Hemangiomas in children can resolve themselves or require immediate medical intervention. How to determine the type and treatment of hemangiomas in children, this article will tell.
Contents of
- Hemangioma in children. Causes of
- Hemangioma in children photo
- Hemangioma on the head in a child
- Hemangioma on the child's lip
- Hemangioma on the child's face
- Hemangioma on the back of the child
- Hemangioma in children before the year
- Hemangioma in newborns
- Hemangioma of the skin in children
- Subcutaneous hemangioma in children
- Vascular hemangioma in children
- Liver hemangioma in children
- Cavernous hemangioma in children
- Treatment for hemangiomas in children
- Removal of hemangioma by laser in children
- Video: What is hemangiomaa - Dr. Komarovsky's school?
One of the ailments of the infant's life of the child is hemangioma - a tumor-like malformation of blood vessels, outwardly resembling a dirty spot on the skin.
 Externally, the hemangioma resembles a dirty spot on the skin
Externally, the hemangioma resembles a dirty spot on the skin Such "spots" can have different colors: from pale pink to purple, but more often there are hemangiomas of reddish-bluish shades.
IMPORTANT: Hemangiomas can appear on the child's body not immediately, but only 1 to 2 months after birth. In female infants, hemangiomas appear somewhat more frequently than in infants-boys.
 The most common color of hemangiomas is reddish-blue
The most common color of hemangiomas is reddish-blue Hemangioma in children. Causes of
The exact causes of the formation and growth of hemangiomas are not known to date, but are likely to be:
- colds and viral diseases of women in early pregnancy( before 12-14 weeks)
- adverse environmental conditions for the future mother
- multiple pregnancies
- strongprematurity of the child
- the age of the mother is 32 to 35 years( the older the pregnant woman, the higher the risk of developing hemangiomas in the fetus)
- fetoplacental insufficiency
IMPORTANT: SuETS opinion that the possibility of occurrence of hemangiomas in infants affected by mode of delivery. According to statistics, in children born by cesarean section, hemangiomas are observed somewhat more often than in babies born naturally.
 Viral diseases transmitted by a woman during pregnancy can cause a hemangioma in a child
Viral diseases transmitted by a woman during pregnancy can cause a hemangioma in a child Hemangioma in children Photo
Hemangiomas in children can be small and light. As a rule, they rarely cause inconvenience and almost never grow.
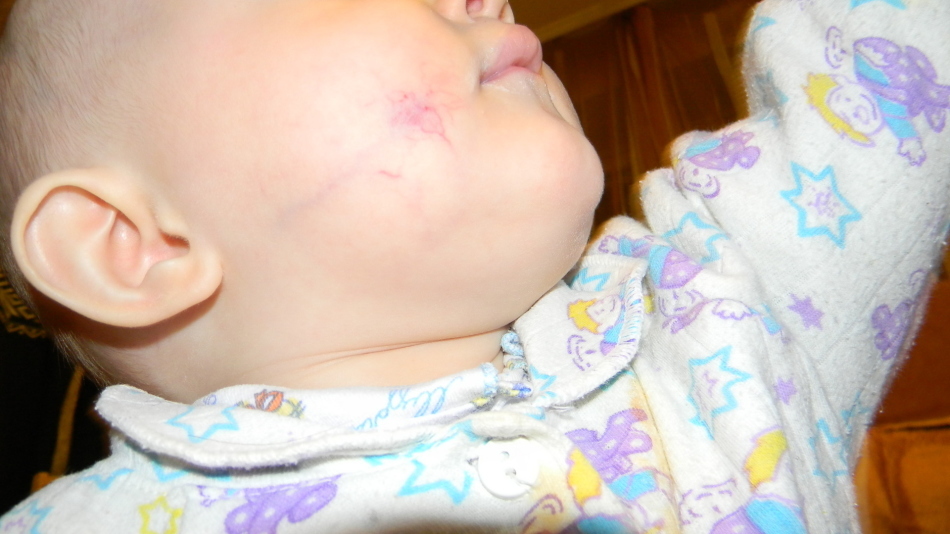 Small light hemangiomas quickly disappear without medical intervention
Small light hemangiomas quickly disappear without medical intervention However, there are also hemangiomas, the appearance and location of which causes a lot of problems and suffering in the child.
