Hip dysplasia is a dangerous disease that can significantly worsen a child's quality of life in the future and affect development. Learn how to identify pathology in order to prevent its further development and ensure a healthy future for a baby!
Contents
- Causes of hip dysplasia in children
- Symptoms of hip dysplasia in children
- Diagnosis of hip dysplasia in children
- Degrees of hip dysplasia in children
- Dysplastic hip dysplasia in children
- What is the risk of hip dysplasia in children?
- Disability and dysplasia of hip joints in children. Can dysplasia turn into a disability?
- Hip dysplasia up to year and year
- Symptoms of hip dysplasia: tips and references
- Video: Congenital hip dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a congenital pathology in which the development of tissues and joint structures is inadequate, resulting in a number of pathological changes, entailing a curvature of the spine, early osteochondrosis, and in severe cases even disability.
Causes of hip dysplasia in children
Disturbance in the development of hip joints is a congenital disease, that is, occurs in the process of intrauterine development. The causes of underdevelopment of the muscular, bone-cartilaginous or ligamentous structure of the joint are:
- genetic factor( if the mother or father of the child had dysplasia, then there is a high risk of the disease in the child)
- pollution of the environment( found that the average disease rate in the country is 2-3%, whereas in the most ecologically contaminated areas the risk of morbidity rises to 12%)
- myelodysplasia( a disease characterized by a spinal or spinal cord developmentI lead to severe consequences, including hip dysplasia)
- the effect of maternal hormones on the fetus( in the last trimester of pregnancy the body of the woman intensively produces hormones that prepare the body for childbirth and help loosen the ligaments)
There are also factors that are not in themselvescontribute to the development of dysplasia, but indirectly lead to it:
- uterus tone during pregnancy
- breech presentation
- large size of the fetus
- anhydrasses of various origins
- improper diet of a pregnant woman, lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet
- female sex in a child( due to greater exposure to maternal hormones)
- toxicosis

It is established that children who are born in late pregnancy( after 45-50 years) are more likely to develop disease,and first-born.
Symptoms of hip dysplasia in children
The disease can be detected both at the birth of the child and in the first year of life. Since hip dysplasia is a serious disease that can affect the child's further development, it is very important to diagnose it in the initial stages. Specialists identify the signs that can be easily noticed by the mother without any outside help:
- the number of folds on the legs of the patient with dysplasia of the child is usually uneven, they are asymmetrically positioned
- one of the legs is shorter than the other
- buttocks are asymmetrical
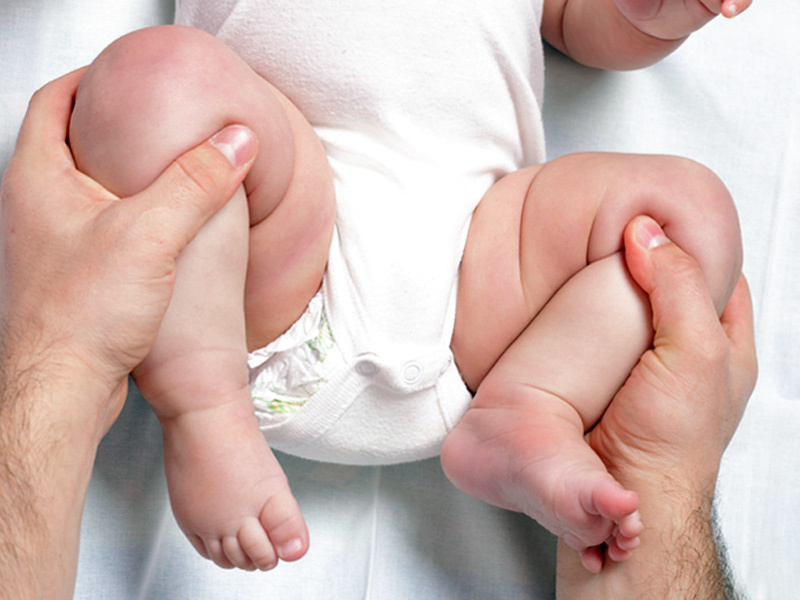
- , while holding the bent legs of the child,not allowing to complete the movement of the
- when the legs of the child are collared, the crotch of the
- is seen at an older age, in the presence of advanced dysplasia, the child has a "duck" gait

