A delicate pulsating area on the head of a newborn, called a fontanel, is not only an object of heightened anxiety of parents, but also an important indicator of the state of the child's body.
Contents of
- Where does the fontanel have a child?
- Video: Rodnichok at the child
- When should a fontanel have a fontanel?
- Dimensions of the fontanel in the child by the month
- Video: When should the fontanelles close?
- Rodnichok at the child in 2 months
- Rodnikoch at the child in 3 months
- Rodnikoch at the child in 4 months
- Rodnikoch at the child in 5 months
- Rodnikoch at the premature child
- Why does the fontanel in the child badly overgrow?
- What should I do if the fontanelle of a child closes early?
- Video: Rodnichok at the newborn. Komarovsky
Most primigravid women very closely follow the fontanel on the baby's head. And this is not surprising, because this tender patch on the child's head requires special attention.
So, the condition of the fontanel
can point to pathology of development and even life-threatening disease. What can say the fontanel of a newborn, when it should close and what kind to have - read in this article.Where is the fontanel?
The is a soft space between the bones of the skull, filled with a connective tissue that ossifies during the growth and development of the child.
 In addition to the large fontanel, there are 5 smaller ones, but they usually close in the birth of
In addition to the large fontanel, there are 5 smaller ones, but they usually close in the birth of . Many do not know that in fact the baby's skull initially has 6 fontanel , and not one. By the time of birth, all 5( or 4, not including the back), except for the large, can overgrow, and may remain of a negligible size. Rodnichki, like everything in the human body, are not at all random - they perform an important role.
During childbirth, thanks to the fontanel, the baby's skull shrinks and passes through the birth canal. After this, already in the extrauterine life, the fontanels that are not overgrown, the play the role of shock absorbers for when striking, preventing damage to the brain.
In addition, fontanels do not allow the bones of the skull to squeeze the fast growing brain of the child , and at elevated temperature play the role of thermoregulators, not allowing the brain to overheat.
 The child's brain is actively growing and the ossified skull does not fully adhere to the cranial
The child's brain is actively growing and the ossified skull does not fully adhere to the cranial . New mothers without outside help know where the infamous large fontanel is located. On the head of the baby it is difficult not to notice, because it occupies the area of 3 by 3 cm in the center of the crown. The small posterior fontanel is located on the back of the head, but due to its small size, it often goes unnoticed.
The appearance of the large fontanel can tell a lot:
- a hollow fontanel on the first weeks of life of crumbs speaks about its transferability, and subsequently - an alarm signal of dehydration
- bulge with pulsation speaks about increased intracranial pressure. If this occurs during crying, then this type of fontanel should be, if at rest - consult a neurologist
- too slow closure may indicate the development of rickets or hydrocephalic syndrome
Be sure to tell about your observations of the fontanel of the baby at the reception of the precinctpediatrician, because the mother is with the child 24 hours a day and notices what escapes the doctor's eye.
Video: Rodnikochka at the child
When should a fontanel be grown in a child?
The timing of the large fontanel fusion is quite individual. There are no strict criteria for when exactly the fontanelle should ossify, but most pediatricians tend to think that this should happen during from 6 to 18 months of .As statistics show, most often the fontanel closes from half a year to year, but there are cases when it occurs earlier or later - in 3 months or up to two years.
 Rodnichki most often close in the period from six months to a year, but can ossify and much later
Rodnichki most often close in the period from six months to a year, but can ossify and much later Do not worry if the fontanel does not close in this most common period. Each child is individual and if the neighbor's baby has already closed the fontanel, and yours does not, then it only indicates his individual development.
Dimensions of the fontanel in the child by the month
At each examination of the child, from the moment of his birth and until complete closure, the pediatrician will measure the fontanel. This is necessary in order to have an idea of the pace of growth and development of the brain and improving the skull of the baby. There are certain norms that show how the size of the fontanel should be by months.
