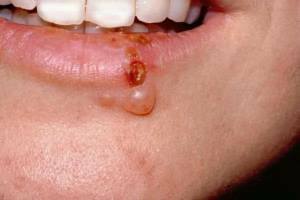
 Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth with the appearance of ulcers and wounds, often the disease appears on the lip, on the inner or outer surface, without affecting the tongue and other mucous membranes.
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth with the appearance of ulcers and wounds, often the disease appears on the lip, on the inner or outer surface, without affecting the tongue and other mucous membranes.
There is a pathogenic process in the form of ulcers, blisters, white coating. This is a common disease both among children and adults.
Contents
- Primary characteristic
- Risk factors and causes
- How do symptoms depend on the form of the disease?
- General clinical manifestations of
- Diagnosis and treatment of
- Childhood - special
- period Preventive measures - warned and armed
Primary characteristic of
Stomatitis is commonly referred to as a number of inflammatory diseases of various etiologies that affect the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips. Causes and factors affecting the development of the disease, a lot. They are very different, so the disease can develop at any age.
Stomatitis on the lip can develop a second time, accompanying various infections( in a child it is usually scarlet fever, measles), or as
 consequence of some chronic diseases of the blood or skin in adults.
consequence of some chronic diseases of the blood or skin in adults. Whatever the cause of the disease, it is always accompanied by an infection of the oral cavity. The pathogenesis of the disease is not exactly established. It is believed that this is a response of the immune system to an external stimulus( trauma, cuts, cracks) or an infection that leads to inflammatory foci in the form of ulcers and vesicles on the lips.
Such lesions of the mucous lips not only spoil the appearance, but also very painful. They cause a lot of trouble, making it difficult to eat and communicate.
The disease occurs in two stages:
- acute , occurs for the first time and is characterized by acute symptoms;
- chronic - arises against the background of a non-cured acute form, it occurs with frequent relapses.
According to morphological changes, stomatitis is divided into three main forms:
- catarrhal;
- aphthous;
- ulcerative.
These forms differ in the degree and nature of the mucosal lesion.
Risk factors and causes of
The main causes of the appearance and development of stomatitis on the lips are:
- any lesions of the mucous lips;
- thermal or chemical burns;
- airing and frequent licking of lips;
- infection of various kinds( bacterial, viral, fungal);
- allergic reaction;
- hormonal disorders, especially in women.
The appearance of the disease is often aided by damage to the skin on the lips. The mucous membrane is tender and thin, so it is easily injured.
The risk factors include:
- the presence of chronic diseases;
- disorders in the circulatory system;
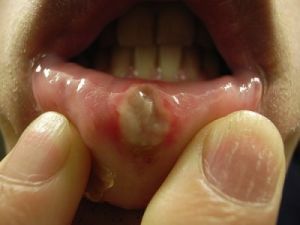
Stomatous ulcer due to injury
- non-compliance with oral hygiene;
- wearing of poor-quality dentures;
- damaged teeth( sharp chipped);
- disorders of the endocrine system;
- improper diet( lack of vitamins);
- heredity;
- stressful situations;
- smoking and drinking alcohol.
The causes of stomatitis are very different. Accordingly, a classification of the types of the disease has been constructed.
How do symptoms depend on the form of the disease?
The classification is based on factors that trigger the development of the disease. The stomatitis arising on lips, happens of several kinds:
- Bacterial .The cause is different bacteria( staphylococci, streptococci).They fall on the mucosa through cracks or microdamages and cause inflammation. It appears in the form of purulent ulcers, the tissues become swollen.
- Herpetic .This is the most common form of the disease developing on the lips. Causes the defeat of the herpes virus. On the mucous membranes appear, filled with liquid, they burst after a few days, then they are covered with a wet crust.
- Candidiasis ( fungal) is typical for children. Infection is provoked by fungi( Candida), which actively multiply with weakened immunity. This type of violation has a characteristic sign in the form of a dense white coating on the oral mucosa and along the lip of the lips. It is easily removed, the mucosa in the lesion is red and edematous.
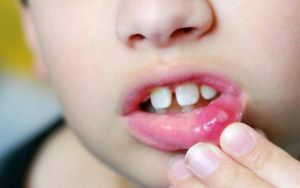
- The aft .Its development is caused by traumas, stresses, beriberi. Appears in the corners of the lips or on the outer surface in the form of concave round erosion, having a yellowish plaque. The edges of the wound often bleed, the lips themselves reddened and inflamed.
