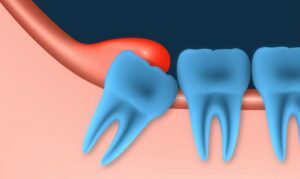
 Most adults are familiar with the unpleasant sensations accompanying the eruption of wisdom teeth.
Most adults are familiar with the unpleasant sensations accompanying the eruption of wisdom teeth.
But there are a number of symptoms, which should be paid special attention, preventing the development of a dangerous pathology - pericoronaritis.
Pericoronitis is the inflammatory process developing in the surrounding tissues of the gum.
This situation can be observed with a prolonged eruption( which is especially characteristic of wisdom teeth), when the gums begin to detach from the tooth, so that a hood contributes to the development of the inflammation of the dentition.
Content
- Causes of
- disease Classification and symptoms
- Festering perikoronit
- Chronic disease
- diagnosis and dental treatment
- Excision hood
- tooth removal
- Laser surgery
- Home Treatment
- Possible complications
Causes of
diseases provoke pericoronitis may as localcauses, and factors associated with delaying the process of eruption.
In the first case, the pathology is caused by:
- disorders in the area of the erupting tooth whiteness of the mucosa of the with the appearance of superficial erosions or small sores;
- trauma surrounding the future soft tissue tooth , applied with a stiff brush or solid food.
The tightening of the eruption process can be the result of the following factors:
-
 High-density forming the alveolar process of bone tissue .As a rule, by the time of the eruption of the "eights", the bone consolidates and hardens because of the absence of milk teeth in the projection of wisdom teeth.
High-density forming the alveolar process of bone tissue .As a rule, by the time of the eruption of the "eights", the bone consolidates and hardens because of the absence of milk teeth in the projection of wisdom teeth. - Absence of in the tooth row of of sufficient space for a cutting tooth.
- Thickening of the gum or covering the jaw of the periosteum at the place of eruption of the "eights".
In addition, the likelihood of the disease depends on age - the older the patient, the more painful and harder the eruption.
All of the above causes lead to the formation of a gingival hood, under which a favorable environment for the multiplication of pathogenic bacteria and microbes is created.
Often the situation is complicated by the improper arrangement of cutting teeth that can come out of the gum at an angle. In such situations, pronounced pericoronaritis is noted with aggravation of characteristic symptoms.
Classification and symptoms of
This disease is classified according to the course( acute or chronic stage) and form( purulent or catarrhal).
Acute form of the disease
Acute catarrhal pericoronaritis is characterized by the appearance of aching pain in the surrounding area of the erupting soft tissue tooth. After a couple of days against the background of increased pain, there is a difficulty in chewing food, opening the mouth and swallowing. The following symptoms of the inflammatory process are manifested:
-
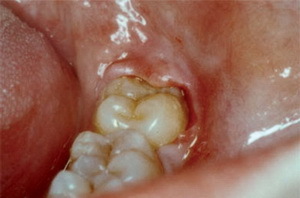 swelling of the tissue fold over the tooth rudiment;
swelling of the tissue fold over the tooth rudiment; - appearance of acute, shooting pain( touching the inflamed area causes pain in the auricle or temple);
- redness of affected tissues and noticeable swelling of the cheeks outside;
- increase in temperature not more than 37.5 degrees;
- headache.
If no appropriate treatment is performed during the acute stage, pus begins to accumulate in the inflamed tissues and the disease can move into the next, more dangerous form, while the patient himself often experiences temporary relief, which is incorrectly regarded as a recovery.
Purulent pericoronitis
In the presence of an open exit for pus in the area of inflamed tissues, against the background of the absence of characteristic symptoms, the infection of surrounding tissues and the spread of inflammation can occur.
The pain is periodic, especially unpleasant moments occur when swallowing and chewing.
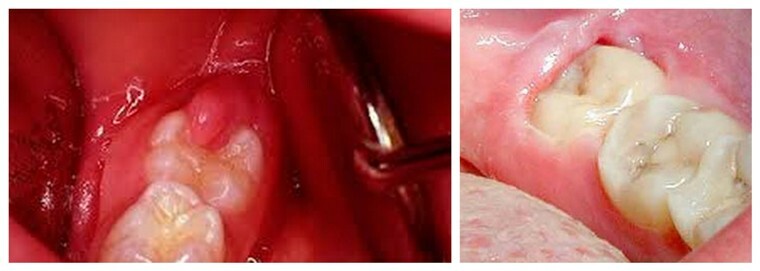
In the photo, variants of pericoronaritis
Chronic course of the disease
In the absence of treatment, a chronic purulent form of the disease develops with the following characteristic symptoms:
-
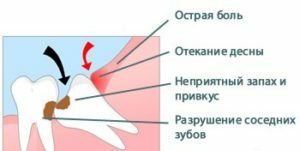 bad breath, caused by the release of purulent contents into the oral cavity;
bad breath, caused by the release of purulent contents into the oral cavity; - lymphadenitis, affecting regional lymph nodes in the submandibular region;
- redness and swelling of the mucous membrane over the cutting tooth.
