it, a small amount of viscous transparent content is allocated. Careful palpation can detect one or more dense formations in the duct.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you find the first clinical signs of salivary stone disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In the diagnosis of the disease, modern medicine has stepped far ahead. The patient can be examined by both the dentist and the  therapist( in the absence of the first).
therapist( in the absence of the first).
When examined, the doctor can identify the main clinical sign - an increase in the size of the salivary gland, swelling in the opening of the outlet duct. In some cases, palpation( when palpating the place of the tumor with your finger), stones are revealed in the salivary gland.
To confirm and clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may order the following examinations:
- radiograph of the upper or lower jaw in a given projection;
- computed tomography;
- ultrasound examination.
After a detailed study of the results of the research the doctor can not only make an accurate diagnosis, but also appoint the only true and effective treatment.
Complex of therapeutic measures
Salivary stone disease most often requires surgical treatment. The invasive method of treatment is used only after the ineffectiveness of the course of conservative therapy.
In the acute phase of the disease, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately. When the disease is transferred to a chronic form, the course of therapy takes a long time, at least two weeks.
Conservative treatment of salivary stone disease includes:
- administration of drugs that enhance the secretion of salivary glands;
- course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs : reduces temperature, reduces edema of tissues, suppresses inflammatory reaction;
- antibacterial therapy ( in case the bacterial infection became the cause of the disease development);
- physiotherapy treatment .
 The methods of conservative treatment include nutrition consisting of crushed and grinded products. Increase the amount of warm drink( decoction of dogrose, fruit drinks) in order to increase salivation.
The methods of conservative treatment include nutrition consisting of crushed and grinded products. Increase the amount of warm drink( decoction of dogrose, fruit drinks) in order to increase salivation.
During the treatment it is necessary to increase the frequency of hygienic procedures: brush your teeth after each meal, rinse the mouth every 2 hours.
Treatment of the disease with folk remedies has an auxiliary significance and should be used only in conjunction with traditional medicine. The most popular folk recipes are rinsing the mouth with soda-salt solutions, resorption of the lemon wedge.
In the case of transition of the disease into a chronic form with episodes of exacerbation, it becomes necessary to perform surgical treatment.
The first stage doctors resort to galvanizing the salivary glands. This procedure consists in the effect on the iron of an electric current of low power.
In some cases this is enough to destroy the stones at the formation stage. If the process could not be stopped, it becomes necessary to perform an operative intervention.
Surgical treatment
In clinical practice, clear indications are given for the operation:
- melting of the gland tissues due to a purulent process;
- complete obstruction of the gland duct with the development of persistent pain syndrome.
Operative treatment consists in opening the duct, installing drainage. Operational access is oral.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The drug is administered in several places, starting from a place 1 to 2 cm behind the stone.
On both sides, two ligatures are placed in parallel to the flow of the duct, which serve as "holders" for the surgeon's assistant. Only after this is performed a transverse incision of the mucosa,
The next step is opening the duct and extracting the calculus. The wound is not sutured, but a drainage tape or tube is inserted. Within 3-5 days, antibacterial drugs are introduced into the area of the postoperative wound in order to prevent inflammation.
Prophylaxis of calculous sialoadenitis
There is no specific prevention of salivary stone disease. The main preventive measures are directed to the hygiene of the oral cavity and the exclusion of mechanical blockage of the duct of the salivary glands.
Complications and prognosis of
Complication of an acute form of disorder is its transition into a chronic form. Chronic salivary stone disease leads to 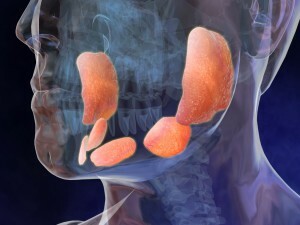 dysfunction of the gland.
dysfunction of the gland.
Prolonged course of the disease provokes the transformation of glandular tissues into fibrous or connective tissue. As a result, the gland acquires a knobby form, loses the ability to perform basic functions. Such a transformation can proceed according to the type of tumor transformation.
The prognosis of the disease is doubtful. In 50% of cases, regardless of the treatment, relapses occur. Secondary prevention is aimed at preventing the development of severe forms and complications.