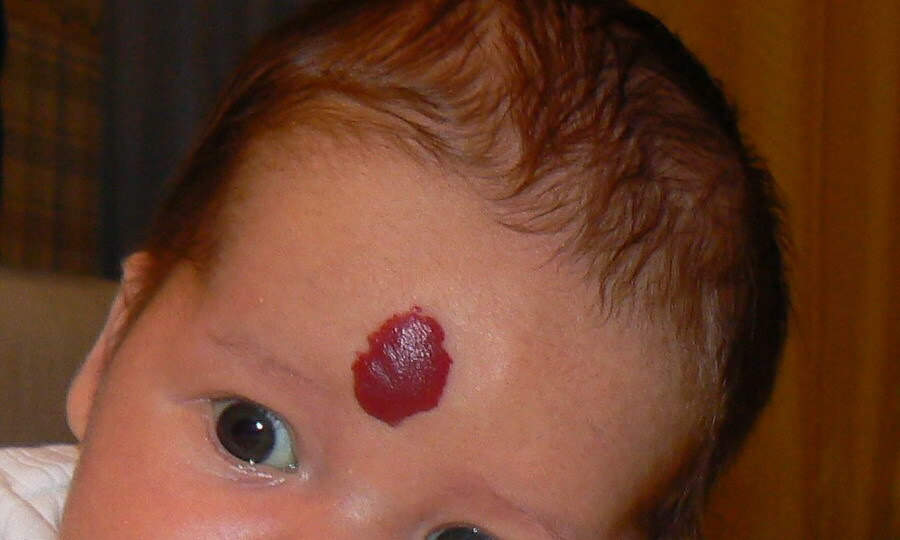 Some hemangiomas look terrible and cause the child a lot of suffering and experiences
Some hemangiomas look terrible and cause the child a lot of suffering and experiences Hemangioma on the head in a child
Hemangioma on the head of a child is a very frequent phenomenon. This benign tumor can appear at any point of the skull. Hemangiomas located on the head are dangerous close proximity to the brain, eyes, ears and respiratory organs.
IMPORTANT: The first signs of formation of a hemangioma on the head can become swelling of the skin and a slight change in its color.
Increasing hemangiomas of the head require medical supervision. If the tumor, increasing, begins to squeeze vital organs, the doctor must decide on its removal.
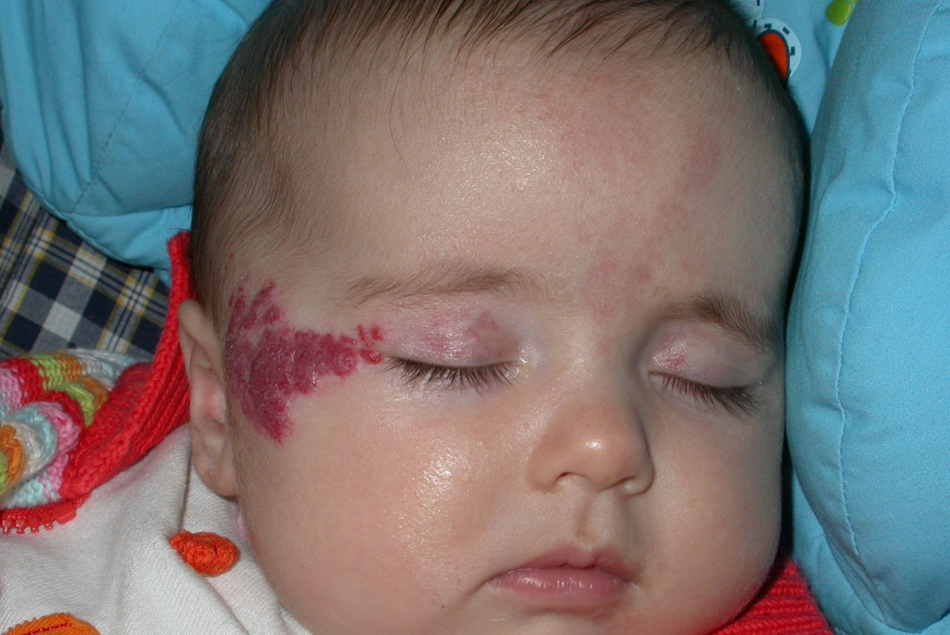 Hemangiomas of the head prone to overgrowth require constant medical supervision
Hemangiomas of the head prone to overgrowth require constant medical supervision Hemangioma on the lips of the child
In addition to the unaesthetic appearance, the hemangioma located on the lips can be a nuisance to the child when taking and chewing food. Infants born with hemangiomas of the lips often refuse breastfeeding, as they can not properly grasp the nipple.