- Allergic .Occurs when exposed to an allergen, as a response. On the mucous there are reddening, which grow into ulcers. All the mucous surface swells, small pimples may appear.
- Traumatic .It develops when the mucous membranes are damaged by solid food, cracks from the impact or wounds from biting. Often, the lips are injured from substandard dentures, resulting in the formation of bleeding wounds. Frostbite or burns( chemical, thermal) also disrupt the mucosa, leading to inflammation.
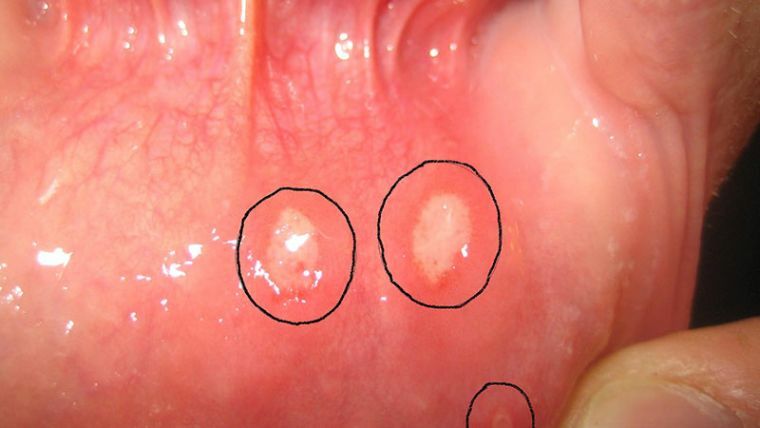
Afts on the mucosa
It is very important to determine the type of disease so that the treatment is effective and fast.
General clinical manifestations of
All types of stomatitis are characterized by a number of common symptoms and clinical manifestations, in adults the development of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- slight local redness on the lips in the initial stage of the disease;
- itching and burning sensation;
- appearance of swelling and redness in the affected area;
- increased salivation;
- bad breath;
- bleeding gums;
- tenderness of affected areas.
If the disease is caused by an infection, ulcers are formed, covered with a thin film, with different contents. This may raise the temperature. Lymph nodes increase.
Diagnosis and treatment of
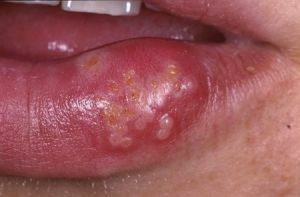 The diagnosis is based on a primary visual examination. During the examination, the doctor determines the nature of the inflammation, its stage. Define the features of lesions, their shape. Characteristic signs determine the form of stomatitis.
The diagnosis is based on a primary visual examination. During the examination, the doctor determines the nature of the inflammation, its stage. Define the features of lesions, their shape. Characteristic signs determine the form of stomatitis.
With obvious signs of infection, tests can be administered to determine the type of pathogen.
Treatment of any kind of stomatitis involves the application of general therapy methods:
- appointment of local procedures( rinsing, lotions, therapeutic ointments);
- administration of drugs with a narrowly focused effect( depending on the type of disease);
- use of analgesic and antipyretic drugs( Panadol, Paracetamol, Spasmalgon);
- visit to the dentist;
- strengthening of immunity;
- power adjustment;
- administration of anti-inflammatory drugs( Kamistad, Actovegin);
- use of special agents that accelerate mucosal healing( Solcoseryl, Vinilin-balm).
When choosing the methods of treatment of the inflammatory process and ulcers on the lip, it is very important to know which form of stomatitis the patient is most:
- with viral infections , including herpes, use antiviral ointments or gels( Acyclovir, Oxolin, Zovirax);
- with allergic form prescribe antihistamines - Erolin, Suprastin, Clemastin, and also exclude contact with
 allergen;
allergen; - bacterial stomatitis treated with antibiotics, in that case, if it is difficult to determine the exact type of bacteria used broad spectrum antibiotics - amoxicillin, Amoxil;
- for inflammation, caused by fungi , use antifungal ointments and preparations( Levorin, Erythromycin);
- for the treatment of aphthous form use antihistamines, local anti-inflammatory and wound-healing ointments( Holisal, Fenistil);
- with traumatic form first remove the traumatic factor, then treat the wound with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory ointments( Synthomycin, rosehip oil).