Diagnosis and dental treatment
For pericoronaritis, diagnostic activities consist of a visual examination by a specialist and radiography, which allows you to assess the area and degree of inflammation. Treatment involves complex therapy.
Excision of the hood
This surgery does not present any difficulties and allows you to save the cutting tooth. Under local anesthesia, the dental surgeon removes the formed mucous fold, preventing further development of inflammation.
Before the operation, the gum is treated with an aseptic preparation, after which, using a surgical scissors or a scalpel, the doctor excludes overhanging soft tissues. Then the wound surface is washed with an aseptic solution, treated with a hemostatic agent and an iodoform turunda is applied.
Tooth Extraction
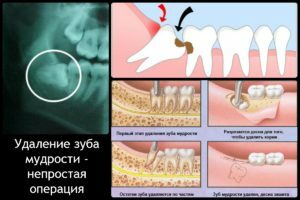 Such a radical method is shown in the following situations:
Such a radical method is shown in the following situations:
- lack of sufficient space in the dentition for a cutting "eight";
- incorrect position of the tooth with the emphasis of the chewing surface in the bone tissue of the alveolar process or the adjacent tooth.
The final decision to remove is taken based on the radiography data. In this case, the operation can be carried out only after removing acute symptoms. After the extraction of the tooth is complete, the socket is cleaned and seams are applied.
Removing the gingival hood with a laser:
Laser operation
This is an effect on the damaged area through the skin using a low-intensity infrared beam. As a result, the blood flow increases in the area affected by the inflammation, the edema and pain sensations are eliminated, the metabolism in tissues improves.
The disadvantage is the high cost of the procedure and its duration( duration of the course is 2 weeks).Contraindication is the presence of cancer in the oral cavity.
 Can I remove my teeth during pregnancy? Read here.
Can I remove my teeth during pregnancy? Read here.
Prefer to treat the gum with folk remedies? All the recipes in this article.
All about gel Kamistad for anesthesia of gums by reference http: //dentazone.ru/sredstva/ kamistad.html
Treatment at home
Immediately it should be noted the impossibility of a full effective effective treatment of pericoronitis at home.
 Rinsings with herbal decoctions and infusions are effective only at the stage of recovery, when the procedures necessary to eliminate inflammation have already been performed in the dental office.
Rinsings with herbal decoctions and infusions are effective only at the stage of recovery, when the procedures necessary to eliminate inflammation have already been performed in the dental office.
Self-treatment and prescription of antibiotics can result in serious consequences, which can be eliminated only in the hospital of the department of maxillofacial surgery.
Use of analgesic gels Kamistad, Holysal will give temporary relief of the condition.
Possible complications of
Untimely treatment can result in the following dangerous health complications:
-
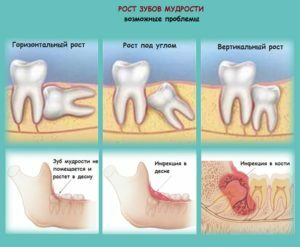 Transition of inflammation under the periosteum( periostitis ) and lesions of nearby teeth .Against the background of fever, swelling, redness and soreness of the gums, general malaise is noted.
Transition of inflammation under the periosteum( periostitis ) and lesions of nearby teeth .Against the background of fever, swelling, redness and soreness of the gums, general malaise is noted. - Abscess in the form of limited purulent inflammation, in which pus is formed due to melting fat and muscle tissue.
- Phlegmon , which is a clear purge of diffuse purulent inflammation, gradually increasing in size.
- Damage to bone marrow of and bone tissue of the jaw( osteomyelitis).As a result, the inflammation can spread to half of the jaw, provoking dissolution of bone tissue and a pathological fracture of the jawbone.
The disease should be treated with the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease.
A timely visit to a doctor and following his recommendations become the key to a quick, successful recovery without the development of long-term treatment complications that can cause serious health problems in general.