IMPORTANT: If the hemangioma has growth tendencies, it may eventually go beyond the lips and "spill over" onto the chin, cheeks, or nasolabial folds.
For the removal of hemangiomas from the child's lips, two methods can be used:
- non-scar laser operation( for capillary hemangiomas)
- liquid nitrogen burning( for cavernous and mixed hemangiomas)
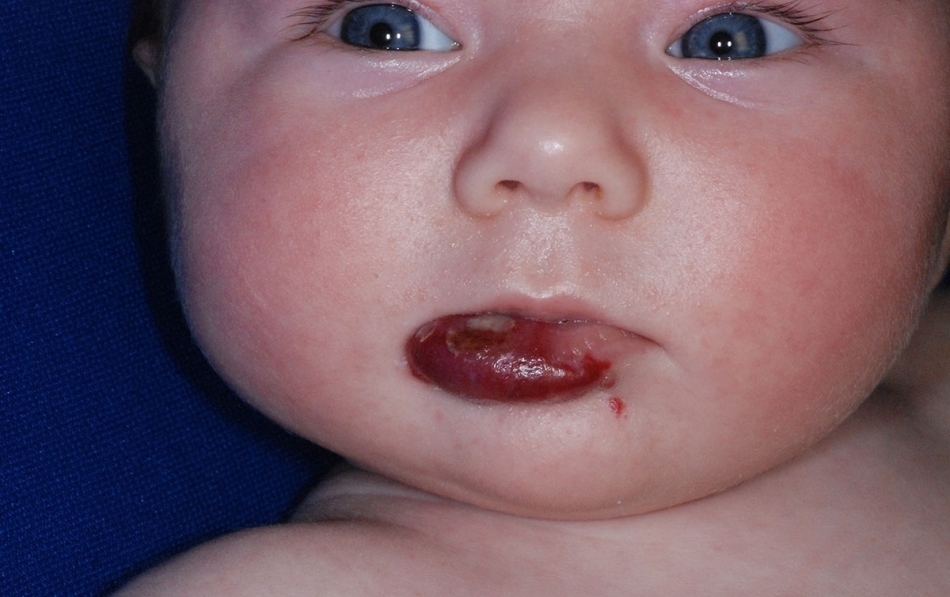 If the hemangioma on the lip increases, over time it will spread to neighboring areasskin
If the hemangioma on the lip increases, over time it will spread to neighboring areasskin Hemangioma on the face of the child
Hemangioma on the face of a child sometimes poses a danger to the normal functioning of the organs of sight, smell and hearing.
In addition, it is a serious cosmetic defect that, over time, can make a child feel "not like everyone else".Regardless of the type, color and shape of the hemangioma on the face, it will invariably attract the sympathetic glances of others.
IMPORTANT: In cases of minor external manifestations of the defect, doctors recommend that parents do not rush to the operation, and for a while observe the condition of the affected area of the skin. Often, the hemangiomas on the face dissolve themselves, without any medical intervention.
