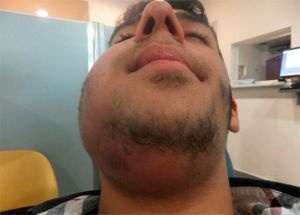
 Adenophlegmon is a foci of infection that forms in the subcutaneous fat layer in the failure of the lymph node( its inability to neutralize the pathogenic, mostly microbial, that is absorbed by it).
Adenophlegmon is a foci of infection that forms in the subcutaneous fat layer in the failure of the lymph node( its inability to neutralize the pathogenic, mostly microbial, that is absorbed by it).
The most common cause of the disease is the suppuration of the lymph node as a result of its infection, followed by melting the pod formed with pus and the exit of detritus containing microbes into fatty tissue, through which the process can freely propagate in any direction. For this reason phlegmon has no clearly delineated boundaries.
The source of the infection is caused by pathogens that penetrated both from the surface or from the thickness of the damaged skin, and penetrated through the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and nose that have lost their protective properties( in the case of phlegmon submaxillary or similar it may be inhabitants of carious teeth, chronic infection of the tonsils or cavitiesmiddle ear).
Another cause may be the introduction of infection from the outside by artificial means( with injuries, injections, bites of sick animals).

Features of the clinical picture
Like any similar purulent process, this pathology occurs with both general toxic and local manifestations.
The first include a rise in body temperature with an increase to critical levels, as well as symptoms of intoxication in the form:
- headache;
- nausea with urge to vomit;
- mental retardation and stunnedness;
- profuse sweating;
- palpitations and rapid breathing;
- of swelling in combination with a drop in diuresis and similar signs of autointoxication.
Local manifestations are the presence of massive and continuing to grow local edema against the background of severe hyperemia of the skin of the affected area( submandibular or otherwise).
With a noticeable bulging of the affected area, the boundaries of the transition to adjacent zones are fuzzy, while the skin of the central zone is tense, tightly tightened by pressure from the inside, expressed painfully both during palpation and by itself( with the subsequent increase in inflammatory phenomena).
In a rather far-reaching case, there is a fluctuation and a breakdown in the function of the systems located in the focus zone( difficulty in swallowing in the case of adenoplegia of the submaxillary region).
Features of the manifestation can also be caused by the region of the location of the involved lymph nodes:
- chin-submandibular;
- neck( with a different topography of the outbreaks);
- inguinal;
- axillary;
- is parotid.
These are the largest zones reporting the names of adenophlegmon in accordance with the generally accepted classification. The difficulty of 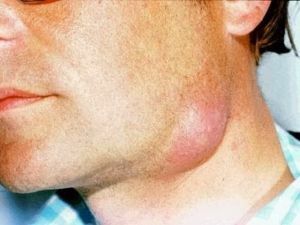 lymph drainage from the organs entering them, not only creates additional difficulties in the functioning of the organism, but also serves as another diagnostic criterion of pathology.
lymph drainage from the organs entering them, not only creates additional difficulties in the functioning of the organism, but also serves as another diagnostic criterion of pathology.
Thus, due to the presence of inguinal adenoplegia, it becomes problematic to urinate due to a significant swelling with spreading to the genital area, adenophlegmon axillary leads to a partial disorder of function and sensitivity in the involved upper limb.
How to recognize the
in time Diagnosis of the disease with a sufficiently characteristic clinical picture is facilitated by:
- conducting a clinical blood test - its analysis for signs of inflammation( leukocytosis with neutrophilia, accelerated ESR) and sterility;
- sowing punctate material on nutrient media with identification of the pathogen of the process and determining its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs;
- instrumental research - ultrasound of soft tissues of the affected area.
Differentiation from tuberculosis and actinomycosis helps the characteristic contents of the punctate from the lymph nodes: in the first case it is curdled, and in the second it is a crumbly consistency. In addition, in the case of these two diseases, the clinic will be rather sluggish.
About the principles of treatment and prevention of
If you suspect a case of adenophlegmone, you should immediately start treatment( after the rapid diagnosis).
 The essence of timely started adenoflegmon therapy is the surgical excision of the affected lymph node( nodes) with all the adjacent structures( up to the boundaries of healthy tissues), without the possibility of leaving pathological cavities - pockets and swells.
The essence of timely started adenoflegmon therapy is the surgical excision of the affected lymph node( nodes) with all the adjacent structures( up to the boundaries of healthy tissues), without the possibility of leaving pathological cavities - pockets and swells.
During melting of the lymph node or their group to the condition of the phlegmon proper, the purulent cavity is opened with careful drainage. It is necessary both during the operation and in the subsequent period( with the management of the postoperative wound by the open method).
Categorically avoid getting purulent detritus in the border of healthy tissue in order to avoid their infection.
In the postoperative period, it is necessary to wash the cavity with solutions of antiseptics( antibiotics), enzyme preparations( neutralizing residues of pathological biomass and accelerating the cleaning of tissues), wound dressings.
Detoxification therapy is also used for intravenous drip injection of saline and low-molecular-protein solutions, anti-inflammatory and desensitizing agents are used.
A necessary measure of the impact on the body( both curative and preventive) is to increase the level of immunity( using immunostimulating and immunomodulating drugs), as well as to release it from foci of chronic infection, and if this radical solution is impossible, suppression and control of their condition.
Diagnostic and timely diagnosis and treatment of adenophlegmons, as well as full-scale explanatory work with the patient provide a favorable prognosis for his life and health.