Treatment of stomatitis is desirable to carry out in a complex. Any medicine should be prescribed by the doctor after identifying the cause and determining the type of the disease.
Children's age - during a special
Children mucosa of the mouth and lips is very delicate, their surface is thin and easily injured, so the disease, develop a child - not uncommon, and even commonplace. Infants and preschool children are especially prone to inflammation. Along with common "adult" causes, the disease can develop:
- from constant falling into the mouth of foreign objects that injure the lips;
- because of immature immunity( any infection quickly joins);
- from unformed salivation. Lips often dry up and crack;
- from taking antibiotics and other medications;
- from poor care of the newborn.
Each type of painful process is characterized by its signs. In children, the disease manifests itself, as a rule, in an acute form. Symptoms are acute:
- the temperature rises;
- on the lips appear rashes in the form of ulcers and vesicles;
- there is a general intoxication of the body;
- , when infected, a yellowish crust appears on the lips, which glues the mouth;
- the child often cries and fits.
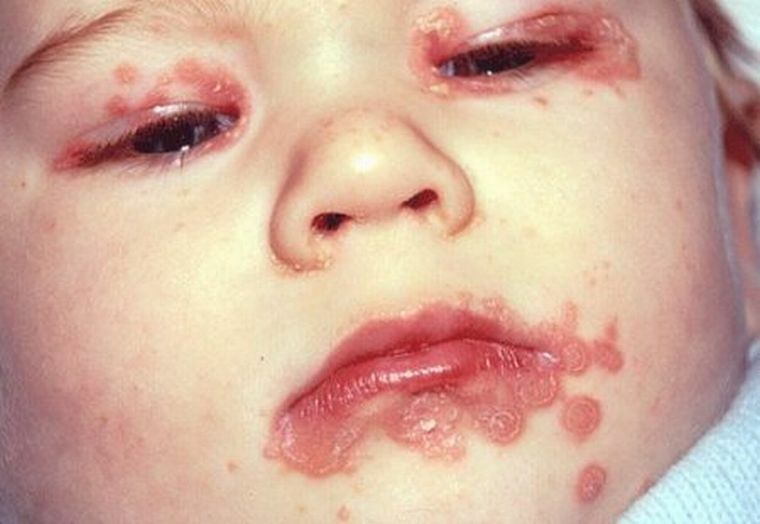
In the photo of the child on the lips of the ulcer that occurs due to herpetic stomatitis combined with blepharitis
 Stomatitis in children can be a distinct disease, and to develop a cold or acute respiratory disease. Each age period corresponds to its type of disease. Breasts are more likely to have a candida form. At a younger age, infectious stomatitis develops. In preschool children, the herpes virus is activated, leading to a herpetic type of lesion.
Stomatitis in children can be a distinct disease, and to develop a cold or acute respiratory disease. Each age period corresponds to its type of disease. Breasts are more likely to have a candida form. At a younger age, infectious stomatitis develops. In preschool children, the herpes virus is activated, leading to a herpetic type of lesion.
General measures for the therapy of any kind of stomatitis are aimed at removing the symptoms of inflammation, treating ulcers and sores on the lip, and also alleviating the general condition of the child. To do this, use:
- power adjustment, because due to the soreness of the mucous the child is difficult to eat;
- increased hygiene measures of the oral cavity;Anesthetics and antipyretic agents;
- sedative procedures for the mucosa.
The basic treatment is similar to an adult, all procedures are prescribed only by a pediatrician. If necessary, then consult with a dermatologist, dentist, lor.
To think that the ailment will pass on its own, it's not right! The disease is threatened with serious consequences:
- enlargement of ulcers, gradual transition of the disease into severe form;
- recurrences recurring into a chronic process;
- the appearance of bleeding from the damaged mucosa;
- attachment of secondary infection.
These complications can be avoided. It is only necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner and undergo a course of treatment.
Preventive measures - warned and armed with
To avoid the development of the disease it is necessary:
- strict observance of personal hygiene rules;
- regular check-ups at the dentist;
- timely treatment of colds and diseases that provoke inflammation of the mucous membranes;
- to avoid injury and damage to mucous membranes;
- rational nutrition, enriched with vitamins.

You can not, especially children, bite your lips and lick them in the wind or cold. These measures are simple, and their observance will help to permanently exclude the risk of stomatitis in both adults and children.