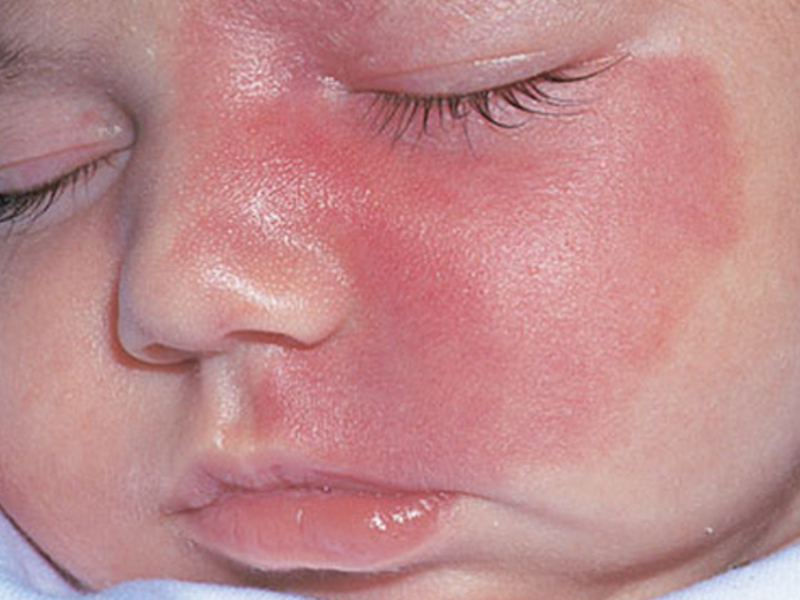 Hemangioma on the face of the child - a serious cosmetic defect
Hemangioma on the face of the child - a serious cosmetic defect Hemangioma on the back of a child
Hemangiomas on the back appear in 19 children out of 100. Most of them are congenital. They are formed on the child's body when it is still in the mother's womb and can be located on the waist, spine, ribs or shoulder blades.
Hemangiomas on the back are in most cases not dangerous for the health and life of children. Capillary formations can grow, and can, on the contrary, decrease and grow pale. Cavernous and mixed hemangiomas do not change their appearance and size and often sprout into the subcutaneous layers.
IMPORTANT: Hemangiomas on the back do not degenerate into malignant tumors, so surgical removal can be delayed. By the age of 5 to 7, the back hemangiomas have completely disappeared without trace from many children.
 Hemangioma on the back does not pose a health risk to the child
Hemangioma on the back does not pose a health risk to the child Hemangioma in children before the year
When children under one year have hemangiomas, parents often panic. In fact, everything is not as scary as it might seem at once.
If the size, shape and location of the hemangioma does not arouse suspicion among doctors, parents should simply observe it and note any changes.
IMPORTANT: 2% of children are born with hemangiomas, and 10% of babies are formed during the first year of life. Of all the cases, 95% are simple( capillary) hemangiomas.
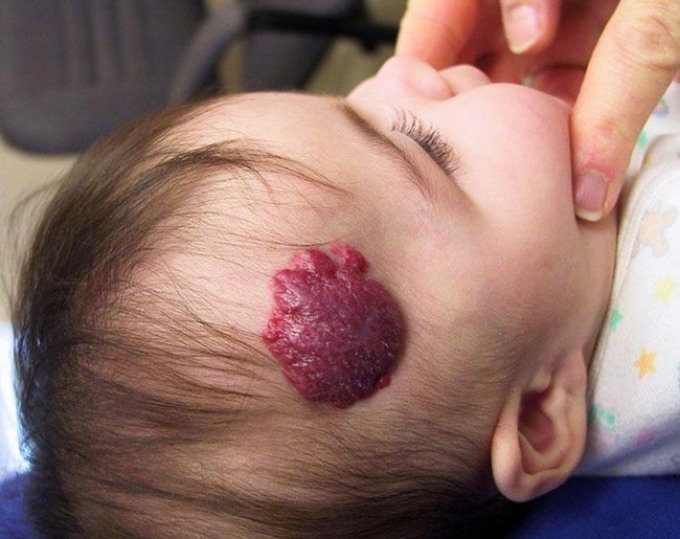 Hemangiomas in children up to one year require continuous monitoring
Hemangiomas in children up to one year require continuous monitoring Hemangioma in newborns
Hemangiomas in newborns are not uncommon. The main reason for the appearance of hemangiomas on the fetal body in the womb is a violation of the normal formation of the vascular system( 3 to 6 weeks of gestation).
Usually the size of hemangiomas in newborns does not exceed 2 cm, but there are exceptions, when skin lesions are extensive and numerous. In most cases, they all resolve themselves during the first years of a child's life.
IMPORTANT: Treatment of hemangiomas in newborns primarily involves monitoring the child by a pediatrician, dermatologist and surgeon.
 Usually the size of hemangiomas in newborns does not exceed 0.5 cm
Usually the size of hemangiomas in newborns does not exceed 0.5 cm Hemangioma of the skin in children
Hemangioma of the skin in children is 2 kinds:
- congenital - if the child was born with a hemangioma
- pediatric - if the defect appeared some time after birth
Congenital hemangiomas do not usuallyvary in size and dissolve up to the age of ten. Children's hemangiomas can then increase, then decrease, until they disappear without a trace.