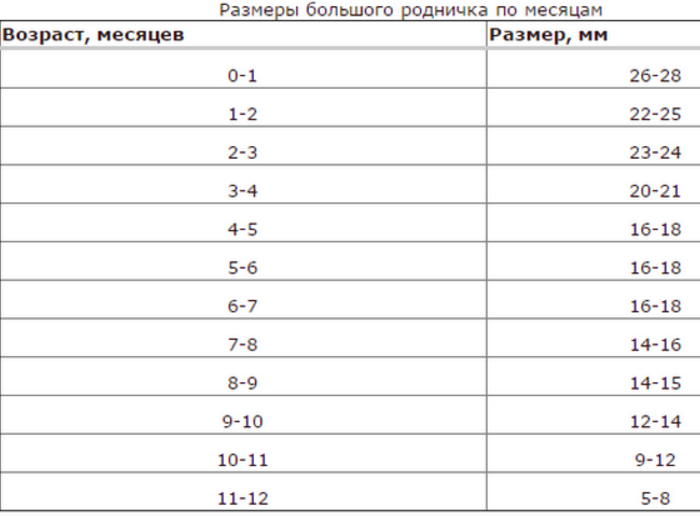 Dimensions of the large fontanel by the month
Dimensions of the large fontanel by the month At birth, the size of the large fontanel, as a rule, is 3 by 3 cm, but can be slightly smaller or larger, which is not considered a deviation from the norm. During the month, the fontanel size can slightly increase , but this should not be frightened. This is observed for the reason that during the delivery the skull of the child was strongly squeezed, and after a while, because of the elasticity of the tissues, the regains its former shape.
Also increase of the fontanel in the first month of life crumbs promotes rapid brain growth.
After the first month, the size of the fontanelle should gradually decrease , until full ossification occurs and the fontanel does not close completely.
Video: When should fontanels be closed?
Rodnichok in a child in 2 months
By the end of the second month of life fontanel can slightly decrease. For parents, these changes can pass and not at all, but the doctor will necessarily pay attention to how the fontanel has changed. To say exactly how should be a fontanel of a two-month-old child is difficult - after all, it is important to consider what it was like at birth.
On average, by 2 months, the fontanel can become the size of 22-25 mm .As a rule, does not have to close the fontanelle so early, and if this happens, it is better to consult a pediatrician, because the baby is still very small, its brain is actively developing and growing, and earlier overgrowing of the fontanelle can be extremely undesirable at this age.
 If the fontanel closes by two months, then it is said about its early closure
If the fontanel closes by two months, then it is said about its early closure Early overgrowing of the fontanel ( up to 3 months) is considered pathological only if there are atypical sizes for the of the head circumference. If the head circumference corresponds to the norms and terms, the child is considered healthy, and earlier the closure of the fontanel is a feature of the individual development of the bone system.
Causes of early overgrowing of the fontanel:
- excess calcium that enters the body
- Brain underdevelopment
- craniosynostosis is a specific disease that occurs against the background of endocrine disease or rickets, which is characterized by the earlier closure of the cranial sutures and multiple concomitant symptoms( very rare)
- brain abnormalities(extremely rare is the cause of overgrowing of the fontanel)
Talking about early overgrowing of the fontanel because of some disease can only qualifyneurologist. And only after the statement of a specific diagnosis can any measures to stop the ossification of the fontanel.
Rodnichok at the child in 3 months
Only in 1% of children the big fontanel grows in 3 months , and at average crumbs to this age it becomes the size 23-24 mm .If your baby refers to this insignificant percentage of children who have to the 3rd month a closed fontanel, then do not raise the alarm and drag the child to the hospitals.
 In 1% of children, the fontanel closes in three months
In 1% of children, the fontanel closes in three months If the large fontanel closes , but the child develops on time, you do not observe any pathologies and strangeness in behavior, and the head circumference of the crumbs corresponds to age, then such closure of the fontanelle is considered a physiological phenomenon.
Rodnichok at the child in 4 months
From 3 to 4 months the fontanel of the child continues to overgrow and its size is about 2 cm .Complete closure of the fontanel at this age is just as rare as in the previous month, but some cases still occur. In general, complete ossification of the skull for 4-month-old child is not characteristic.
Parents should not worry - if the overgrowing of the fontanel is not according to the terms , then the pediatrician at the next reception will definitely say about it. If necessary, the crumb will be prescribed vitamin D or they will recommend increasing the calcium content in the ration of the nursing mother.