If you identify these symptoms should be addressed as soon as possible to an orthopedic specialist!
A qualitative examination of newborns in the maternity hospital excludes the option that the disease can be overlooked, but every mother should be vigilant and pay special attention to the development of her child, not relying on doctors. It is also important to carry out routine examinations of the baby from the orthopedist, which are performed at the first, third, sixth month of the child's life, as well as at one-year-old age.
Diagnosis of hip dysplasia in children
If you have identified any symptom of dysplasia in your child, it will help to find out if the baby has a pathology experienced orthopedist. At the reception, the doctor will collect an anamnesis, during which he will ask his mother a number of questions that require truthful and detailed answers. At this stage of diagnosis, the doctor is interested in whether there is a genetic predisposition to the disease, the peculiarity of the course of pregnancy, and also the developmental features of the child.

After specifying the necessary information, the orthopedic doctor conducts a direct examination. He examines the child in the position on the abdomen and on the back, conducts appropriate methods of detecting violations identified for each age. Even if the expert sees any deviations from the norm, he has no right to diagnose without further investigation.
Only ultrasound and radiography can accurately confirm dysplasia of the hip joints.

Degrees of hip dysplasia in children
DTS may not be definite immediately and may go into a more severe stage, requiring a prolonged, not always effective, treatment. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose pathology at an earlier stage for successful treatment and harmonious development of crumbs. Modern medical classification distinguishes such stages of the disease:
- The immaturity of the joint is a condition in which there are minor deviations from the norms of tissue development, which is easy to diagnose with the help of ultrasound. As a rule, the immaturity of the joints is characteristic of premature infants and is not a disease, but is considered a boundary line between the norm and the pathology of
- . The anterior joint is a developmental disorder of joints without a dislocation of the pelvic bone, which gives symptoms and is perfectly diagnosed by X-ray. May occur in newborns, adolescents, elderly people
- Subluxation of the joint - at this stage, the femur is slightly displaced
- Congenital dislocation - a condition in which the femur extends beyond its site of localization
Bilateral dysplasia of the hip joints in children
For bilateral hip dysplasiapathology of tissue development occurs symmetrically. The danger of the disease is the difficulty of diagnosing.
Parents can determine the pathology at a later stage of its development, when hip dysplasia is already started, as the main methods of self-detection of the disease, on the basis of asymmetry, are unproductive.
This condition is complicated by the fact that a whole complex of measures aimed at treating the disease and a long recovery period is required. Timely advice from an orthopedist will help avoid bilateral dysplasia of the hip joints.
What is the danger of hip dysplasia in children?
Hip dysplasia is an extremely dangerous pathology that can adversely affect a child's development and affect the rest of his life. With untimely diagnosing and improper treatment, the disease can lead to a number of diseases:
- osteochondrosis
- curvature of the spine
- arthritis
- disorders in the anatomy of the pelvis