IMPORTANT: The diagnosis of "hemangioma" can not be made independently. If you notice an unusual reddish stain on the baby's skin, contact a dermatologist to find out the nature of the defect.
The presence of hemangiomas on the skin of a child in most cases does not affect its physical and mental development.
 Often the hemangioma of the skin remains just a cosmetic defect.
Often the hemangioma of the skin remains just a cosmetic defect. Subcutaneous hemangioma in a child
Subcutaneous hemangioma has clear boundaries on the surface of the skin and is red or blue. A bright spot on the skin will turn pale if you press your finger a little.
This is due to a rapid outflow of blood. Subcutaneous hemangioma feels a little warmer than the healthy areas of the skin.
IMPORTANT: Subcutaneous hemangioma is dangerous for complications such as bleeding, phlebitis and thrombophlebitis if it is damaged.
 Subcutaneous hemangioma
Subcutaneous hemangioma Vascular hemangioma in children
Vascular hemangioma consists of vessels, lymph nodes and other tissues. Externally, it appears on the baby's skin, like red or blue spots, ranging in size from 0.5 to 10 cm. It is most often localized in the head region.
The color and consistency of the formations are determined by the tissues entering the tumor. At the site of the skin with vascular hemangioma, the blood supply has been disturbed, but this should not frighten the parents of the child, since such defects tend to be self-eliminated.
 Vascular hemangioma
Vascular hemangioma Hemangioma of the liver in children
Hemangioma of the liver in a child may not be noticed by the parents. If its size does not exceed 5 cm, then no symptoms of its presence can be detected. Most likely, eventually it will resolve and never again remind of itself.
If the dimensions of the hemangioma of the liver increase over time to 10 cm or more, the child will complain of aching pain in the right upper quadrant, a feeling of constriction in the stomach and intestines.
IMPORTANT: Of a benign tumor, the hemangioma of the liver, which is a tangle of vessels, can be transformed into a malignant one. Dangerous also the rupture of the hemangioma of the liver - because of this the child may experience internal bleeding.
When a liver hemangioma is detected in a child, parents should exclude from their diet acute, greasy, smoked, salted and fried foods. In return, you can offer strawberries, carrots, beets, fish, liver or dairy products.
 Strawberry is a product recommended for liver hemangiomas
Strawberry is a product recommended for liver hemangiomas Cavernous hemangioma in children
Cavernous hemangioma is a formation consisting of two or more vascular cavities filled with blood. It grows from the subcutaneous fat layer. If the cavernous hemangioma begins to grow, the skin covering it will acquire a bluish purple hue.
Only a doctor can diagnose this type of hemangioma, based on the results of ultrasound and laboratory tests.
IMPORTANT: If a child is diagnosed with cavernous hemangioma, treatment should be started immediately.
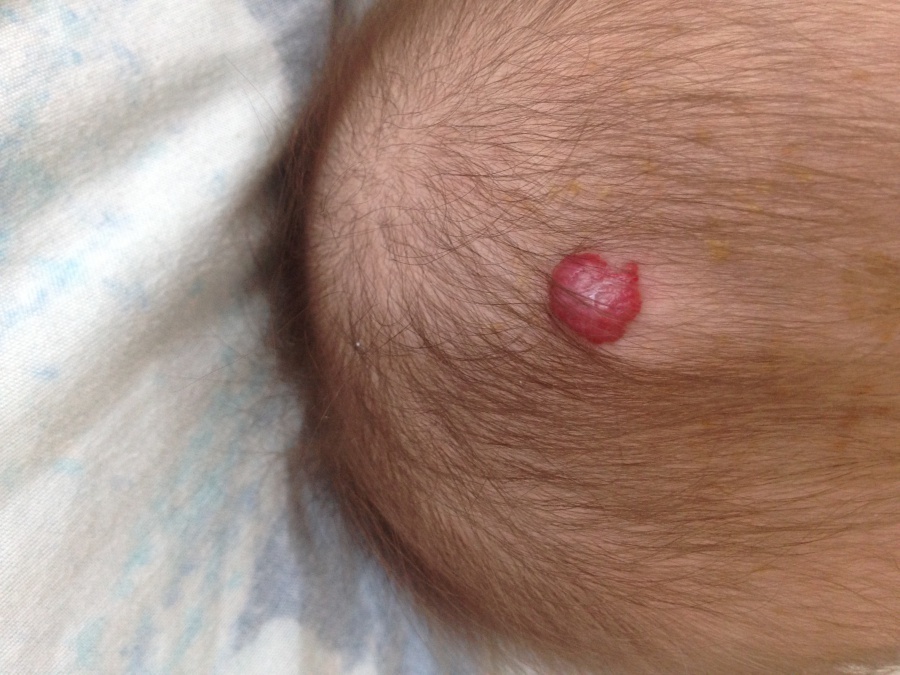 Cavernous hemangioma
Cavernous hemangioma Treatment of hemangiomas in children
According to statistics, 10% of children have hemangiomas per year, 50% - to five, and 70% - to 7 years. However, if the hemangioma increases in size or threatens the health of the child, it is necessary to deal with its treatment.