Spring at the child in 5 months
With 5 months the size of the big fontanel becomes about 17 mm .Most likely, during the next two to three months it will remain unchanged, but quite often, to 6-7 months fontanel completely closed. Closing the fontanel in the following months is not considered pathology - this is quite normal.
On average, the fontanel has such approximate sizes up to a year:
- 8-9 months - 1.4-1.5 cm
- 9-10 months - 1,2-1,4 cm
- 10-11 months - 0,9-1,2 cm
- 11 months - year - 0,5-0,8 cm
 If the head circumference corresponds to the timing, then the fontanel closure is considered physiological
If the head circumference corresponds to the timing, then the fontanel closure is considered physiological As a rule, to the one-year-old age , the fontanel closes, and in many cases thisoccurs earlier.
Rodnichok in a premature baby
In preterm infants at birth, there are fontanelles of large sizes and in addition to the front and rear there are lateral fontanels .So, as premature crumbs are born earlier than the deadlines, their development differs in many respects from the development of their peers and the overgrowing of the fontanels also happens differently.
The closure of the fontanel in preterm infants occurs somewhat later than is usually considered the norm, but is not a cause for concern .Even if the child in development lags far behind the peers, its rate of development will come to normal by three years and will equal the one-year period.
 Rodnichok in premature babies closes later than in peers
Rodnichok in premature babies closes later than in peers As a rule, a large fontanel in premature babies is closed in one and a half or two years .In rare cases ossification occurs later - in 2,5 years.
Premature babies are under special control of pediatricians and, with the slightest suspicion of any pathology, the doctor will prescribe an appropriate examination in order to exclude the possible development of pathology in the . However, if any changes in the fontanel of your child are troubling you, then please consult a specialist.
Why does the fontanel in a child overgrow?
As already mentioned, the ossification of the skull and the tightening of the large fontanel in each child occurs in different ways. How fast the fontanel is fastened, is affected by such factors:
- fullness of - if the child was born before the term, then he will lag behind in development from peers and the closure of the fontanel will occur much later than in full-term children
- food - in children who are on breast-feeding, the fontanel ossifies earlier than the artificial ones. This is due to the fact that the mother's milk contains a sufficient amount of calcium, necessary for the formation and strengthening of the skeleton. An important role in the closing of the fontanel is played by the intake of vitamin D, which helps calcium assimilate.
 With slow closing of the fontanel, the doctor can prescribe vitamin D
With slow closing of the fontanel, the doctor can prescribe vitamin D - the development rate of - if the child grows slowly, then fontanel will grow at this rate
- heredity
- the presence of endocrine, neurological, genetic diseases
What if the early fontanelle of a child has closed early?
Recently, cases of early closure of the fontanelle have become more frequent in pediatric practice. Pediatricians attribute this primarily to the fact that during pregnancy, expectant mothers have taken complex vitamin preparations. In consequence, in the child's body there is an overabundance of calcium, which leads to early closure of the fontanel.
If ossification occurs too early, many specialists say about multiple negative consequences, because a fast-growing brain slows down its development, squashed by a cranium. In fact, there has been no scientific research on this subject and to say that it is really dangerous to close the fontanel first - is impossible.
 A frequent cause of early closure of the fontanel is considered to be a violation of the exchange of
A frequent cause of early closure of the fontanel is considered to be a violation of the exchange of . Therefore, if your pediatrician, after measuring the head circumference and other parameters, does not see any deviations from the norm, then no action on your part to prevent the fontanel closureit takes.
If the doctor finds that fast closure of the fontanel is due to metabolic disorders , namely - due to excess calcium, he will recommend reducing the intake of food containing calcium and vitamin D. Self-limiting the child in such important substancesnot worth it.
The rounder plays a big role for the both in the process of the birth of a child and after the birth of the child. This delicate area of the child's body requires special control and awe, because he can tell a lot about about the state of the child and its development. If you are concerned about the appearance of the fontanelle or its closure, you should definitely consult a pediatrician.
Video: Rodnichok at the newborn. Komarovsky
Save
Save