In addition, dysplasia of the hip joints in the future is manifested by a "duck" gait, difficulty in movement and frequent pains, and in heavier painscauses of disability.
Disability and dysplasia of hip joints in children. Can dysplasia turn into a disability?
Untimely treatment of hip dysplasia or inaccurate diagnosis can lead to serious complications, up to disability in the future. If the child is not indicated the necessary care and modern methods of treatment, dysplasia can develop into coxarthrosis of the hip joint.
Coxarthrosis is accompanied by severe pain, the joint becomes stiff, the muscles atrophy, and one leg becomes shorter than the other. As a result, lameness and limited movement during walking are formed.
Hip dysplasia before year and year
The sooner the treatment of hip dysplasia begins, the greater the chances of a full recovery and the less the duration of treatment. Methods and methods of treatment are strikingly different in children up to a year and after.
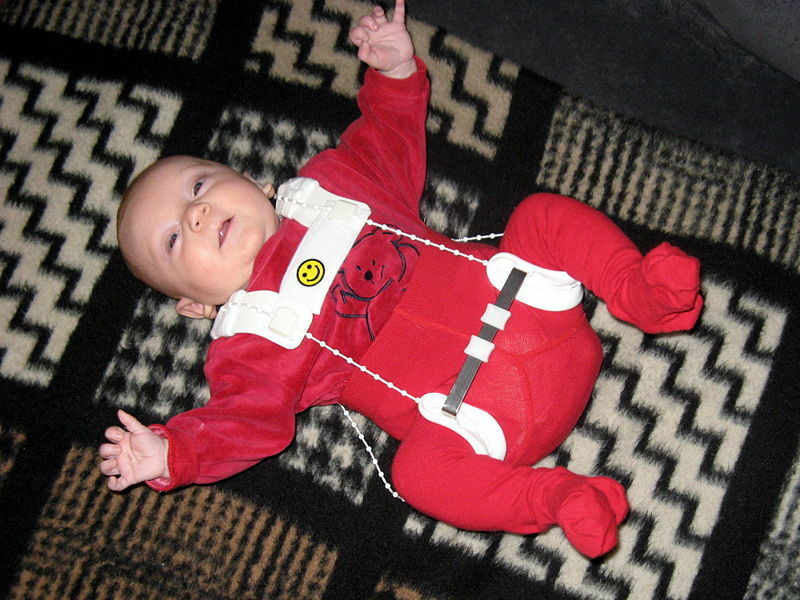
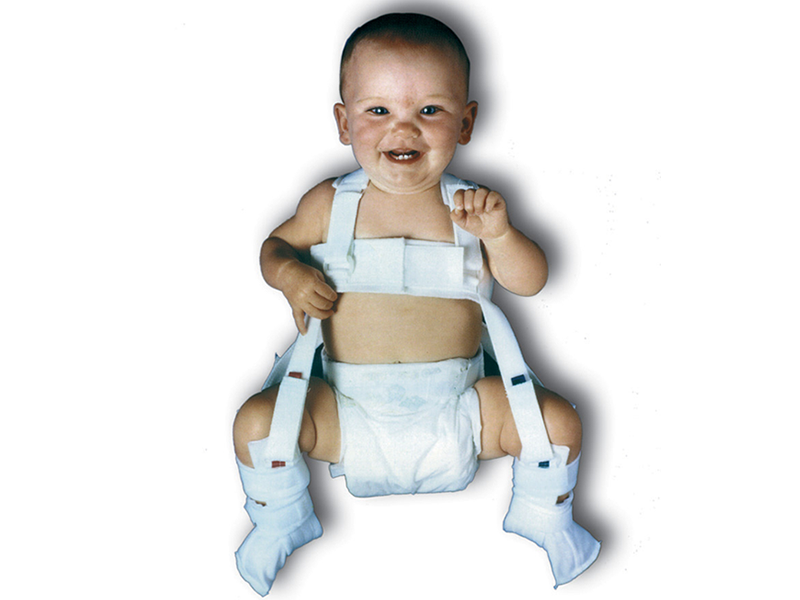
Children of the first year of life are assigned a soft swaddling and gymnastics. Various rigid designs are not used at such an early age, only soft pads are allowed. For older children, specific orthopedic tools are used:
- Pavlik stirrups
- Gniewkowski
- device
- splinting
- shoe bus
If the disease can not be cured by conservative methods, after a year the operation is assigned to the child.
Symptoms of hip dysplasia: tips and testimonials
The experience of many moms, whose children are suffering from hip dysplasia, shows that getting a doctor in a timely manner can completely cure the disease. It is important to be very vigilant to your baby so as not to miss the development of a serious illness and provide the necessary treatment on time.

In no case should you apply any folk remedies and independently decide whether to take medication or apply massages to your child - this can exacerbate the problem and lead to the loss of precious time.