You can treat hemangiomas using one of the following methods:
- with
- medication by cryotherapy
- by cauterizing
- with
- laser sclerosing injections
- using
folk remedies. IMPORTANT: In each individual case, treatment is chosen individually depending on the type, size and severity of the defect.
 Treatment of hemangioma should be prescribed by a doctor
Treatment of hemangioma should be prescribed by a doctor Removal of a hemangioma by a laser in children
Modern removal of hemangiomas in children is a painless effect on the affected area of the skin with a laser.
The laser "reduces" the tumor to minimum dimensions, while eliminating traces from it. Wounds after this procedure heal very quickly, without complications.
IMPORTANT: Removal of hemangiomas by laser is the safest way to solve the problem. The result of the removal procedure depends only on the qualifications of the surgeon who conducted it.
The disadvantage of this method is the inability to remove hemangioma at a time. On average, a complete disappearance of the defect will take 3-5 treatments with an interval of 2 to 3 weeks.
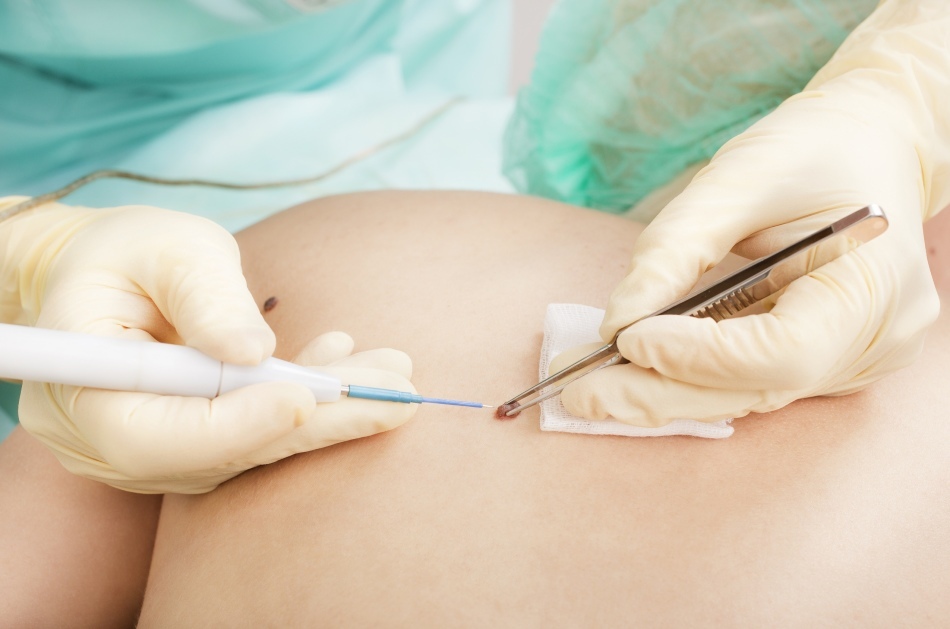 Removal of hemangioma by laser
Removal of hemangioma by laser If you notice a suspicious spot on the body of your child, similar to a hemangioma, do not despair. Show the child to an experienced doctor who, when examined, will accurately determine the origin of the skin defect and, if necessary, prescribe adequate treatment.
